
An infection with the dangerous FoxSearch Redirect leads to serious security issues. Victims can restore and protect their computers by following our complete removal guide.
Remove FoxSearch Redirect and Restore PC
Manual Removal Guide
Skip all steps and download anti-malware tool that will safely scan and clean your PC.
SpyHunter anti-malware tool will diagnose all current threats on the computer. By purchasing the full version, you will be able to remove all malware threats instantly. Additional information about SpyHunter / Help to uninstall SpyHunter
Distribution of FoxSearch Redirect
FoxSearch is a new malware which has been reported in various attacks worldwide. At the moment the security experts have not been able to identify a single tactic that is being used to infect the targets. We presume that the hackers are using several of the most important methods to carry out the malicious campaigns.
A common way of setting browser hijacker attacks is the use of email spam messages. They may directly distribute malicious file attachments containing scripts that lead to an infection. Other cases can utilize complex social engineering tricks and hyperlinks that are specifically made to confuse the intended targets into infecting themselves. Two more scenarios that are used in combination with email messages rely on infected files used as payloads ‒ documents and software installers.
- Infected Software Installers ‒ The criminals craft malicious packages made out of legitimate software installers. They are taken from the official vendor download sites, modified and then posted on online sites or attached (either as file attachments) or linked in the email messages.
- Infected Documents ‒ They represent dangerous files that usually come in the form of some of the most popular document types: rich text documents, spreadsheets and databases. When the users open them up a notification prompt will ask them to enable the built-in scripts (macros). If this is done then the malware is installed on the victim computer.
The malware browser plugins can be uploaded to hacker-controlled sites and P2P networks like BitTorrent as well. The hacker operators frequently utilize template design, text and images to create portals that look like legitimate download sources. They may also use domain names that are very similar to legitimate sites and advertise them via pop-ups or ad networks.
The browser hijacker code associated with the FoxSearch Redirect can be found in numerous malware toolbars. They are usually made for the most popular web browsers: Mozilla Firefox, Google Chrome, Internet Explorer, Safari, Microsoft Edge. They can be distributed on such download sites or even on the browsers repositories (such as the Chrome Web Store for Google Chrome) using fake developer accounts.
Impact of FoxSearch Redirect
The Foxsearch redirect is a new browser hijacker that has recently been featured in a large scale attack campaign. The initial analysis shows that it bears the same malware behavior patterns as other related threats by seeking to implant itself deep into the available browsers and potentially cause other damage to the victim system as well.
The security researchers indicate that the Fox Search is being distributed using the most widely used strategies. It seeks to modify the most important settings on the compatible web browsers. Hackers behind such hijackers usually make the code compatible with all major software including: Mozilla Firefox, Google Chrome, Safari, Microsoft Edge, Internet Explorer and Opera. The initial infection campaign begins with the modification of the default home page, search engine and new tabs page. This is to make the computer users navigate to the FoxSearch site the first time they open their browser windows.
When the Foxsearch redirect is imposed on a victim computer serious security and privacy consequences, the first time the site is visited a tracking cookie is instituted on the web browsers. Together with other technology such as web beacons the operators of the site can continously monitor the users behavior. Bear in mind that hijackers like this one may also extract sensitive information from the applications including the following: cookies, settings, history, bookmarks, account credentials, form data and passwords. In addition they can also deliver other malware to the infected computers. The way the site is designed will appeal to many users that will probably think that this is part of the web browser or a substitute for their own home page. This is especially true following browser updates which may confuse certain beginner users. Furthermore the logo of the Foxsearch redirect is similar to the Mozilla Firefox image.
The center of the site showcases the logo with the search box underneath it. At the bottom of the page there are the terms of use and the privacy policy along with uninstall instructions. Our analysis shows that advanced versions may install themselves in a persistent way which effectively makes the simple removal instructions non-effective.
The privacy policy reads some of the dangerous privacy and security implications associated with its use. When a browser window is invoked immediately the user interactions are recorded and transmitted to the operators.
Some of the harvested data types include the following:
- Cookies
- Settings
- Site Interactions
- Personally-identifiable information related to the user such as their real name, telephone number, address, age and etc.
- User preferences and interests
Usually the collected data is recorded in large databases that are shared between several sites and hijackers. The harvested records are then sold to marketing agencies or shared with partners that may abuse the data.
FoxSearch Redirect is a very dangerous threat that must be eliminated completely to prevent any privacy and security risks for the victim users. This is why we we recommend that all users remove the active infections by following our in-depth removal guide.
Remove FoxSearch Redirect and Restore PC
WARNING! Manual removal of the FoxSearch Redirect requires being familiar with system files and registries. Removing important data accidentally can lead to permanent system damage. If you don’t feel comfortable with manual instructions, download a powerful anti-malware tool that will scan your system for malware and clean it safely for you.
SpyHunter anti-malware tool will diagnose all current threats on the computer. By purchasing the full version, you will be able to remove all malware threats instantly. Additional information about SpyHunter / Help to uninstall SpyHunter
FoxSearch Redirect – Manual Removal Steps
Start the PC in Safe Mode with Network
This will isolate all files and objects created by the ransomware so they will be removed efficiently. The steps bellow are applicable to all Windows versions.
1. Hit the WIN Key + R
2. A Run window will appear. In it, write msconfig and then press Enter
3. A Configuration box shall appear. In it Choose the tab named Boot
4. Mark Safe Boot option and then go to Network under it to tick it too
5. Apply -> OK
Remove FoxSearch from Windows
Here’s a way to remove the program. This method will work regardless if you’re on Windows 10, 8, 7, Vista or XP. Simply selecting the program and pressing delete won’t work, as it’ll leave a lot of small files. That’s bad because these leftovers can linger on and cause all sorts of problems. The best way to delete a program is to uninstall it. Here’s how you can do that:
1. Hold the “Windows” button (It’s between CTRL and Alt on most keyboards) and press “R”. You’ll see a pop-up window.
2. In the textbox, type “appwiz.cpl”, then press“ Enter ”.
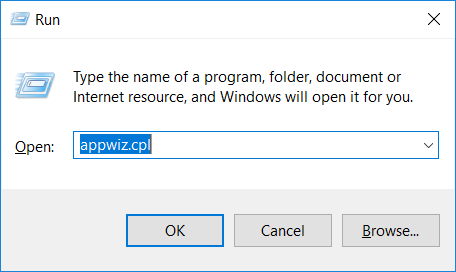
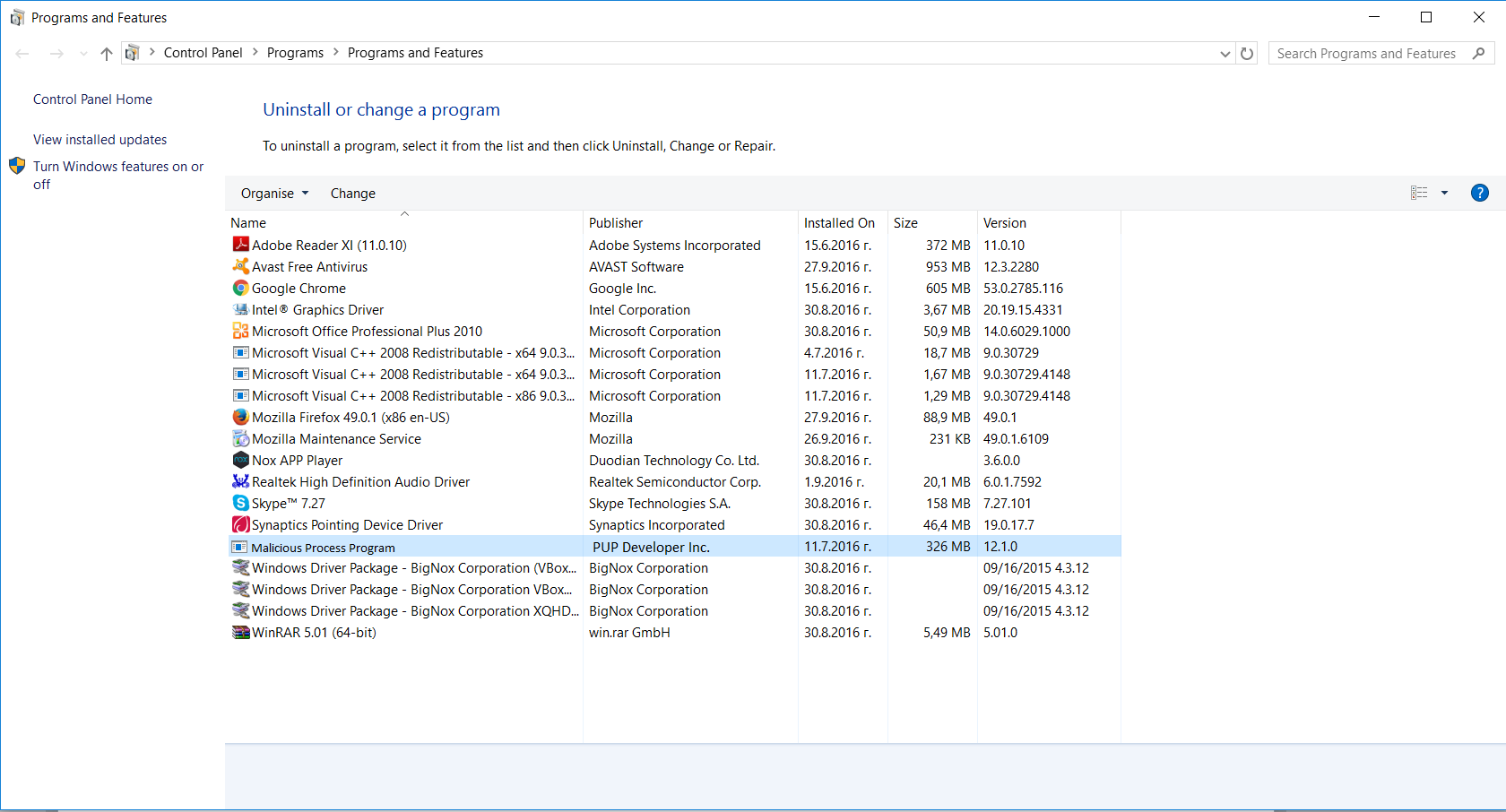
3. The “Programs and features” menu should now appear. It’s a list of all the programs installed on the PC. Here you can find the program, select it, and press “Uninstall“.
Remove FoxSearch Virus From Your Browser
Before resetting your browser’s settings, you should know that this action will wipe out all your recorded usernames, passwords, and other types of data. Make sure to save them in some way.
-
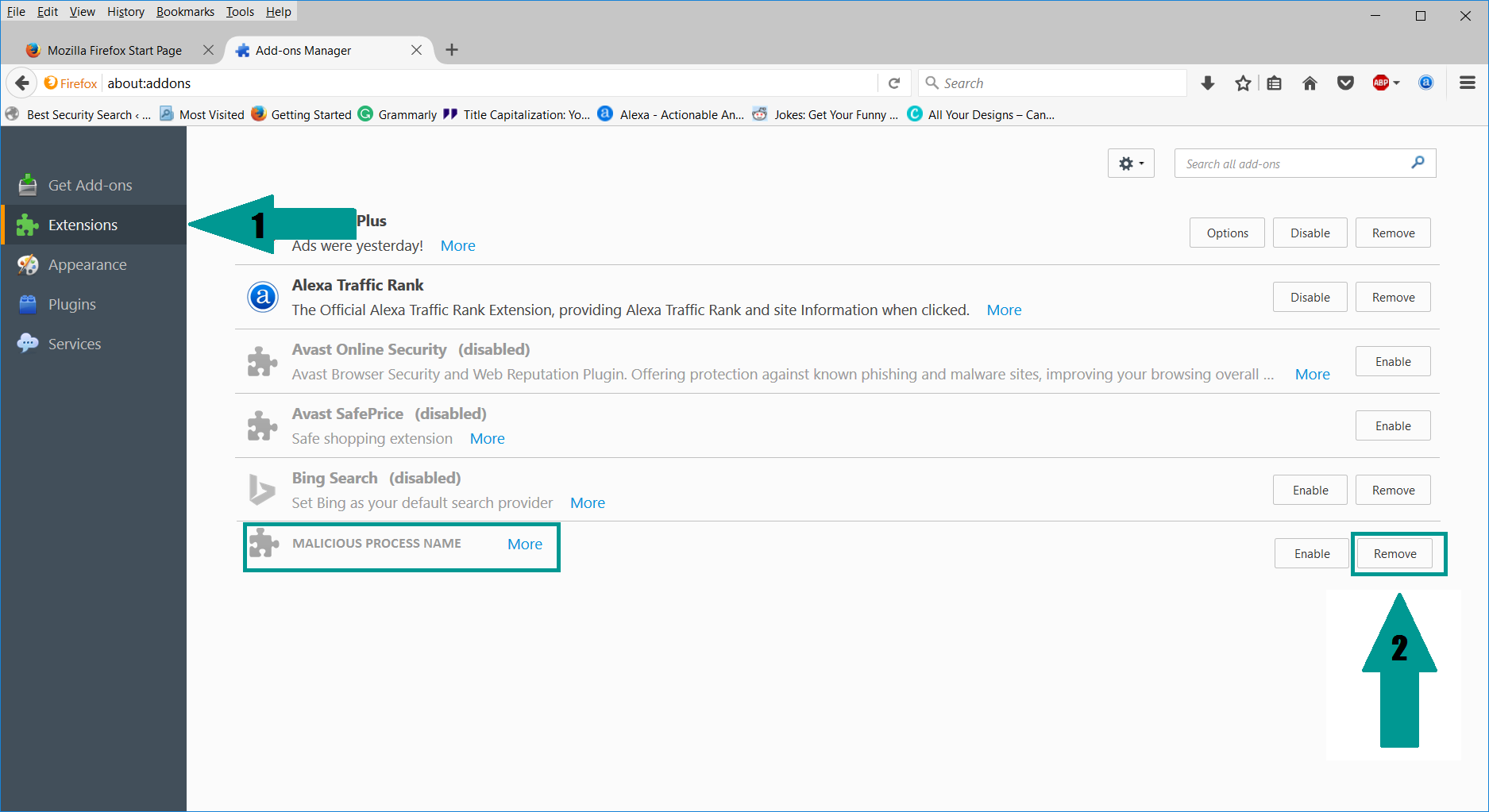
1. Start Mozilla Firefox. In the upper right corner, click on the Open menu icon and select “Add-ons“.

2. Inside the Add-ons Manager select “Extensions“. Search the list of extensions for suspicious entries. If you find any, select them and click “Remove“.
3. Click again on the Open menu icon, then click “Options“.

4. In the Options window, under “General” tab, click “Restore to Default“.
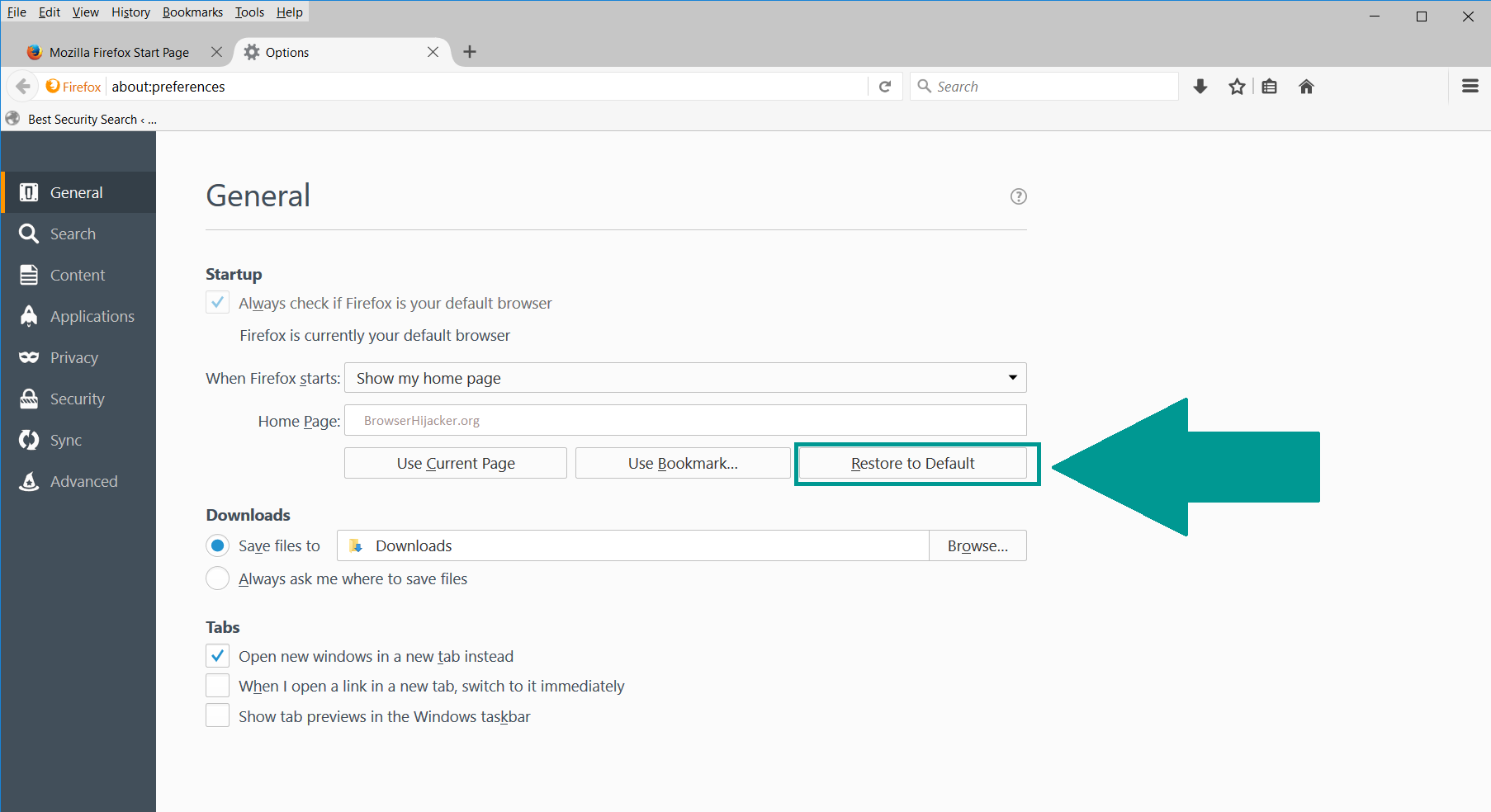
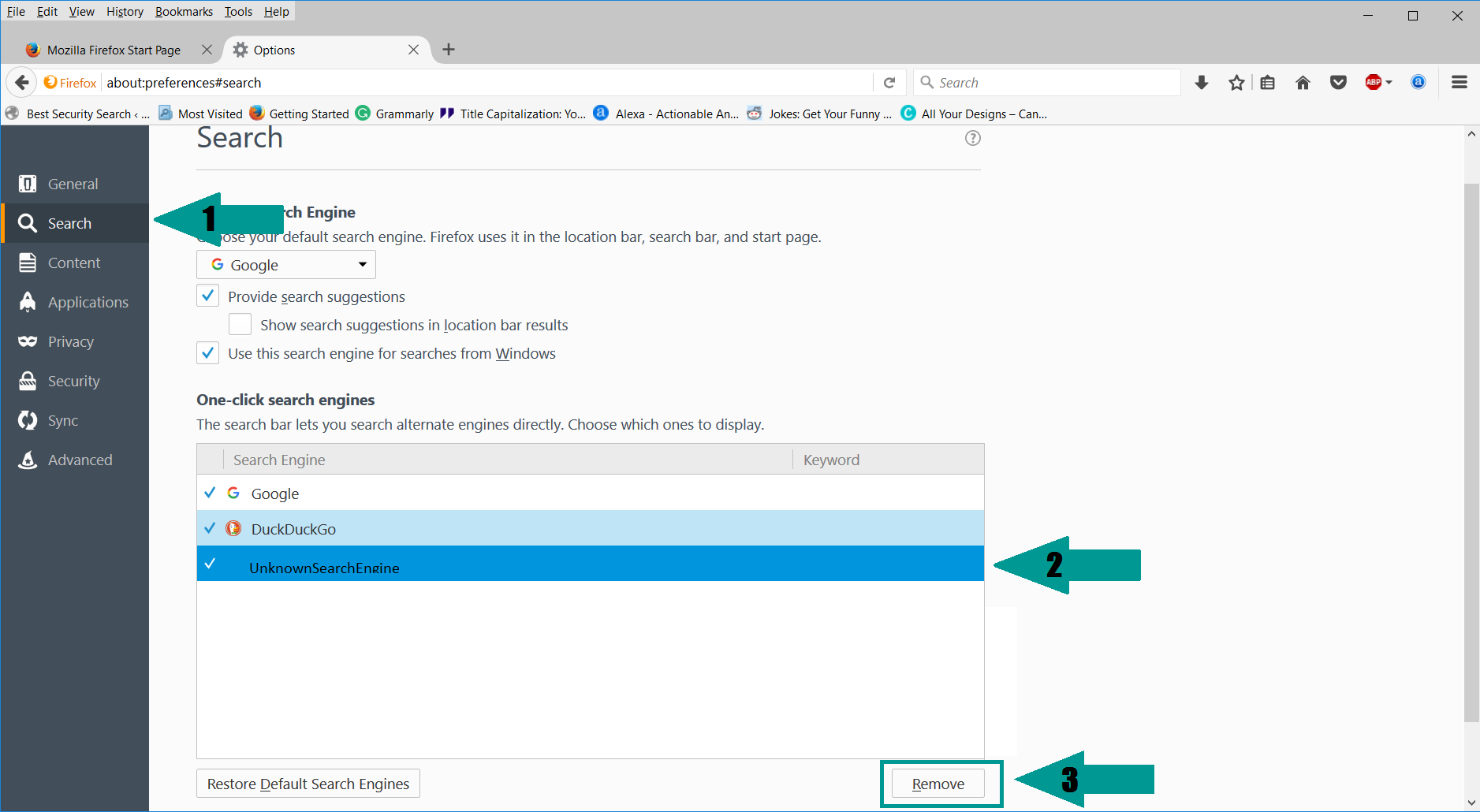
5. Select “Search” in the left menu, mark the unknown search engine and press “Remove”.
-
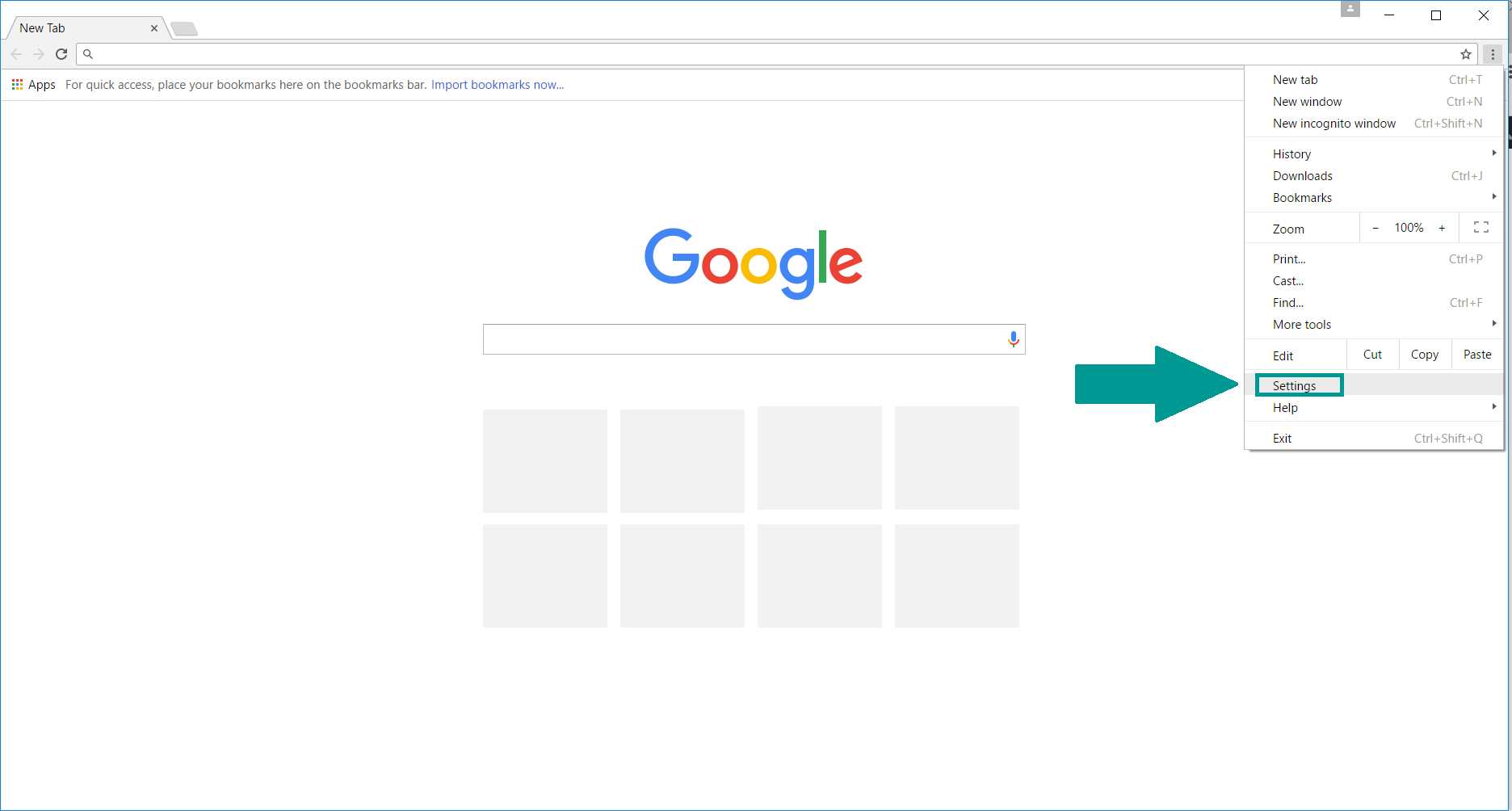
1. Start Google Chrome. On the upper-right corner, there a “Customize and Control” menu icon. Click on it, then click on “Settings“.
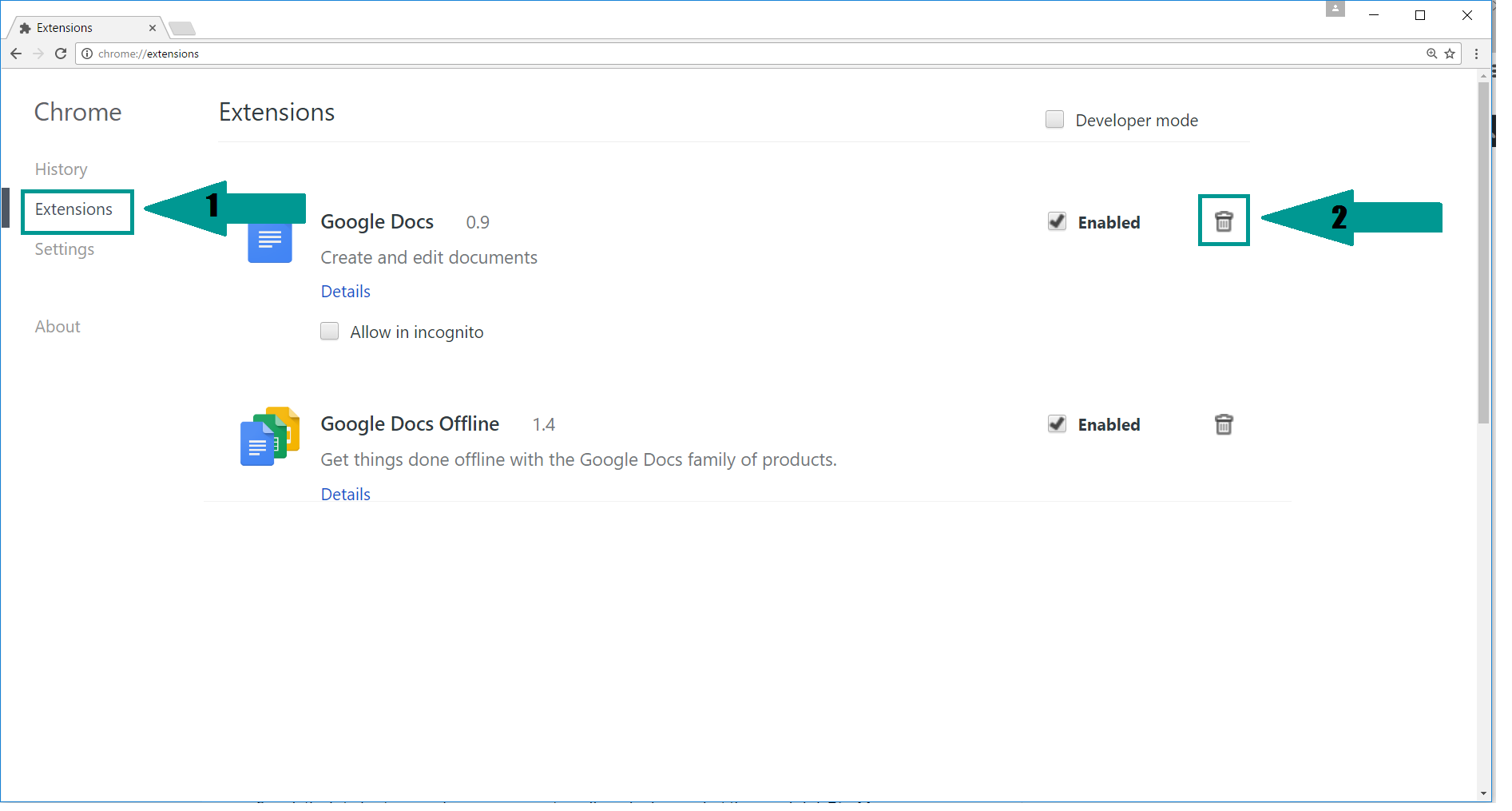
2. Click “Extensions” in the left menu. Then click on the trash bin icon to remove the suspicious extension.
3. Again in the left menu, under Chrome, Click on “Settings“. Go under “On Startup” and set a new page.
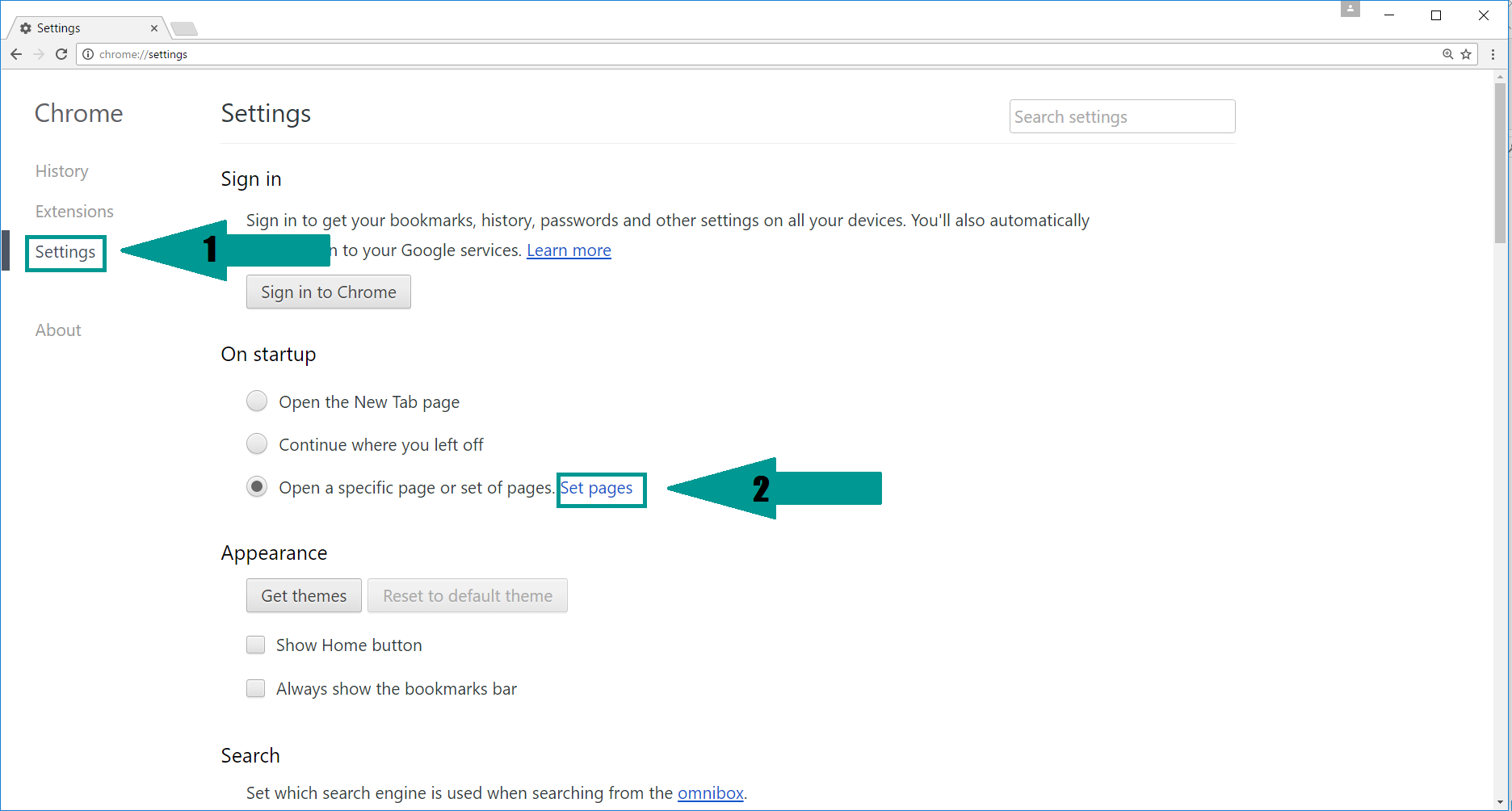
4. Afterward, scroll down to “Search“, click on “Manage search engines“.
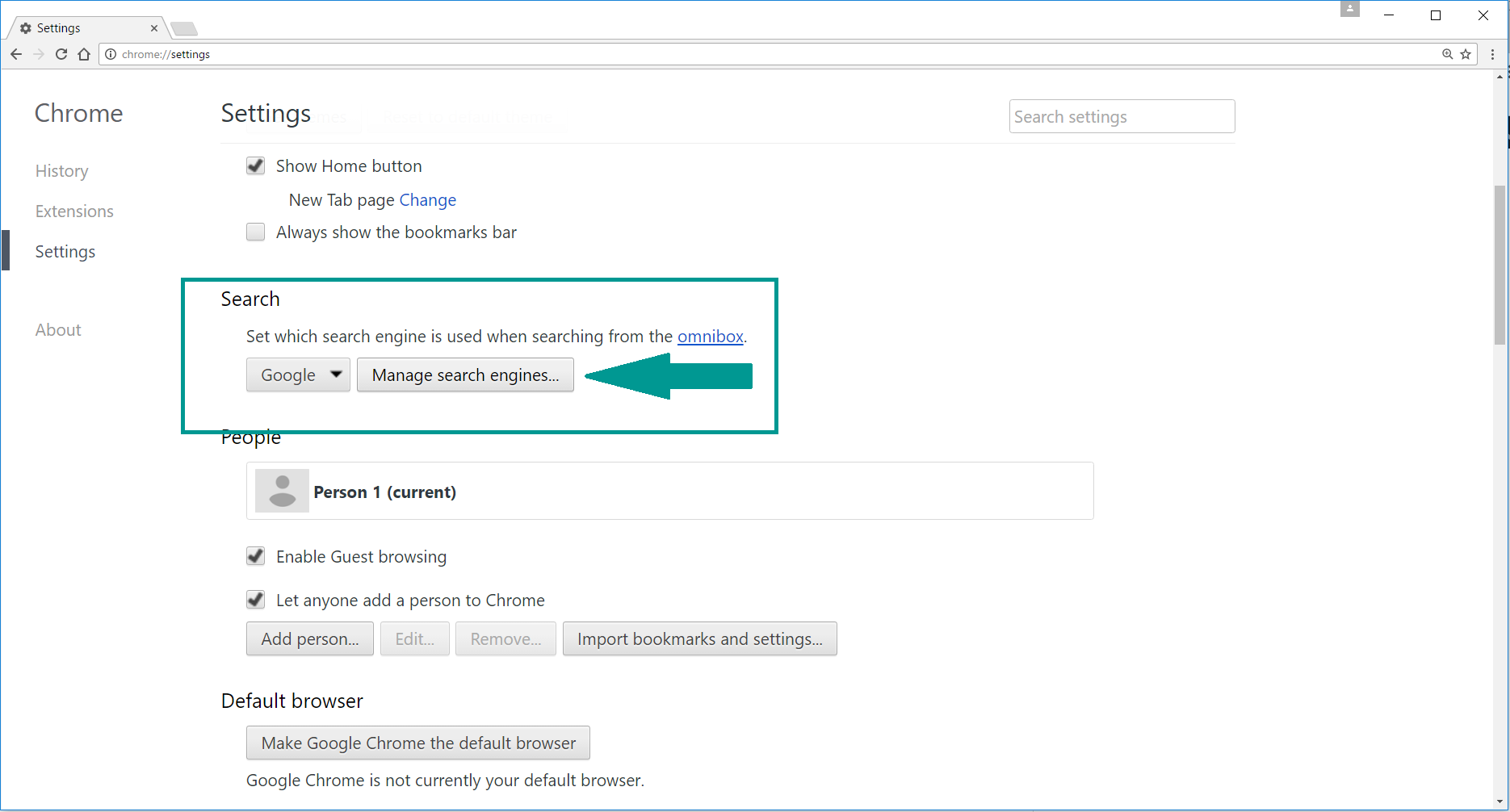
5. In the default search settings list, find the unknown search engine and click on “X“. Then select your search engine of choice and click “Make default“. When you are ready click “Done” button in the right bottom corner.
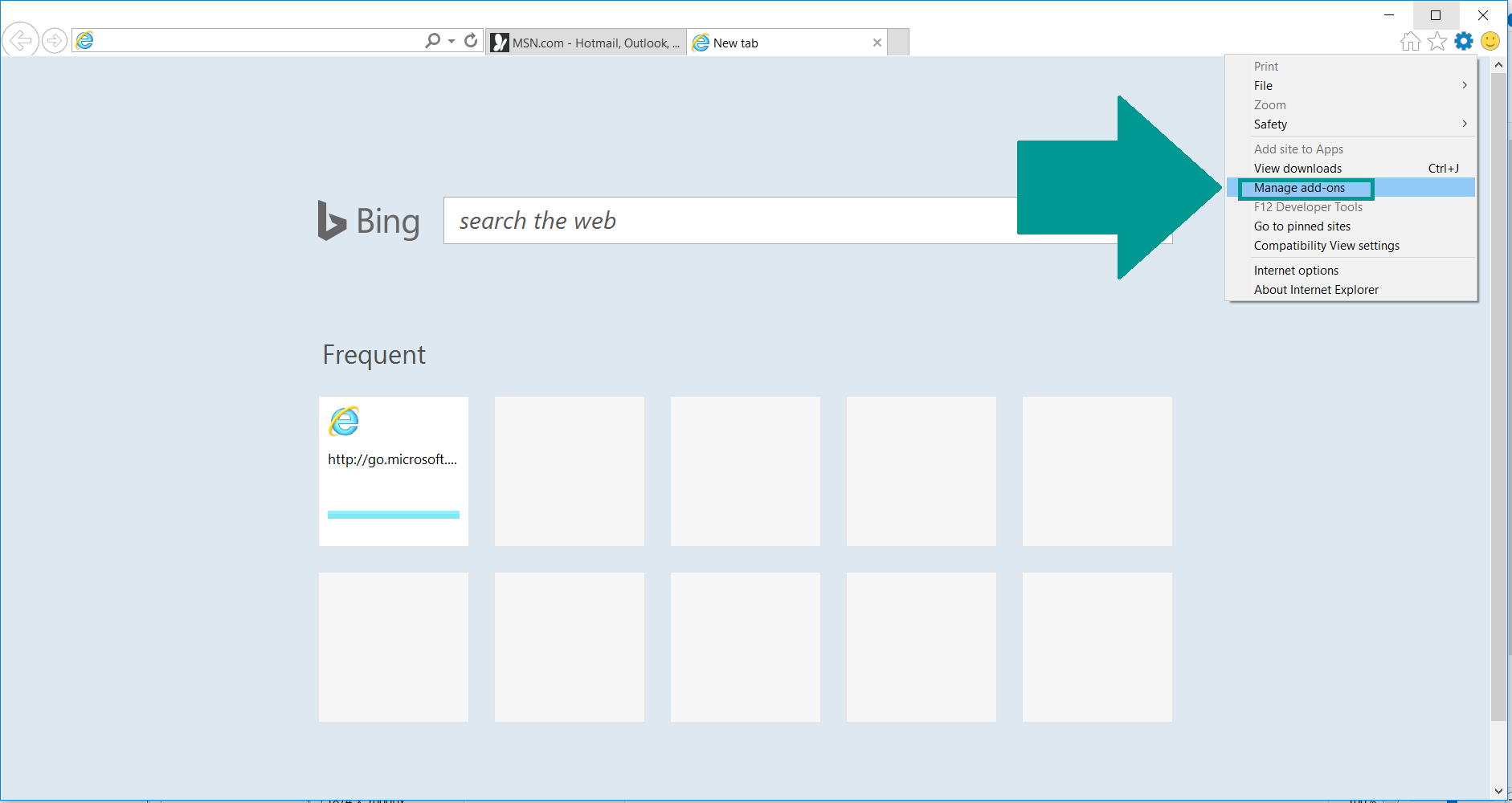
2. In the “Manage add-ons” window, bellow “Add-on Types“, select “Toolbars and Extensions“. If you see a suspicious toolbar, select it and click “Remove“.
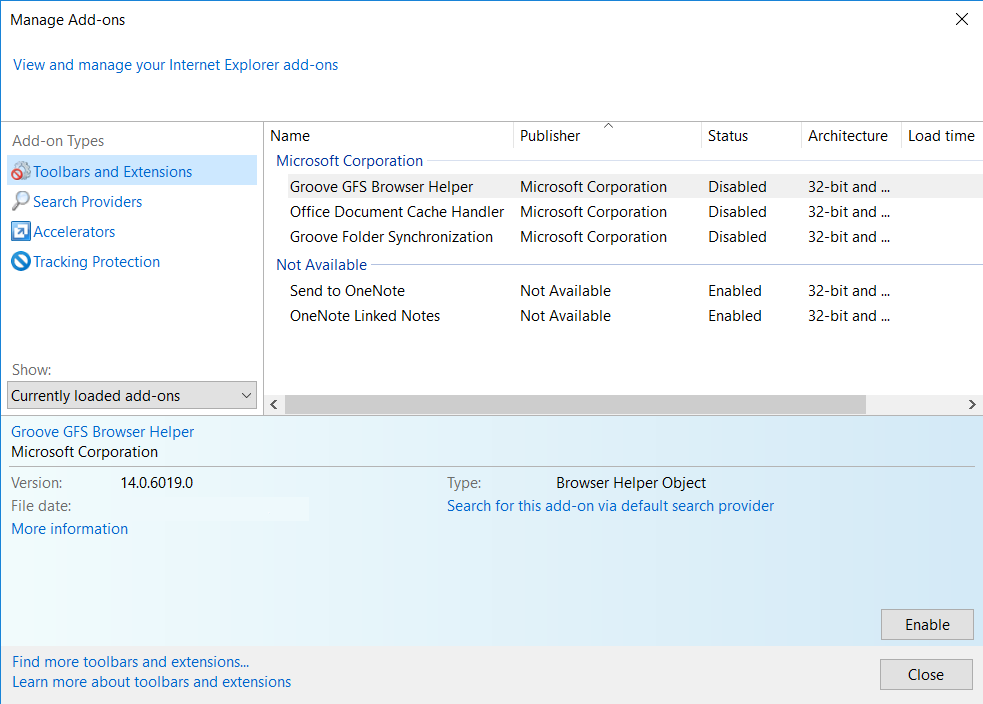
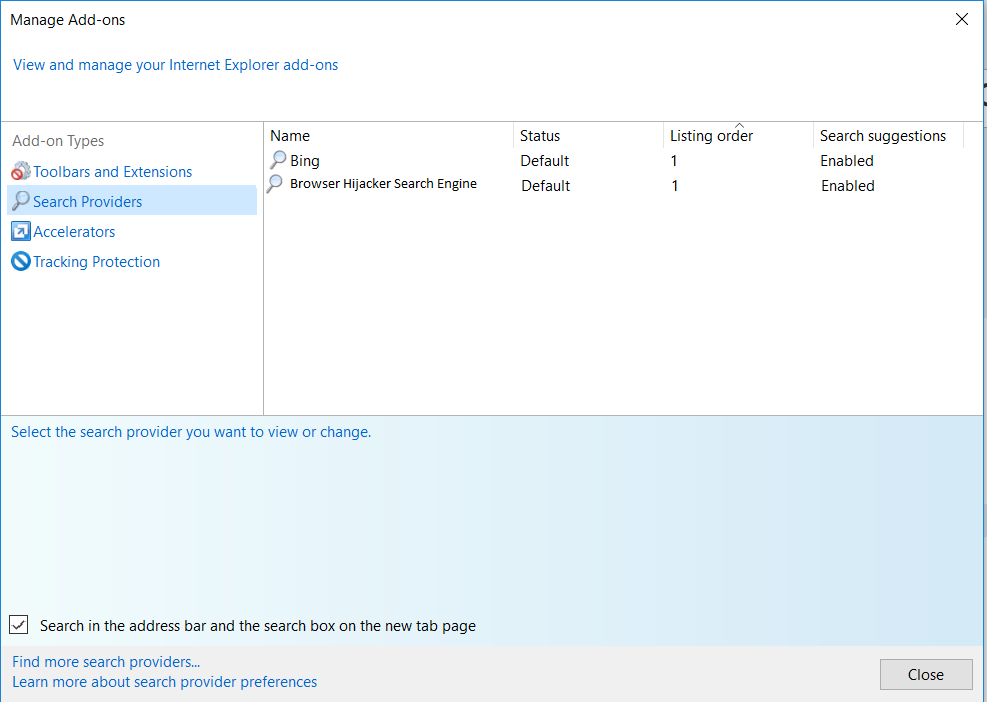
3. Then again in the “Manage Add-ons” window, in “Add-on Types“, Select “Search Providers“. Chose a search engine and click “Set as default“. Select the unknown search engine and click “Remove and Close”.
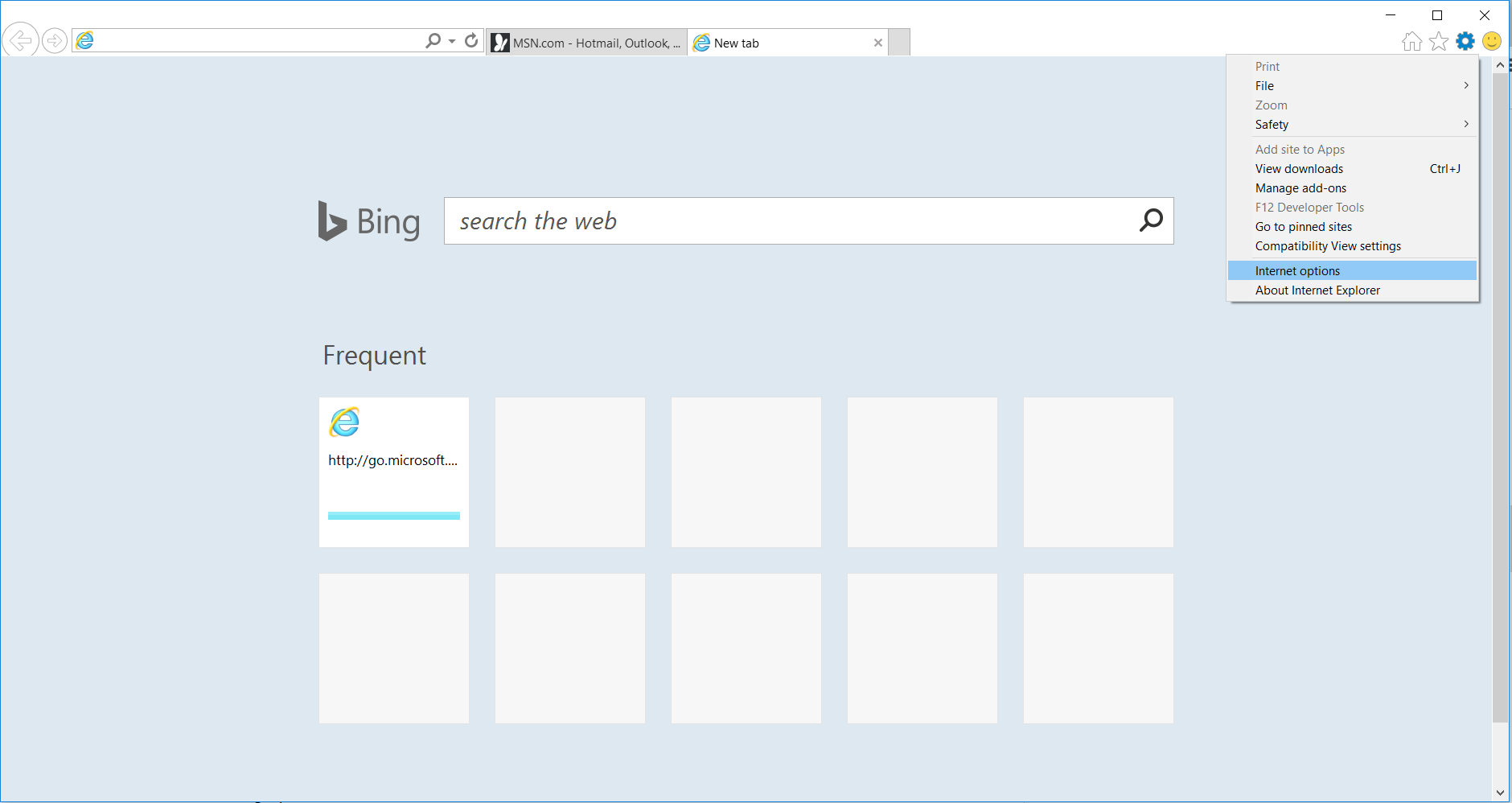
4. Open the Tools menu, select “Internet Options”.
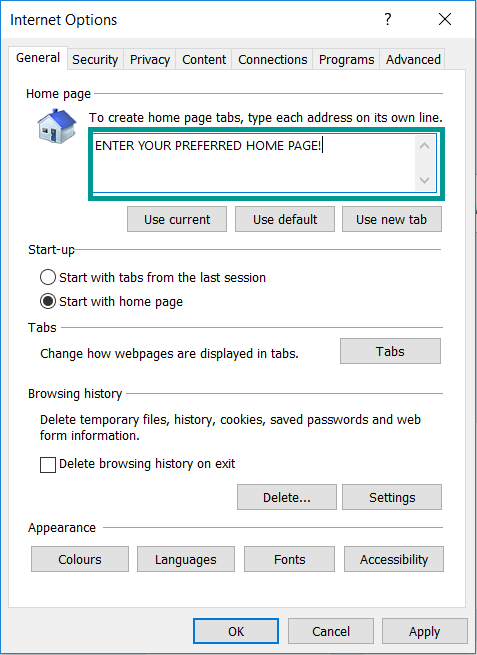
5. In the “General” tab, in “Home page”, enter your preferred page. Click “Apply” and “OK”.
Repair Windows Registry
1. Again type simultaneously the WIN Key + R key combination
2. In the box, write regedit and hit Enter
3. Type the CTRL+ F and then write the malicious name in the search type field to locate the malicious executable
4. In case you have discovered registry keys and values related to the name, you should delete them, but be careful not to delete legitimate keys
Click for more information about Windows Registry and further repair help



