An infection with the dangerous Waffle Ransomware leads to serious security issues. Victims can restore and protect their computers by following our complete removal guide.
Remove Waffle Ransomware and Restore PC
Manual Removal Guide
Skip all steps and download anti-malware tool that will safely scan and clean your PC.
SpyHunter anti-malware tool will diagnose all current threats on the computer. By purchasing the full version, you will be able to remove all malware threats instantly. Additional information about SpyHunter / Help to uninstall SpyHunter
Distribution of Waffle Ransomware
The Waffle ransomware is a new virus which has been sighted in a limited attack campaign. At the moment the security researchers cannot determine the primary infection strategy. We presume that the most widely used tactics are going to be employed.
Among them are the email messages created in an automated way and sent to large lists of potential victims. The Waffle ransomware can be directly attached to the messages. This is one of the easiest way for the criminals to attempt the infection. However a lot of email hosting providers usually capture the signatures of the virus and as such discard such messages or label them as dangerous or spam. Other infection methods related to this one is the option of inserting hyperlinks in the body content of the messages. The links are usually labeled as leading to a familiar website or a file of user interest. Redirects can redirect to hacker-controlled sites, infected payloads or other instances that can lead to an Waffle Ransomware infection.
The computer criminals behind the malware can create malicious sites or download portals which distribute malware of different kinds, including the Waffle Ransomware. A popular option is the use of infected documents which may be of different types ‒ spreadsheets, rich text documents, presentations and databases. They are modified to initiate the virus once the built-in scripts are run. Usually when the files are opened a notification will ask the users to run the macros (scripts). If this is done the infection follows.
The hacker-controlled sites are specialist portals that have been created either manually or automatically by the criminals behind the Waffle Ransomware. They can either directly distribute the threat by initiating various scripts or automated operations or link to such instances. Redirects are usually caused by email interaction, ad networks or other browsing activity. However one of the main sources is the availability of browser hijackers. They are malicious addons made for the most popular web browsers ‒ Mozilla Firefox, Google Chrome, Internet Explorer, Opera, Microsoft Edge and Safari. Once installed they not only infect the users with the malware, but also redirect the victims to a hacker-controlled site. Depending on the configuration the browser hijackers can also steal sensitive information such as any stored passwords, account credentials, history, bookmarks, form data and settings.
Impact of Waffle Ransomware
The malware known as the Waffle ransomware is a recently discovered virus threat which has started to infect computers on a global scale. At the moment the number of found strains are limited in number however we presume that the number will rise as the infections spread further. The initial code analysis did not find any correlation with any of the famous malware families. It is very likely that the virus has been created by its creator ‒ an unknown hacker or criminal collective. Waffle ransomware contains a base engine which is able to perform several pre-infection checks as defined by its operators.
The hackers include a sequence of commands which are executed on the local machine once the infections have been made. A partial list includes the following items:
- Hardware Componens
- Software Installations
- User Settings
- Account Credentials
- Saved Passwords
- Saved Terminal Session Keys
One of the key characteristics of the Waffle ransomware is the fact that the engine is capable of extracting the accounts and passwords of services such as the remote desktop sharing. This makes it very easy for the hackers to take over control of the systems without resorting to the use of Trojan components. Furthermore the Waffle ransomware virus engine also extracts a lot of data from the victim machines, including regional settings. This is a widely used tactic which is used to select the proper ransomware note as advanced malware strains typically have several ones written in different languages.
Stealth Detection measures have also been used, the developers have used the time delay trick to fool some anti-virus signature testing mechanisms. Once the virus has been deployed there is a large delay imposed between the actual intrusion and the start of the Waffle ransomware code execution. Additionally other related implementations are used ‒ the Waffle virus code can, in some extent, protect itself from virtualization and debugging environments.
Once all preliminary stages have been complete the Waffle ransomware engine is loaded and started. Like other popular malware strains it uses a built-list of target file type extensions. The threat targets files such as the following: backups, configuration files, images, videos, music, documents, databases and etc. As a result all victim files are renamed with the .waffle extension.
Next, an application frame is instituted which is a type of lockscreen instance. It displays the ransomware note and actively blocks any ordinary user interaction with the message. A background image of an Waffle with red text over it is shown. The message reads the following:
Hello you have been infected by Waffle Ransomware
This is not a joke if you shut off your PC your files will be deleted. You must pay 50$ USD bitcoin and you will recieve a key and your files will be unencrypted.
Our bitcoin address is:158mxePDNmy2nuf44XXadd7rW5WxePAWGX
You have 24 hours.
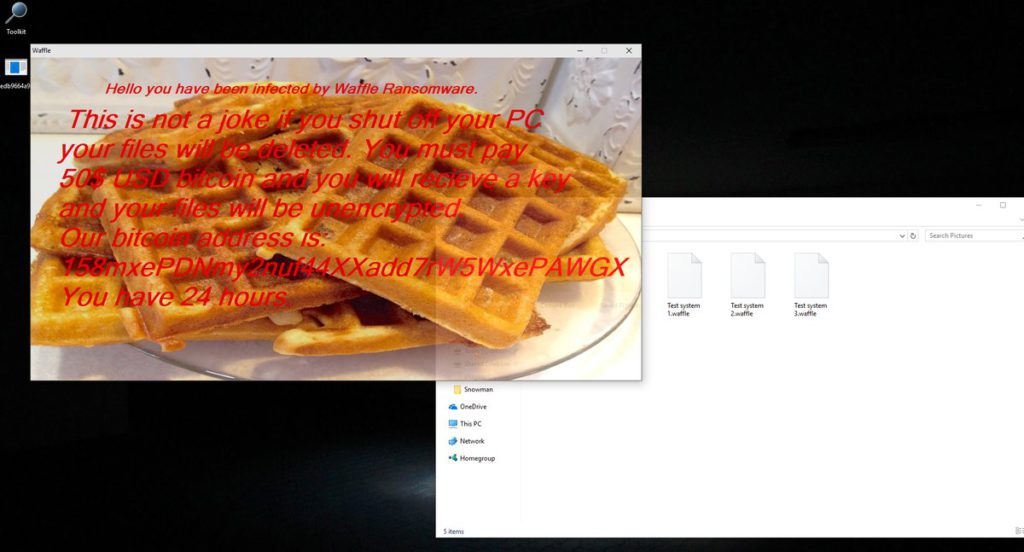
As usual the hacker operators blackmail the victims into paying them the sum of $50 in Bitcoins to the designated address. We recommend that all users abstain from communicating with the hackers and use our full Waffle ransomware removal guide below to recover their data and delete the active infections
Remove Waffle Ransomware and Restore PC
WARNING! Manual removal of the Waffle Ransomware requires being familiar with system files and registries. Removing important data accidentally can lead to permanent system damage. If you don’t feel comfortable with manual instructions, download a powerful anti-malware tool that will scan your system for malware and clean it safely for you.
SpyHunter anti-malware tool will diagnose all current threats on the computer. By purchasing the full version, you will be able to remove all malware threats instantly. Additional information about SpyHunter / Help to uninstall SpyHunter
Waffle Ransomware – Manual Removal Steps
Start the PC in Safe Mode with Network
This will isolate all files and objects created by the ransomware so they will be removed efficiently. The steps bellow are applicable to all Windows versions.
1. Hit the WIN Key + R
2. A Run window will appear. In it, write msconfig and then press Enter
3. A Configuration box shall appear. In it Choose the tab named Boot
4. Mark Safe Boot option and then go to Network under it to tick it too
5. Apply -> OK
Remove Waffle from Windows
Here’s a way to remove the program. This method will work regardless if you’re on Windows 10, 8, 7, Vista or XP. Simply selecting the program and pressing delete won’t work, as it’ll leave a lot of small files. That’s bad because these leftovers can linger on and cause all sorts of problems. The best way to delete a program is to uninstall it. Here’s how you can do that:
1. Hold the “Windows” button (It’s between CTRL and Alt on most keyboards) and press “R”. You’ll see a pop-up window.
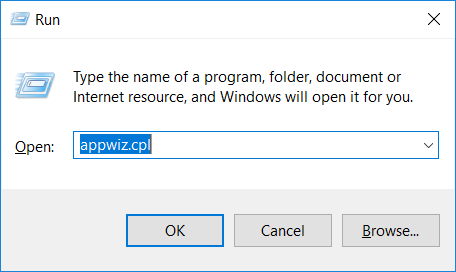
2. In the textbox, type “appwiz.cpl”, then press“ Enter ”.
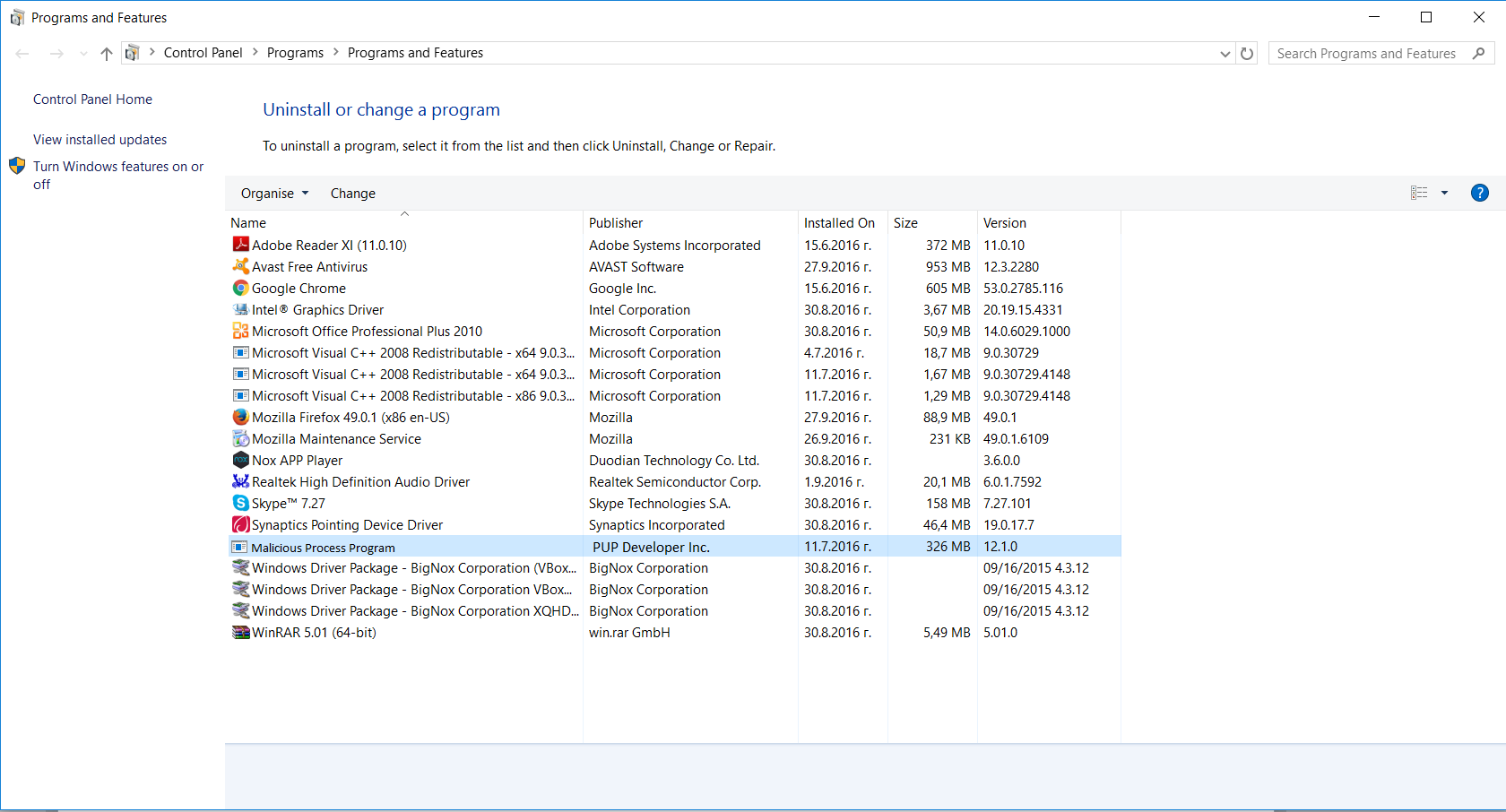
3. The “Programs and features” menu should now appear. It’s a list of all the programs installed on the PC. Here you can find the program, select it, and press “Uninstall“.
Remove Waffle Virus From Your Browser
Before resetting your browser’s settings, you should know that this action will wipe out all your recorded usernames, passwords, and other types of data. Make sure to save them in some way.
-
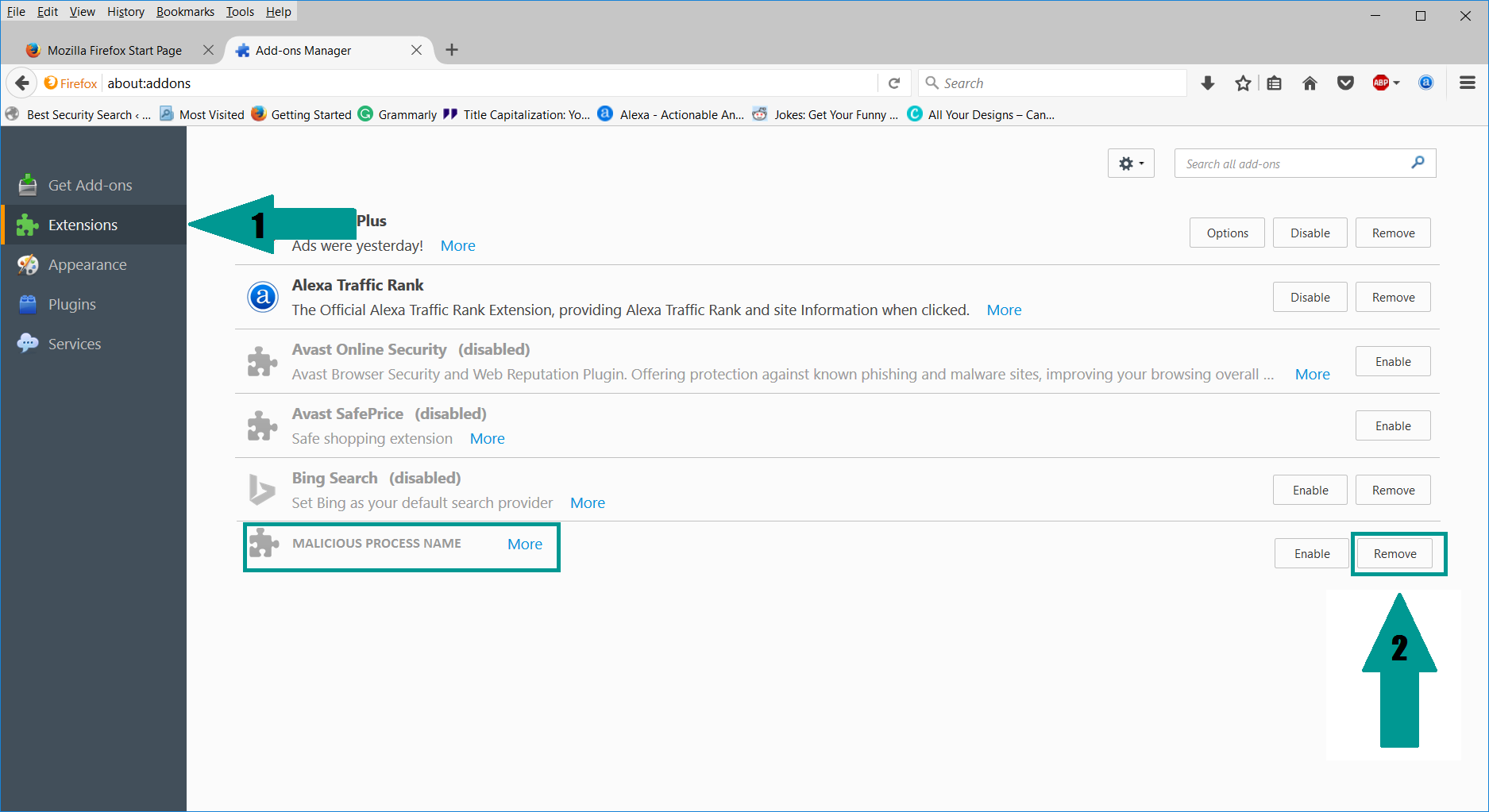
1. Start Mozilla Firefox. In the upper right corner, click on the Open menu icon and select “Add-ons“.

2. Inside the Add-ons Manager select “Extensions“. Search the list of extensions for suspicious entries. If you find any, select them and click “Remove“.
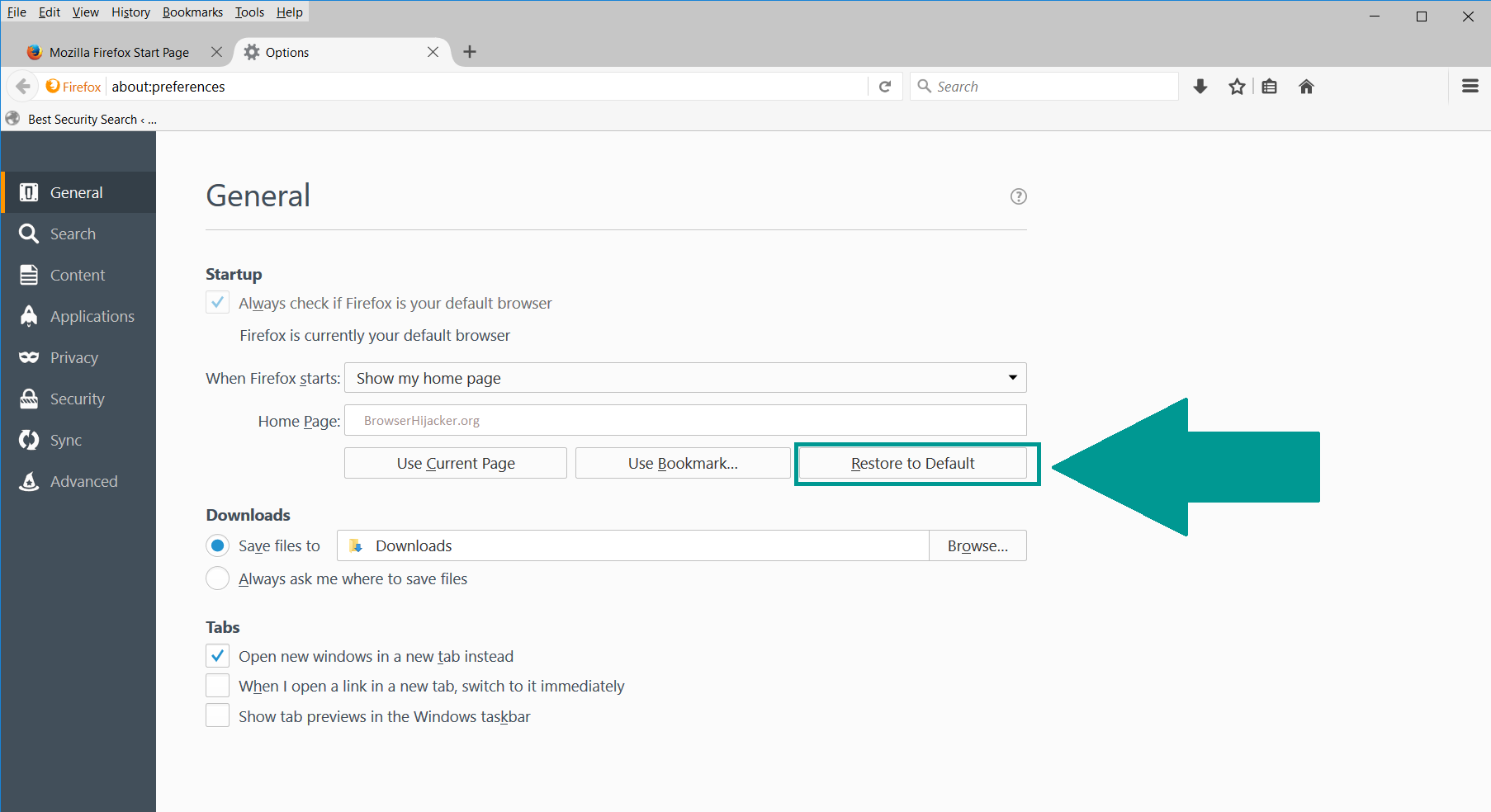
3. Click again on the Open menu icon, then click “Options“.

4. In the Options window, under “General” tab, click “Restore to Default“.
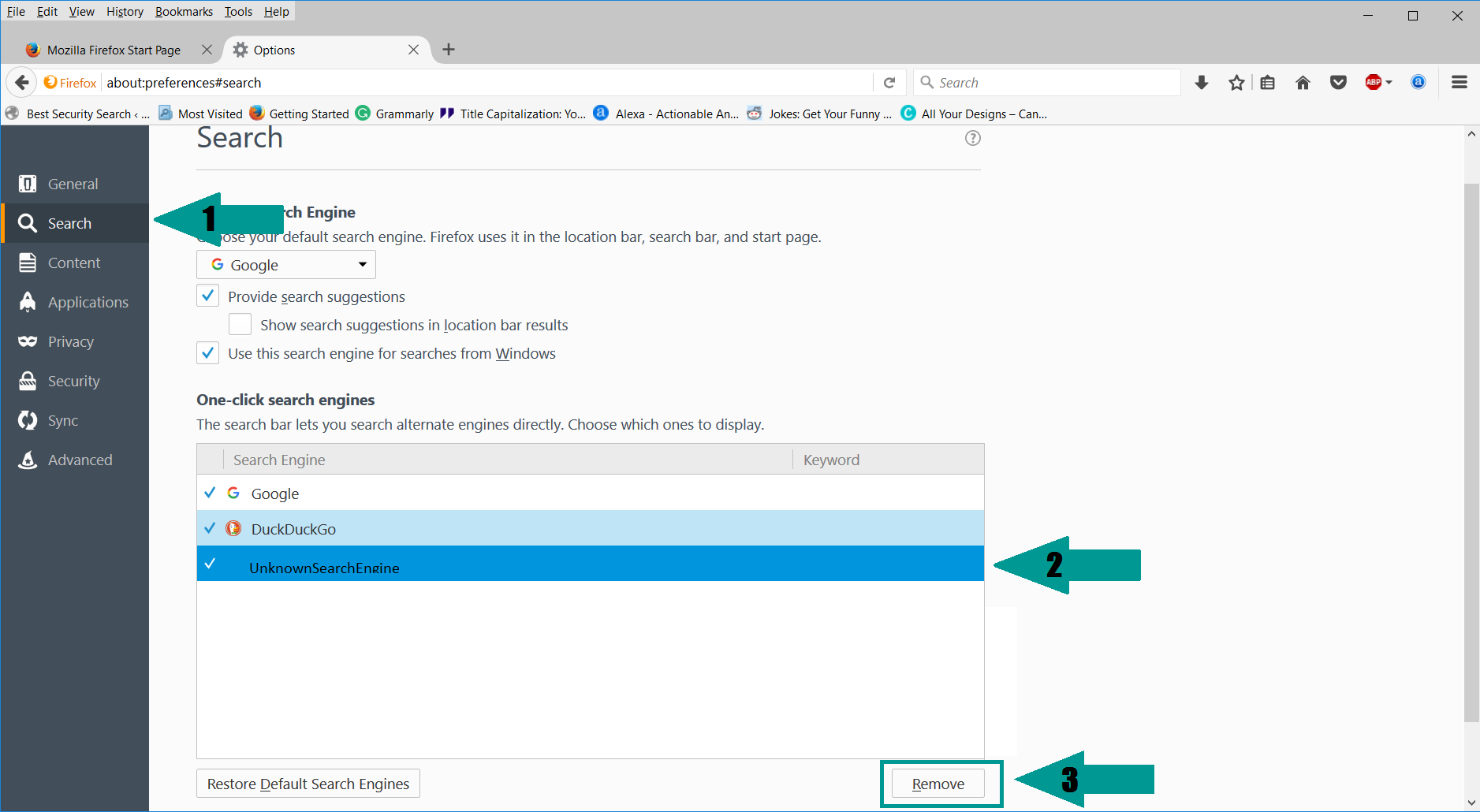
5. Select “Search” in the left menu, mark the unknown search engine and press “Remove”.
-
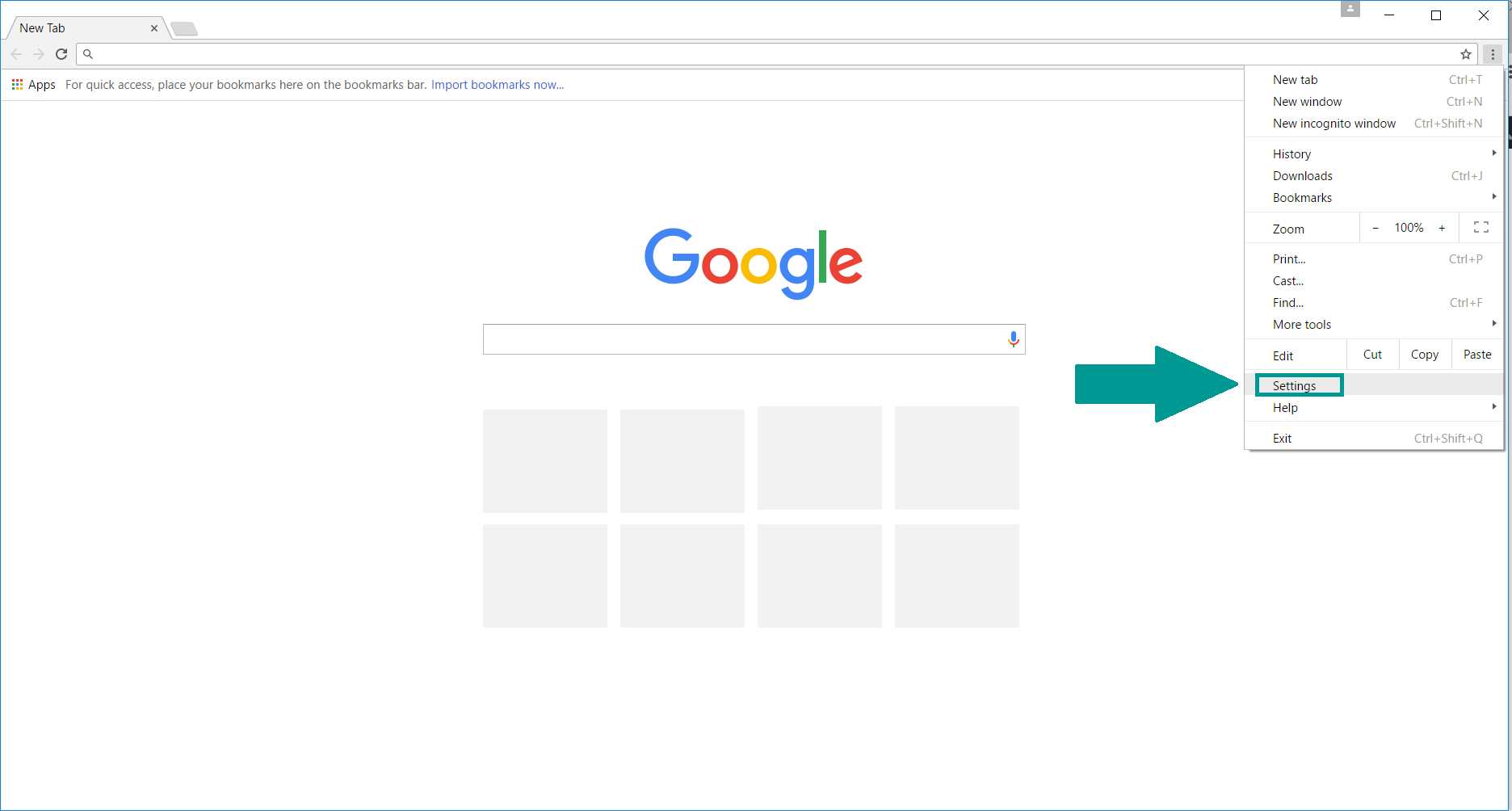
1. Start Google Chrome. On the upper-right corner, there a “Customize and Control” menu icon. Click on it, then click on “Settings“.
2. Click “Extensions” in the left menu. Then click on the trash bin icon to remove the suspicious extension.
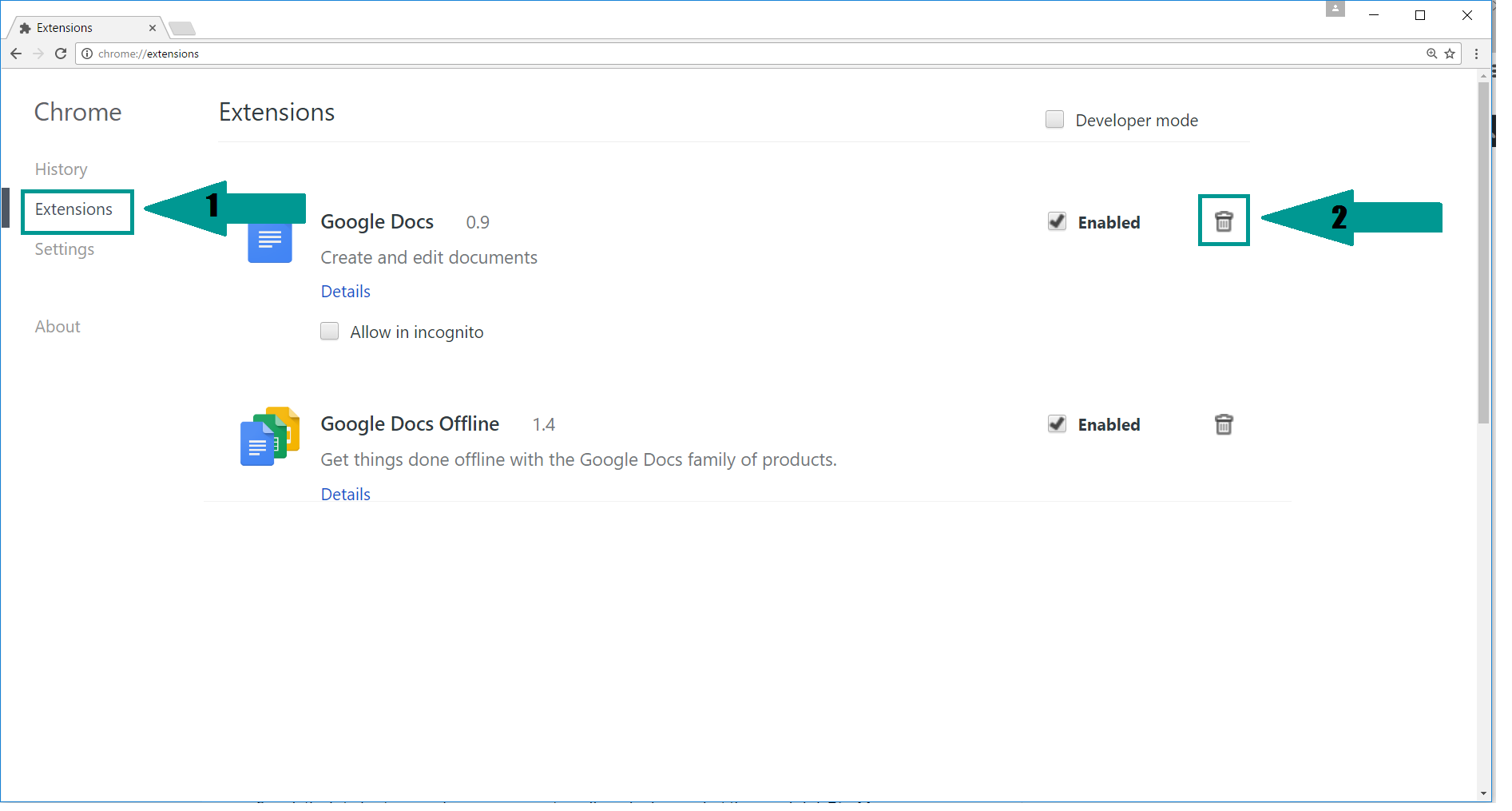
3. Again in the left menu, under Chrome, Click on “Settings“. Go under “On Startup” and set a new page.
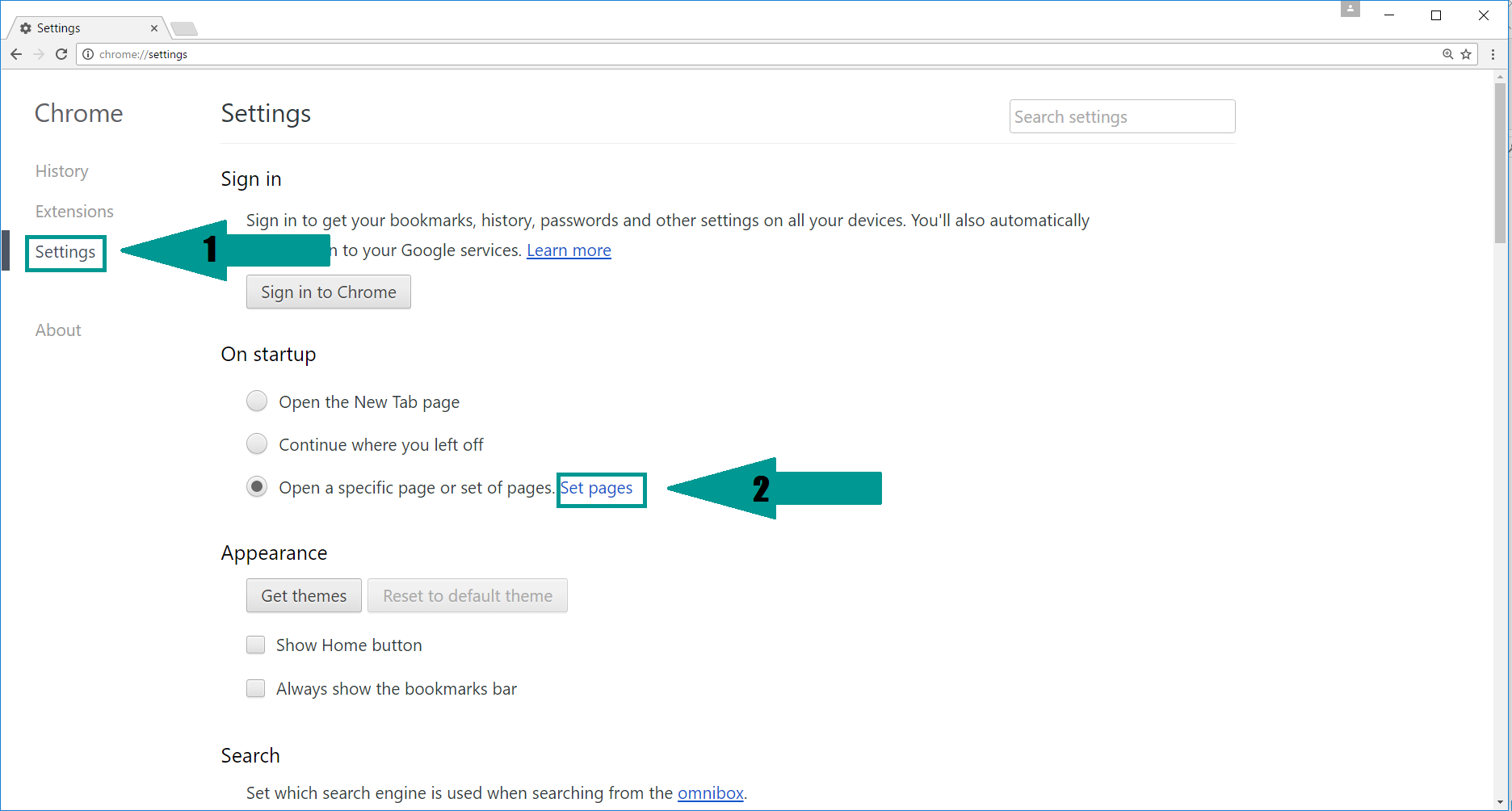
4. Afterward, scroll down to “Search“, click on “Manage search engines“.
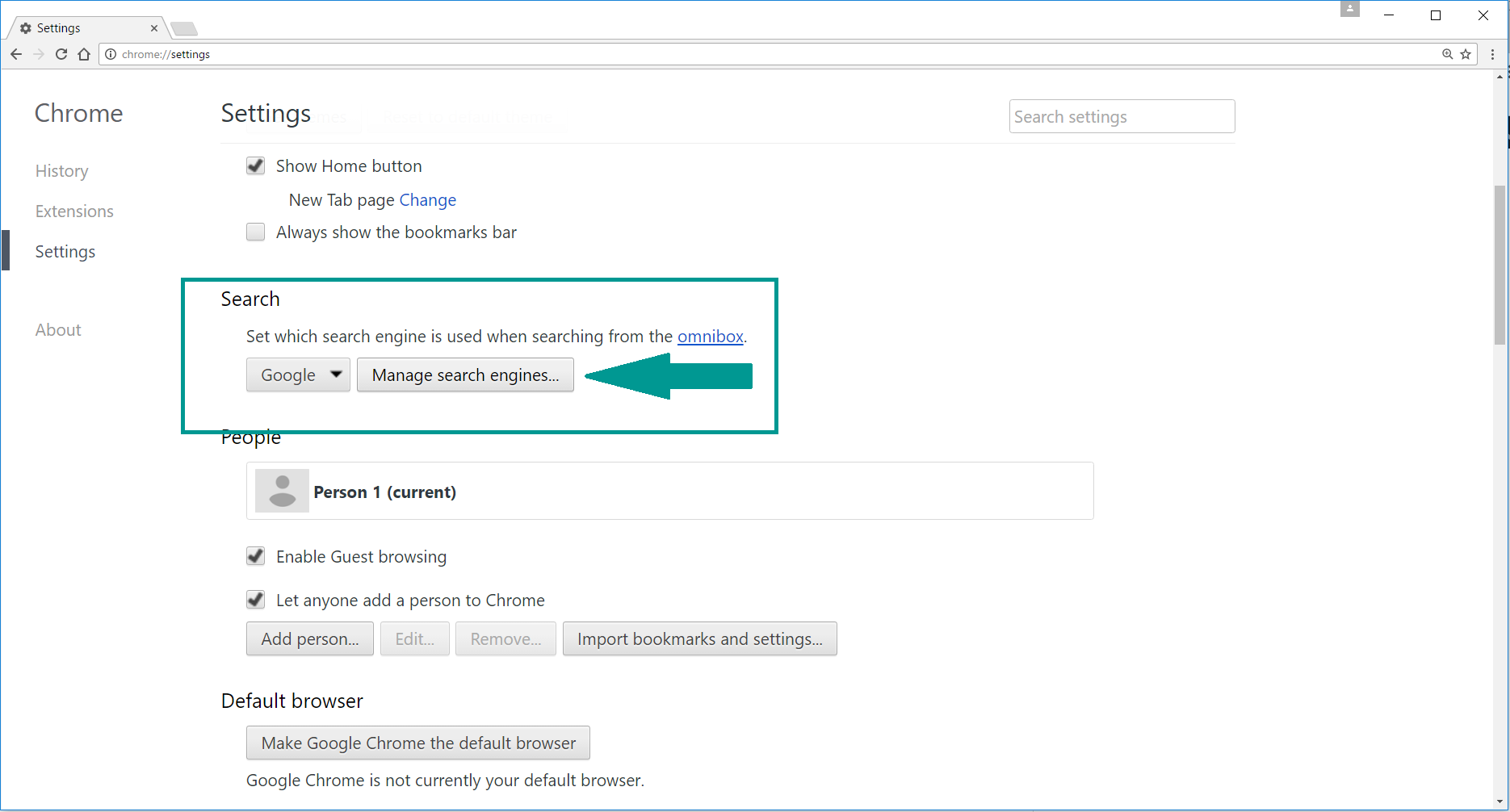
5. In the default search settings list, find the unknown search engine and click on “X“. Then select your search engine of choice and click “Make default“. When you are ready click “Done” button in the right bottom corner.
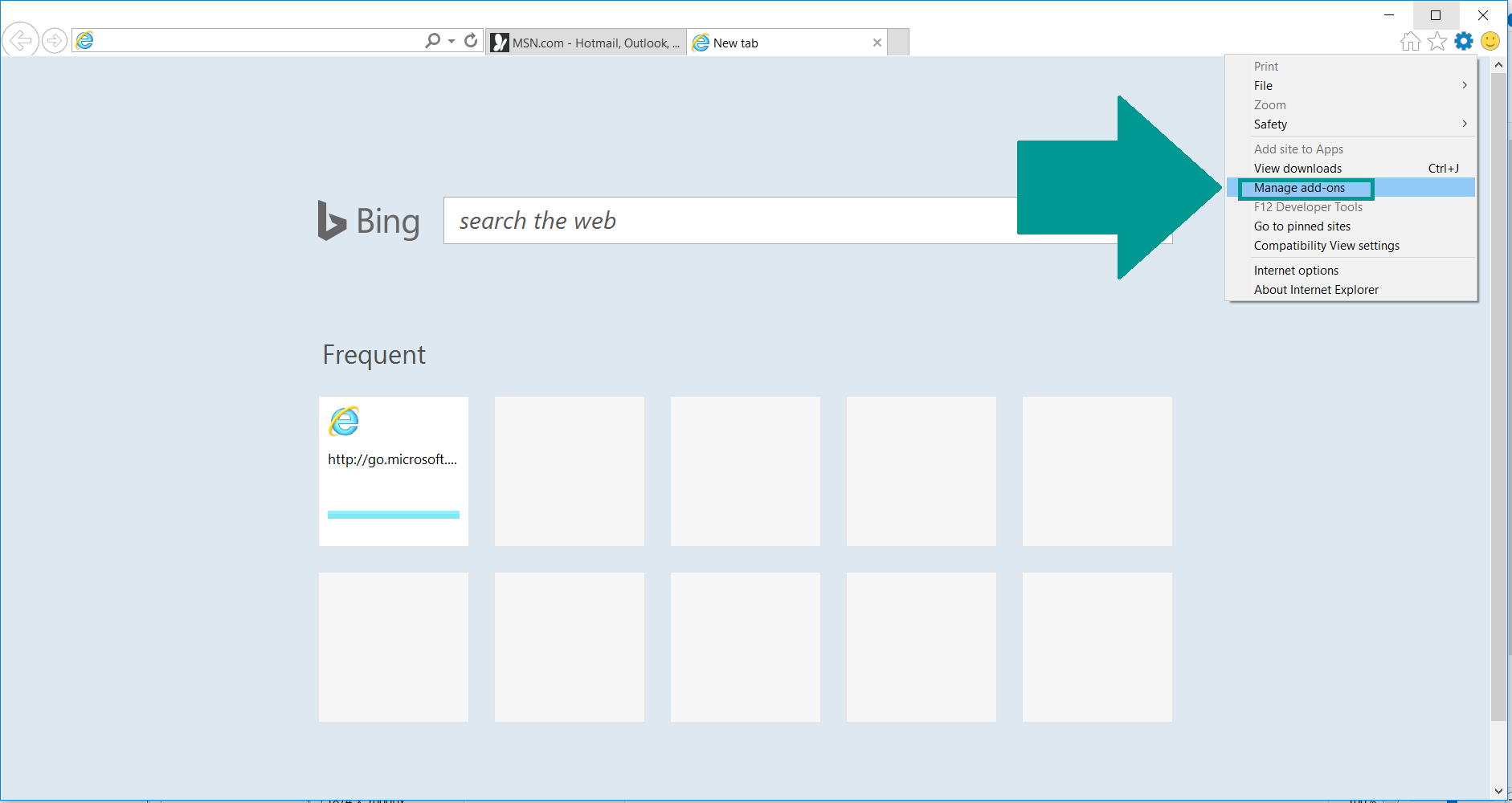
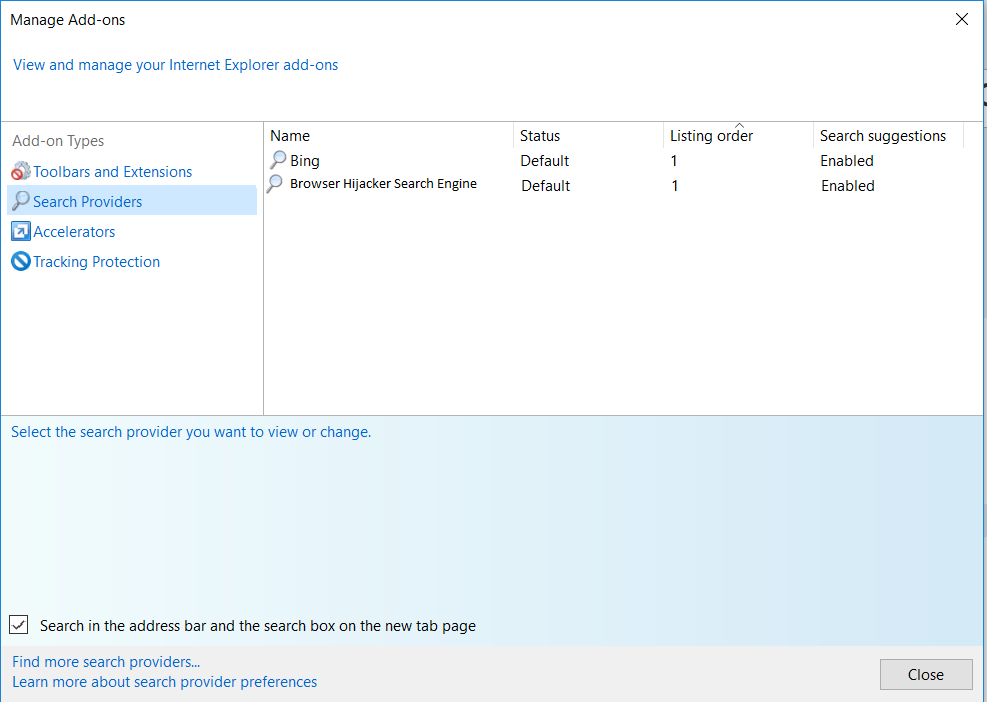
2. In the “Manage add-ons” window, bellow “Add-on Types“, select “Toolbars and Extensions“. If you see a suspicious toolbar, select it and click “Remove“.
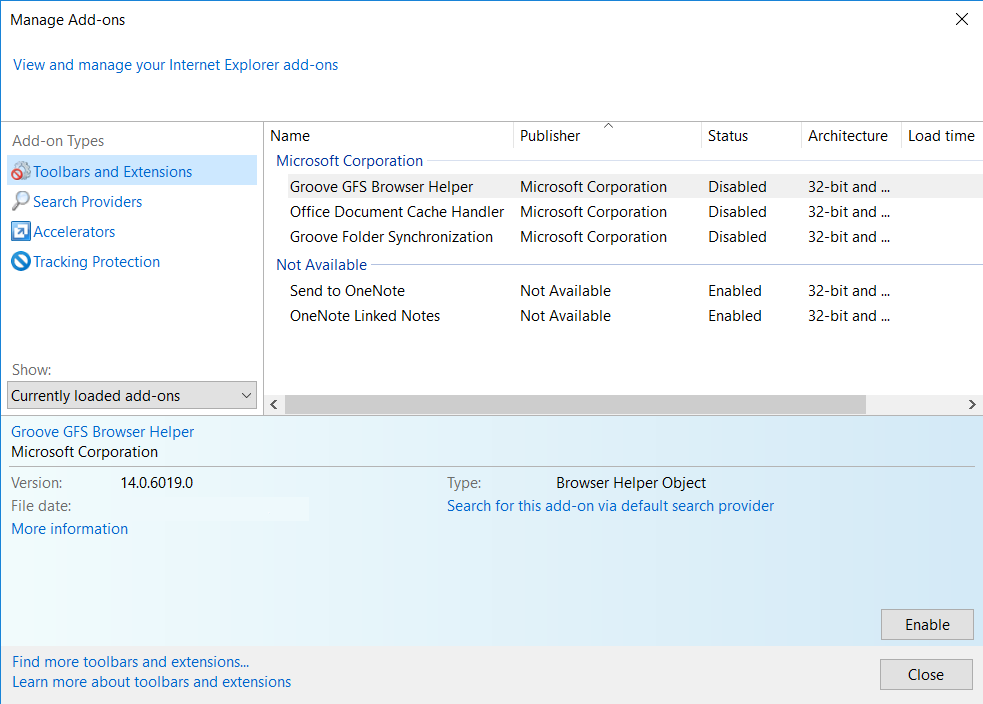
3. Then again in the “Manage Add-ons” window, in “Add-on Types“, Select “Search Providers“. Chose a search engine and click “Set as default“. Select the unknown search engine and click “Remove and Close”.
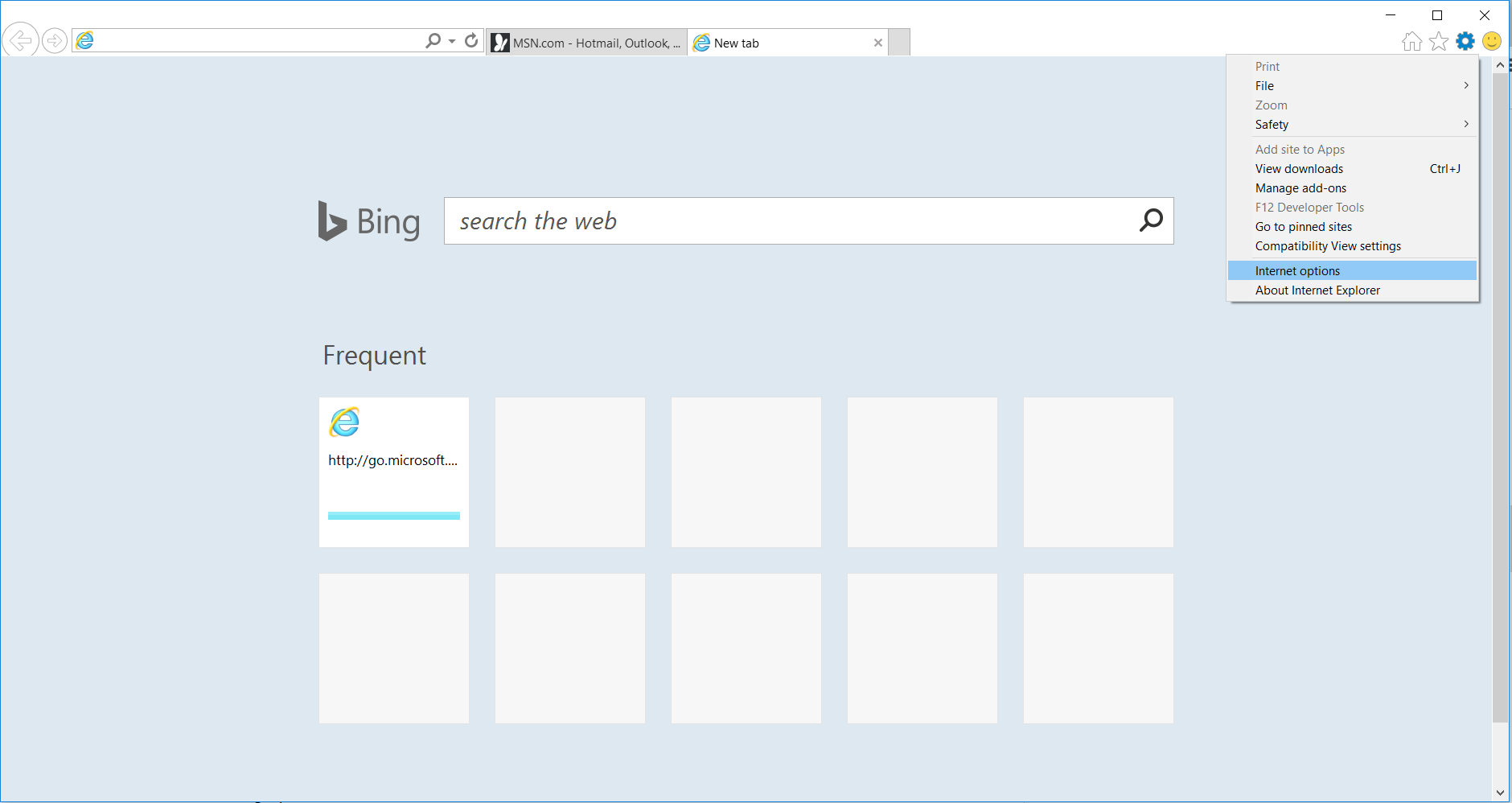
4. Open the Tools menu, select “Internet Options”.
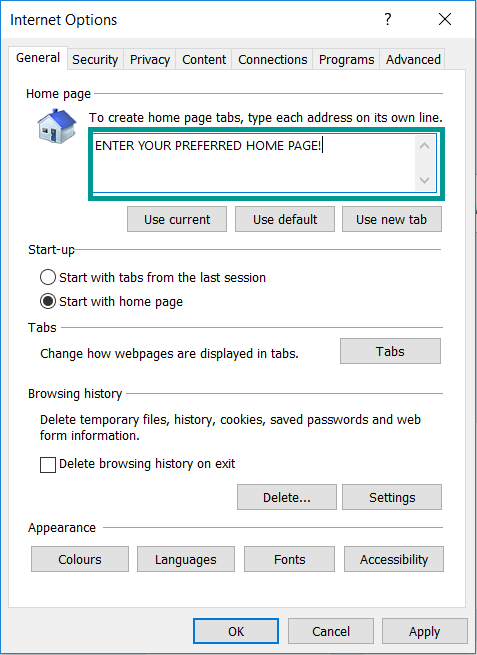
5. In the “General” tab, in “Home page”, enter your preferred page. Click “Apply” and “OK”.
Repair Windows Registry
1. Again type simultaneously the WIN Key + R key combination
2. In the box, write regedit and hit Enter
3. Type the CTRL+ F and then write the malicious name in the search type field to locate the malicious executable
4. In case you have discovered registry keys and values related to the name, you should delete them, but be careful not to delete legitimate keys
Click for more information about Windows Registry and further repair help



