Oops, your important files are encrypted (Petya) Ransomware Virus is one of the most dangerous viruses that are being distributed at the moment. It shut down numerous critical and industry facilities all over the world and has been labeled as one of the most advanced iterations of the Petya malware family. Read our in-depth removal guide to learn more about it and how your computers and data can be recovered.
Manual Removal Guide
Recover Oops, your important files are encrypted (Petya) Ransomware Virus Files
Skip all steps and download anti-malware tool that will safely scan and clean your PC.
SpyHunter anti-malware tool will diagnose all current threats on the computer. By purchasing the full version, you will be able to remove all malware threats instantly. Additional information about SpyHunter / Help to uninstall SpyHunter
How Does Oops, your important files are encrypted (Petya) Ransomware Virus Infiltrate the System?
The Oops, your important files are encrypted Petya Ransomware Virus is being distributed using several different main methods.
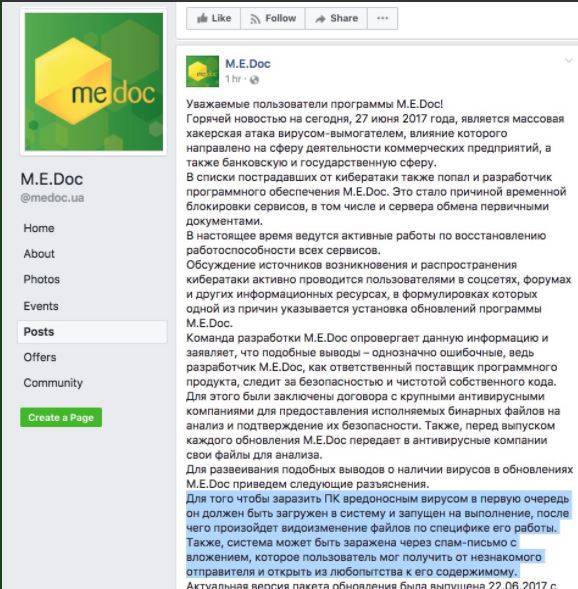
The majority of victims from Ukraine were lured by a dangerous software update for one of the popular accounting application used by businesses – M.E. Doc. The computer criminals were able to infiltrate the software vendor’s update servers and modify the binary files issued to their clients. As a result the ransomware was bundled and delivered to many machines in the country.
When the outbreak started to spread on large scale the company issued a security advisory stating that their servers have been compromised. An English version of the posted message reads the following:
Attention!
Our servers are carrying out a virus attack.
We apologize for the temporary inconvenience!
Its important to note that this is not the first time a dangerous ransomware virus is being delivered through infected payloads. The M.E. Doc software has been used to spread another malware in the past, namely the XData ransomware.
According to the statistical data gathered from the first night of attacks the majority of the attacks are reported as originating from Russia and Ukraine where the application is popular among business owners. The researchers traced the ransomware as utilizing a worm-like behavior that allows the ransomware virus to locate other nodes on the local network. By using a password harvesting module it is able to infect as many computers as possible. Its important to note that the Petya ransomware virus is able to penetrate the network using the WMIC (Windows Management Instrumentation Commandline) utility. This is done by using a dump program called Mimikatz (or similar). Effectively this allows the malware to infect even those computers that are patched and protected against the Eternal Blue vulnerability.
It is possible for the computers to protect themselves against this method by blocking the execution of the process explorer and WMIC tools that are used by the exploit. This is possible by blacklisting them using the Windows registry.
A security researcher proposes the use of a technique called Image File Execution Options (FEO) that is able to temporarily or permament block such executables from executing. You can attempt to protect yourself by following these instructions:
- Open the “Run” dialog by opening the Windows Menu and typing “Run” or press the “Win button + R”.
- Navigate to the “HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Image File Execution Options” location.
- Create a new registry entry by right clicking and choosing “New –> String Value”.
- Right click on the value and click “Modify”. Enter “svchost.exe” and press “OK”.
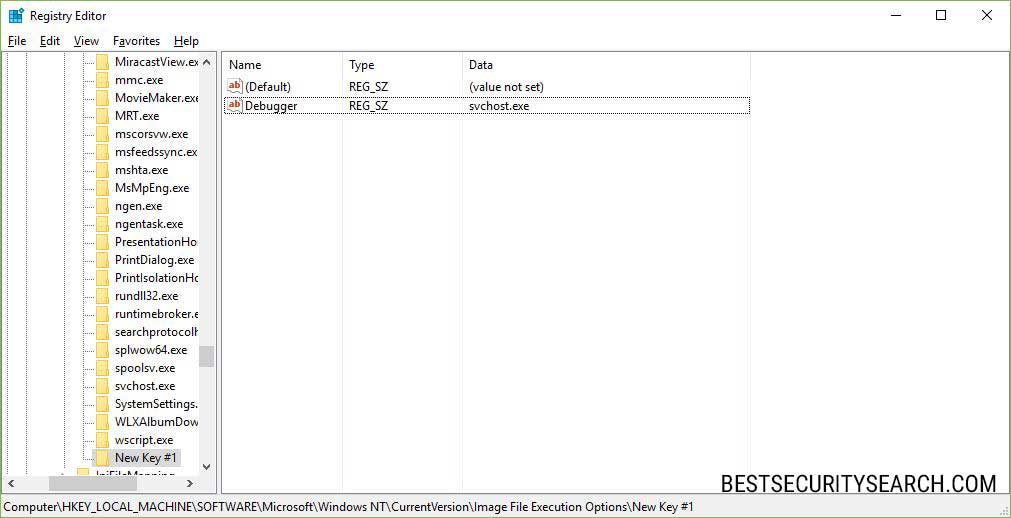
The same procedure should be done for the wmic.exe key.
The other major intrusion mechanisms is the use of the infamous exploits ETERNALBLUE and ETERNALROMANCE. The first one is known as the main module that is used to infiltrate computers with the WannaCry ransomware. The vulnerable component is the Samba file and network sharing protocol, namely its version 1 implementation (SMBv1) in the Microsoft Windows operating system.
The new Petya ransomware virus is different from WannaCry as it spreads only through compromised internal networks and not the Internet. And while the WannaCry ransomware was spread to a small number of hosts and then spread rapidly through infections, the new Petya virus strain is being launched in a large-scale attack.
There are also reports of email spam messages that deliver the new Petya ransomware virus samples. The security researchers presume that this is a secondary option as such distribution tactics are not effective against facilities, government institutions and companies. They are usually made with social engineering tricks that blackmail the victims into infecting themselves with the malware. This is achieved by using text and graphics derived from legitimate sources. In most cases the Petya ransomware virus is distributed as either file attachments or linked in the body contents.
In other cases the criminal developers can opt to use payload mediums. They are software bundles or infected documents that rely on user interaction. Examples include spreadsheets and rich text documents that feature built-in scripts (macros). When the computer users open the files they are presented with a prompt that asks them to run the scripts. If this is done the Petya ransomware virus is downloaded from a remote server and the infection is started.
Related: PetrWrap Ransomware, Goldeneye Ransomware
Infection Flow of Oops, your important files are encrypted (Petya) Ransomware Virus
Upon infection the new Petya strain initiates several preliminary checks. One of them checks the host to determine if it is a real device or a sandbox environments. Such instances are used by programmers and security experts to analyze the captured viruses. The Petya ransomware can detect systems such as debugging environments, honeypots and virtual machines. The virus will automatically shut down and delete itself from the compromised system to conceal itself from detection.
Detailed system information is then retrieved from the computers. The updated Petya ransomware variant can harvest data such as the installed components and software on the compromised machines, as well as their configuration. The physical drives are scanned, as well as any connected removable storage devices and accessible network shares.
The new Petya ransomware virus can modify the Microsoft Windows configuration settings and also manipulate important services. The experts note that the new Petya ransomware virus reads the language settings used by the computer users. This is done by advanced strains as it allows the hackers to initiate several infection case scenarios:
- Based on the harvested data the virus may display the appropriate ransomware note. It may either be built-in or translated using web services in real time.
- Previous large-scale attacks use the language as the means of sorting out the intended targets.
- The language data can be used by the hackers to plot out an upcoming attack. The gathered statistics can be useful to the criminals in refining their campaigns.
Other harvested data include the following: machine time, timezone, system locale, Windows settings, computer name, registered users, installed software and etc.
The updated Petya virus contains a network module that alerts the remote hackers by sending a control message (beacon). The signal confirms that another machine infection has been complete. We may see new strains of this updated Petya ransomware that feature Trojan functions. This would allow the hackers to take over control of the machines, execute arbitrary commands and steal valuable data.
After this is done the new Petya ransomware virus starts its encryption engine. It targets the master boot record (MBR) and then installs a schedules task which reboots the computer after one hour by utilizing the schtasks.exe system service.
As usual the new Petya ransomware virus uses a strong algorithm to process the data. The captured samples associated with the virus feature a combination of AES-128 and RSA. Its interesting to note that the RSA public key is hardcoded:
M II BCg KCAQEAxP/Vq KcOyLe9Jh Vq FMQGwU ITO6WpXWnKSN QAYT0065Cr8PjIQI nTeHl(XEjf02n2J mURWV/u HBOZrIQ/wcYJ BwLhQ9EqJ3i DqmN190o7NtyEUmbYmopcq +YLI BZzQ2ZTKOA2DtX4GRKx EEFLCy7yP12EYOPXknVy/+ mfOJFWixz29QiTf5oLu15wVLONCuEibGaNN pgq + CXsPwfITDbDDmdrRI iU EUw6o3pt5pN Os kf0J bMan 2TZu6zf hzuts7KafP5UA8/0H mf5K3/F9Mf9SE68EZjK +cl iFIKeWnd PDXf RCYX19ANCea0u7CXF6U0AVNnNjvLe0n42LHFUK4o6JwIDAQAB
The next step is to clear the events log in an attempt to hide traces of the infection. This is done by executing a hardcoded system command:
- wevtutil cl Setup & wevtutil cl System & wevtutil cl Security & wevtutil cl Application & fsutil usn deletejournal /D %c:
When the system is rebooted the ransomware message is displayed on the computer’s screen as the modified MBR (master boot record).
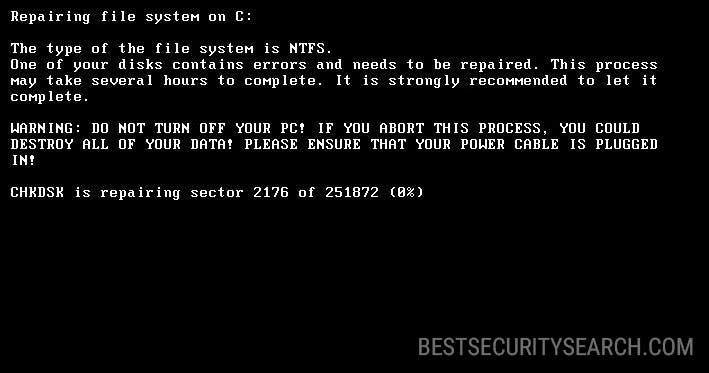
The initial infection poses as the check disk (CHKDSK) program, Microsoft Windows’s built-in disk optimization utility. It shows the typical message:
Repairing file system on C:
The type of the file system is NTFS.
One of your disks contains errors and needs to be repaired. This process
may take several hours to complete. It is strongly recommended to let it complete.WARNING: DO NOT TURN OFF YOUR PC! IF YOU ABORT THIS PROCESS, YOU COULD
DESTROY ALL OF YOUR DATA! PLEASE ENSURE THAT YOUR POWER CABLE IS PLUGGED
IN!CHKDSK is repairing sector 2176 of 251872 (0%)
The Petya ransomware virus does not permit the Windows operating system to load as it has overwritten and deleted the boot manager. As a result the computer and its associated files cannot be used if the ransomware has not been removed completely by a quality anti-spyware solution (see our in-depth instructions below).
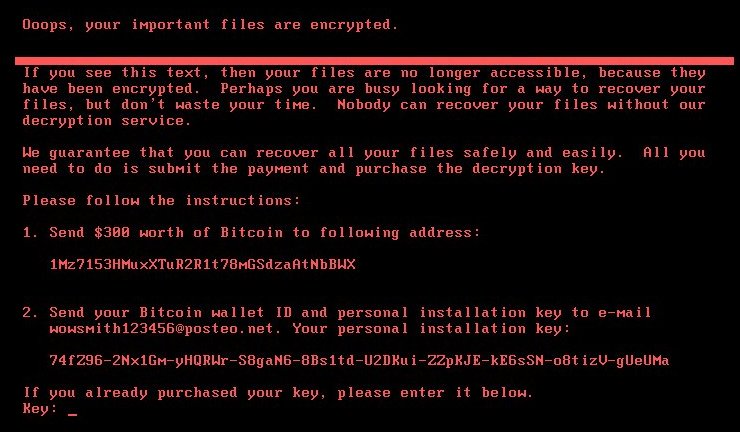
The following message is shown with red text on a black background:
Ooops, your important files are encrypted.
If you see this text, then your files are no longer accessible, because they
have been encrypted. Perhaps you are busy looking for a way to recover your
files, but don’t waste your time. Nobody can recover your files without our
decryption service.We guarantee that you can recover all your files safely and easily. All you
need to do is submit the payment and purchase the decryption key.Please follow the instructions:
1. Send $300 worth of Bitcoin to following address:
1Mz7153HMuxXTuR2R1t78mGSdzaAtNbBWX
2. Send your Bitcoin wallet ID and personal installation key to e-mail
[email protected]. Your personal installation key:X86GcZ-7PRNBE-3mNFMp-z88vnG-uF5nhF-4wzxwZ-XdNrr6-FYG89D-xk4rNz-9yPzJS
If you already purchase your key, please enter it below.
key:
There is a slight chance to recover part of the affected data. This is possible by plugging out the power card and then booting from a Windows recovery disk and issuing the commands related to boot restoration. However only the combination of a quality anti-spyware solution and a professional-grade data recovery application can remedy the infection.
From this note we can see that the Petya virus uses several dangerous tactics that are typical for advanced ransomware:
- Petya ransomware displays the famous “Oops, your files have been encrypted …” or the “Ooops, your files have been encrypted” (with three “o” letters) that are associated with other dangerous viruses as well.
- In addition to the inflicted damage so far the threat also encrypts file type extensions based on a built-in list.
- The used exploits are modified to work in the best possible way with Petya’s engine.
- Some of the resources are signed as being distributed by Microsoft.
- The ransomware engine creates the private decryption key in a secure way that does not permit the victims to unlock their computers by themselves.
- A low ransomware sum of 300 US Dollars is specified. As usual the payment method is the Bitcoin digital currency where transactions cannot be traced to an individual or group.
- Depending on the sample a different email address can be specified by the hackers. So far 4 have been identified in the attack campaign: [email protected], [email protected], [email protected], [email protected].
The Petya virus is able to spawn its own processes.
The Petya virus like other famous ransomware also encrypts sensitive system and user data. The following list has been extracted from the captured samples:
.3ds .7z .accdb .ai .asp .aspx .avhd .back .bak .c .cfg .conf
.cpp .cs .ctl .dbf .disk .djvu .doc .docx .dwg .eml .fdb .gz .h .hdd .kdbx
.mail .mdb .msg .nrg .ora .ost .ova .ovf .pdf .php .pmf .ppt .pptx .pst .pvi
.py .pyc .rar .rtf .sln .sql .tar .vbox .vbs .vcb .vdi .vfd .vmc .vmdk
.vmsd .vmx .vsdx .vsv .work .xls .xlsx .xvd .zip
In addition cyber security experts were able to shut down some of the email addresses associated with the first attack campaign. This however did not stop the hackers from receiving large amounts of ransomware fees. According to one of the reports the hackers behind the Petya virus were able to gain about 6000 US dollars from one of the addresses alone.
So far high-profile victims of the Petya ransomware include the following:
- Several automated taller machines (ATMs) stopped working in Ukraine as part of a large network attack.
- According to several reports the Chernonyl nuclear power plant and its associated facilities fell victim to the Petya virus. Since the incident it does not work, however the radiation control controllers were infected. As a result the workers were forced to manually monitor the facility.
- Several of the world’s largest companies in their respective industries were impacted. The list includes Maersk (the Danish Shipping company) and Merck (pharmaceuticals industry leader).
- The Rosneft Russian oil company also fell victim.
- So far more than 14 countries have been impacted. We expect to see more infections as the virus unfolds in the next few days.
Remove Oops, your important files are encrypted (Petya) Ransomware Virus and Restore Data
WARNING! Manual removal of Oops, your important files are encrypted (Petya) Ransomware Virus requires being familiar with system files and registries. Removing important data accidentally can lead to permanent system damage. If you don’t feel comfortable with manual instructions, download a powerful anti-malware tool that will scan your system for malware and clean it safely for you.
SpyHunter anti-malware tool will diagnose all current threats on the computer. By purchasing the full version, you will be able to remove all malware threats instantly. Additional information about SpyHunter / Help to uninstall SpyHunter
Oops, your important files are encrypted (Petya) Ransomware Virus – Manual Removal Steps
Start the PC in Safe Mode with Network
This will isolate all files and objects created by the ransomware so they will be removed efficiently. The steps bellow are applicable to all Windows versions.
1. Hit the WIN Key + R
2. A Run window will appear. In it, write msconfig and then press Enter
3. A Configuration box shall appear. In it Choose the tab named Boot
4. Mark Safe Boot option and then go to Network under it to tick it too
5. Apply -> OK
Show Hidden Files
Some ransomware threats are designed to hide their malicious files in the Windows so all files stored on the system should be visible.
1. Open My Computer/This PC
2. Windows 7
-
– Click on Organize button
– Select Folder and search options
– Select the View tab
– Go under Hidden files and folders and mark Show hidden files and folders option
3. Windows 8/ 10
-
– Open View tab
– Mark Hidden items option
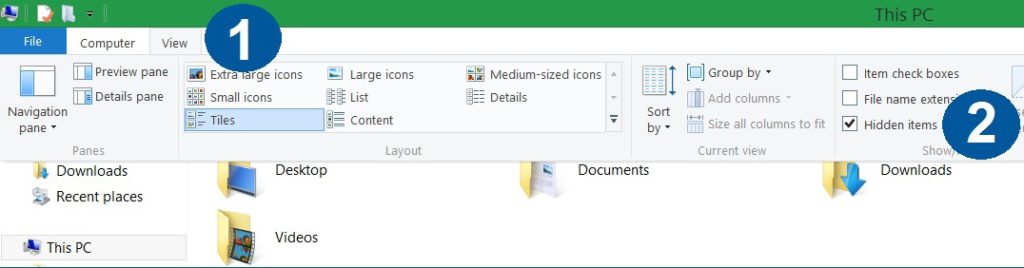
4. Click Apply and then OK button
Enter Windows Task Manager and Stop Malicious Processes
1. Hit the following key combination: CTRL+SHIFT+ESC
2. Get over to Processes
3. When you find suspicious process right click on it and select Open File Location
4. Go back to Task Manager and end the malicious process. Right click on it again and choose End Process
5. Next, you should go folder where the malicious file is located and delete it
Repair Windows Registry
1. Again type simultaneously the WIN Key + R key combination
2. In the box, write regedit and hit Enter
3. Type the CTRL+ F and then write the malicious name in the search type field to locate the malicious executable
4. In case you have discovered registry keys and values related to the name, you should delete them, but be careful not to delete legitimate keys
Click for more information about Windows Registry and further repair help
Recover Oops, your important files are encrypted (Petya) Ransomware Virus Files
WARNING! All files and objects associated with Oops, your important files are encrypted (Petya) Ransomware Virus should be removed from the infected PC before any data recovery attempts. Otherwise the virus may encrypt restored files. Furthermore, a backup of all encrypted files stored on external media is highly recommendable.
DOWNLOAD Oops, your important files are encrypted (Petya) Ransomware Virus Removal ToolSpyHunter anti-malware tool will diagnose all current threats on the computer. By purchasing the full version, you will be able to remove all malware threats instantly. Additional information about SpyHunter / Help to uninstall SpyHunter
1. Use present backups
2. Use professional data recovery software
Stellar Phoenix Data Recovery – a specialist tool that can restore partitions, data, documents, photos, and 300 more file types lost during various types of incidents and corruption.
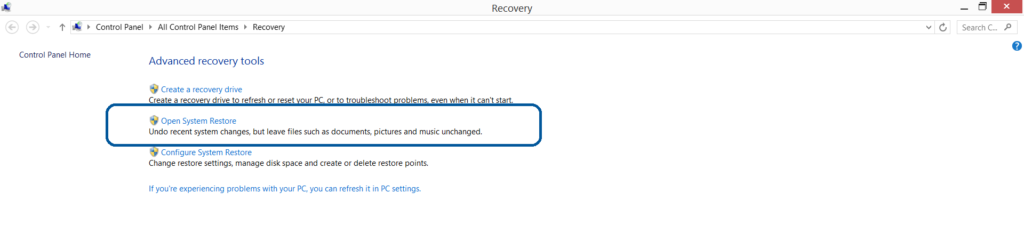
3. Using System Restore Point
-
– Hit WIN Key
– Select “Open System Restore” and follow the steps
4. Restore your personal files using File History
-
– Hit WIN Key
– Type restore your files in the search box
– Select Restore your files with File History
– Choose a folder or type the name of the file in the search bar
– Hit the “Restore” button



