Security analysts alarmed us of the discovery of Cerber 2017 ransomware, learn all about the new strain of the virus family in our in-depth removal guide.
Cerber 2017 Ransomware Description
The end of March has brought us another serious incident which has already marked the end of the first quarter with serious implications as security analysts discovered a newly redesigned strain that is derived from the Cerber ransomware. The newly evolved variant is dubbed as Cerber 2017 ransomware and we have collected all the important about it in this article, so that you can be informed on its implications.
The initial security analysis shows that it the virus contains a lot of advanced features which are related to stealth protection. In the first stage of infection the engine performs several extensive environment checks which ensure that the infected host does not contain any anti-virus software, sandboxes, honeypots, virtual machines or debuggers of any kind. This is done to make sure that the infection is done in the most efficient way and until its final steps is not stopped by any process or user action.
On top of the stealth protection schemes its developers have also added another interesting feature which is related to the ability of the engine to register a top-level exception handler which is used to counter any future debugging attempts by the analysts. This technique is used to counter analysis post-infection to make it more difficult for the vendors to construct a full definition for the threat. The environment checks also include query calls which are related to both machine time and the local system’s regional settings. We suspect that this is related to the distribution and infection of the Cerber 2017 ransomware. In some instances it is possible for the operators to define specific instructions as to when the payload is activated. This means that the hackers can group possible targets into various groups – infections by language, location and time of delivery. Such advanced forms of predefined customizations can be used further in large-scale, targeted and effective attack campaigns.
Like the previous Cerber strains this one also utilizes the self-extracting process of delivery into the system. The virus engine infects in several stages which is an effective way of spreading – not only is the payload small in size, but it also can be configured and customized according to the target. The engine uses PowerShell commands to change important settings on the affected machines – Software Policy Settings which are related to privilege escalation. Such changes allow the virus to manipulate all other processes, including system ones. Furthermore bundled PowerShell commands also allow the hackers to embed their own system certificate which makes the virus appear as a legitimate and trusted component of the operating system.
By tradition the Cerber 2017 ransomware communicates with remote C&C (command and control) malicious servers to report of the infection. As always the hackers can use the included virus capabilities to also issue the following scenarios:
- Remote Control – The hackers can take over full control of the machines in any given moment.
- Spying and Information Harvesting – The remote attackers can use the built-in capabilities to spy on the users activities and transfer any file from the infected machines to them. The stealing component can also be used to gain access to stored account data, web history, cookies and settings from the installed web browsers and other useful information from other applications and tools.
- Additional Payload Delivery – The attackers may opt to install additional threats to the compromised machines.
- Botnet Recruitment – Victims of the Cerber 2017 ransomware can be recruited into a worldwide botnet. Such a large force can be used to launch spam email sites or DDOS attacks against predefined targets.
A high severity alert has been raised as the engineers discovered an alarming characteristic which is associated with this particular strain – some of the modules that are part of the main engine use machine learning algorithms. This means that this iteration can prove to be one of the most advanced ones to date. Its interesting to note that the virus is capable of fooling the users into thinking that its an ordinary application or process by spawning various files that appear to be non-obtrusive and clean. In fact the virus can modify and create various files and processes at will to both increase its effectivity and speed of deployment.
Apart from interacting with other files and processes the Cerber 2017 ransomware can also interact and load control libraries and the .NET runtime environment. A built-in instruction scans for the availability of several Windows-related API calls. We suspect that they can be used as an infection vector as well.
During the C&C communications phase the analysts spotted that the criminals have used several global network which include direct host connection and proxy transfers. So far the identified servers are located in The United States of America, Germany and France. Three ports are used – 53 (Domain Name System – DNS), 80 (Hypertext Transfer Protocol – HTTP) and 6892 (Associated with the Live Messenger client but used for file transfer operations). The virus engine modifies any firewall settings so that all communications passes without issues. The Cerber 2017 ransomware uses an user agent identification which is typical for web browsers to conceal itself from automated network analysis.
When the initial stage of infection is complete and the virus has finally nested itself in the local machine it starts to encrypt a predefined list of target file type extensions. They can be configured at will, but in the most common case contain the most commonly used user data – archives, music, photos, videos, configuration files, databases and etc. Like other Cerber ransomware a randomly-named extension is appended to the affected files.
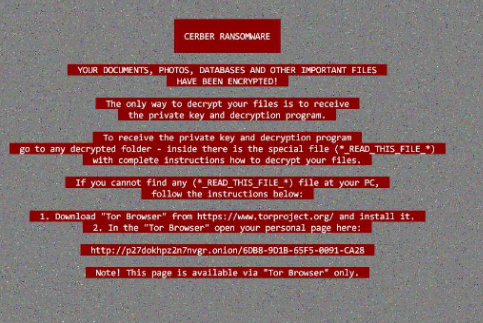
As usual the familiar looking ransomware note is shown to the victims:
CERBER RANSOMWARE
YOUR DOCUMENTS, PHOTOS, DATABASES AND OTHER IMPORTANT FILES
HAVE BEEN ENCRYPTED!The only way to decrypt your files is to receive
the private key and decryption program.To receive the private key and decryption program
go to any decrypted folder – inside there is the special file (*_READ_THIS_FILE_*)
with complete instructions how to decrypt your files.If you cannot find any (*_READ_THIS_FILE_*) file at your PC< follow the instructions below: 1. Download "Tor Browser" from https://www.torproject.org.org/ and install it. 2. In the "Tor Browser" open your personal page here: http://p27dokhpz2n7nvgr.onion/6088-9D1B-65F5-0091-CA28 Note! This page is available via "Tor Browser" only.
Like its previous versions the virus does not specify a ransom fee which is a widely used extortionist tactic. The victims need to visit the payment gateway site to view the needed amount of money which is usually requested in Bitcoins, the popular digital currency. Transactions made in this form are anonymous and cannot be easily traced to an individual or group which is the reason why this is a preferred payment method.
A distinct feature of the threat is that it is able to interact with the Windows volume manager which might indicate that the virus engine has the ability to spread over the internal network.
Cerber 2017 Ransomware Distribution
Its not surprising that the Cerber 2017 ransomware uses the same old infection tactics as previous strains of the malware family. All target attacks so far have been rated as extremely effective and this is the reason why the hacker operators continue to utilize them.
The primary method of spreading the virus samples is by sending out bulk email phishing messages. This is usually achieved by botnet networks of infected computers or hacked web servers. The criminal operators construct message bodies that appear as being sent by a legitimate user, company, organization or government institution. There are several types of emails that are associated with Cerber ransomware distribution:
- Emails with Malicious Hyperlinks – The hackers create convincing looking messages that include links that lead to dangerous download sites and portals or the hosted malicious file directly.
- Emails With Malicious Attachments – These messages contain the virus attached as a file of user interest, posing as a letter, invitation, invoice or something else. This is one of the most popular methods for distributing the Cerber 2017 ransomware strain. The hackers utilize infected documents which upon interaction deliver the payload via dangerous embedded scripts (macros). Various file types can be used such as text files, spreadsheets, databases and presentations.
- Hybrid Combinations – Such email campaigns are a combination of the above two methods and have the highest infection ratio of all.
Other distribution methods include the creation, maintenance and popularization of hacker-controlled download sites and portals. They typically appear as legitimate sources of popular freeware or trial versions of popular software such as applications, games, patches or utilities. P2P networks like BitTorrent are another popular source for ransomware. The hackers may opt to spread the virus files directly or combine them with the relevant application installers.
Another possibility is the use of malicious scripts and malicious ad networks. They infiltrate the browsers and redirect the users queries and actions to hacker-controlled sites which both generate income and invade their privacy. The malicious browser extensions, also known as hijackers, are a well-known example. They pose as useful search engines or other new features and upon installation modify essential settings of the installed web browsers (Mozilla Firefox, Google Chrome, Opera, Safari, Internet Explorer and Microsoft Edge) such as the default home page, default search engine and new tabs page. In addition they can steal stored information such as the browser history, stored account credentials, cookies and settings.
Of course direct attacks either by automated means (usually by exploit kits) or other techniques are used by the hackers to spread the Cerber 2017 ransomware.
Summary of Cerber 2017 Ransomware
| Name |
Cerber 2017 Ransomware |
| File Extensions |
Randomly-named file extensions |
| Ransom |
Varies |
| Easy Solution |
You can skip all steps and remove Cerber 2017 Ransomware ransomware with the help of an anti-malware tool. |
|
Manual Solution |
Cerber 2017 Ransomware ransomware can be removed manually, though it can be very hard for most home users. See the detailed tutorial below. |
| Distribution |
Spam Email Campaigns, malicious ads & etc. |
Cerber 2017 Ransomware Ransomware Removal
STEP I: Start the PC in Safe Mode with Network
This will isolate all files and objects created by the ransomware so they will be removed efficiently.
-
1) Hit WIN Key + R

- 2) A Run window will appear. In it, write “msconfig” and then press Enter
3) A Configuration box shall appear. In it Choose the tab named “Boot”
4) Mark “Safe Boot” option and then go to “Network” under it to tick it too
5) Apply -> OK
Or check our video guide – “How to start PC in Safe Mode with Networking”
STEP II: Show Hidden Files
-
1) Open My Computer/This PC
2) Windows 7
-
– Click on “Organize” button
– Select “Folder and search options”
– Select the “View” tab
– Go under “Hidden files and folders” and mark “Show hidden files and folders” option
3) Windows 8/ 10
-
– Open “View” tab
– Mark “Hidden items” option

4) Click “Apply” and then “OK” button
STEP III: Enter Windows Task Manager and Stop Malicious Processes
-
1) Hit the following key combination: CTRL+SHIFT+ESC
2) Get over to “Processes”
3) When you find suspicious process right click on it and select “Open File Location”
4) Go back to Task Manager and end the malicious process. Right click on it again and choose “End Process”
5) Next you should go folder where the malicious file is located and delete it
STEP IV: Remove Completely Cerber 2017 Ransomware Ransomware Using SpyHunter Anti-Malware Tool
SpyHunter anti-malware tool will diagnose all current threats on the computer. By purchasing the full version, you will be able to remove all malware threats instantly. Additional information about SpyHunter / Help to uninstall SpyHunter
STEP V: Repair Windows Registry
-
1) Again type simultaneously the Windows Button + R key combination
2) In the box, write “regedit”(without the inverted commas) and hit Enter
3) Type the CTRL+F and then write the malicious name in the search type field to locate the malicious executable
4) In case you have discovered registry keys and values related to the name, you should delete them, but be careful not to delete legitimate keys
Further help for Windows Registry repair
STEP VI: Recover Cerber 2017 Files
SpyHunter anti-malware tool will diagnose all current threats on the computer. By purchasing the full version, you will be able to remove all malware threats instantly. Additional information about SpyHunter / Help to uninstall SpyHunter
How To Restore Cerber 2017 Files
- 1) Use present backups
- 2) Use professional data recovery software
-
– Stellar Phoenix Data Recovery – a specialist tool that can restore partitions, data, documents, photos, and 300 more file types lost during various types of incidents and corruption.
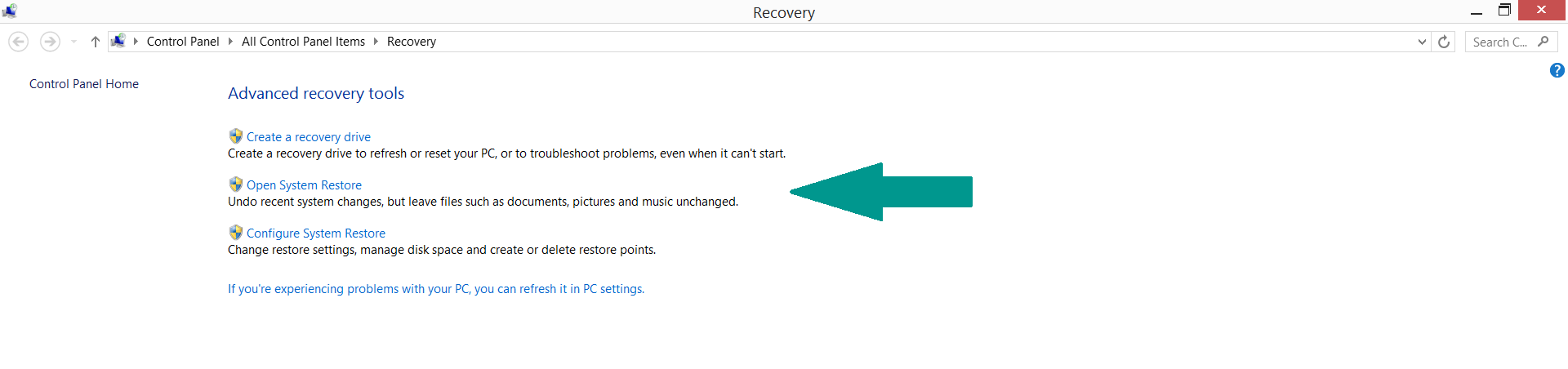
- 3) Using System Restore Point
-
– Hit WIN Key
– Select “Open System Restore” and follow the steps
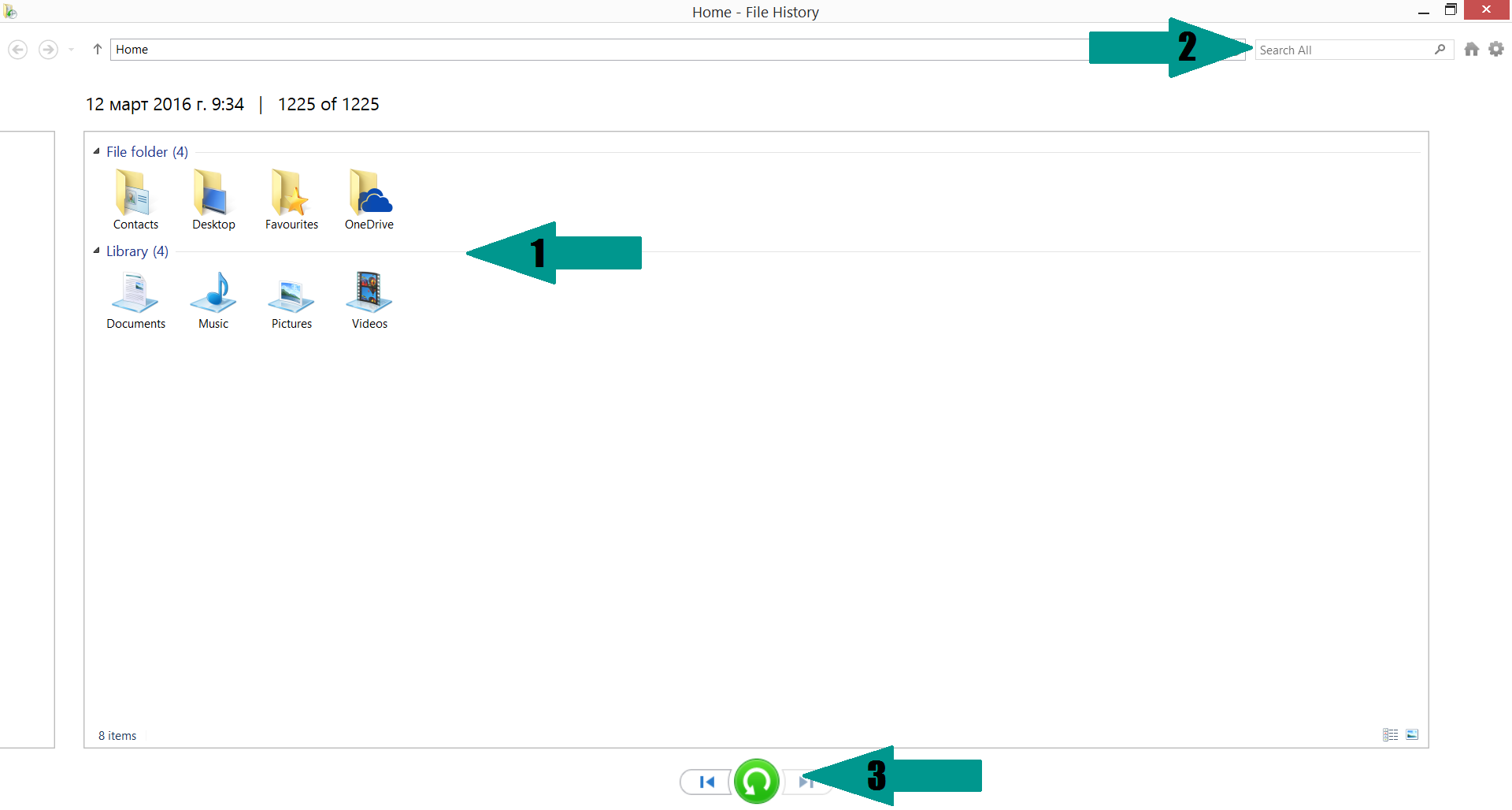
- 4) Restore your personal files using File History
-
– Hit WIN Key
– Type “restore your files” in the search box
– Select “Restore your files with File History”
– Choose a folder or type the name of the file in the search bar
- – Hit the “Restore” button
SpyHunter anti-malware tool will diagnose all current threats on the computer. By purchasing the full version, you will be able to remove all malware threats instantly. Additional information about SpyHunter / Help to uninstall SpyHunter



