The first comprehensive security study on smart car software has been carried out by a team of researchers. The experts reveal security issues in the MirrorLink standard that can be exploited by malicious users.
Proprietary Systems and the MirrorLink Protocol
Damon McCoy from the New York University Tandon School of Engineering with a group of students from the George Mason University released the first comprehensive security study of the MirrorLink standard. This is one of the most widely used in video infotainment and app platforms that are used in the new generations of cars.
The researchers point out that the contemporary automobiles are “are increasingly controlled by computerized systems that are directly or indirectly connected to the Internet. This, in turn, means that automobiles are potentially vulnerable to attack from adversaries who can gain control of one of these external devices”. Previous audits have demonstrated that attackers that possess access to the car’s Controller Area Network (CAN) connection or can connect remotely to the platform can infiltrate the host system via security exploits. Despite the risks, the number of user devices that are used with these types continues to increase.
The researchers note that there is a recent trend of connecting smartphones to In-Vehicle-Infotainment systems (IVI) via the CAN bus connection. The connection is usually made using a designed application installed on the user devices. At the current moment, they are closed source and utilize only a handful of trusted third-party applications. Contemporary platforms include the Ford Sync AppLink, Toyota Entune, BMW ConnectedDrive and others. These proprietary systems tie manufacturers to complex and costly development plans as they need support a large number of protocols for both modern and legacy products. This is one of the major reasons why modern automobile infotainment systems such as Android Auto, Apple CarPlay, and MirrorLink have been devised. They are standardized protocols that amend most of these issues found in the proprietary standards.
MirrorLink Features
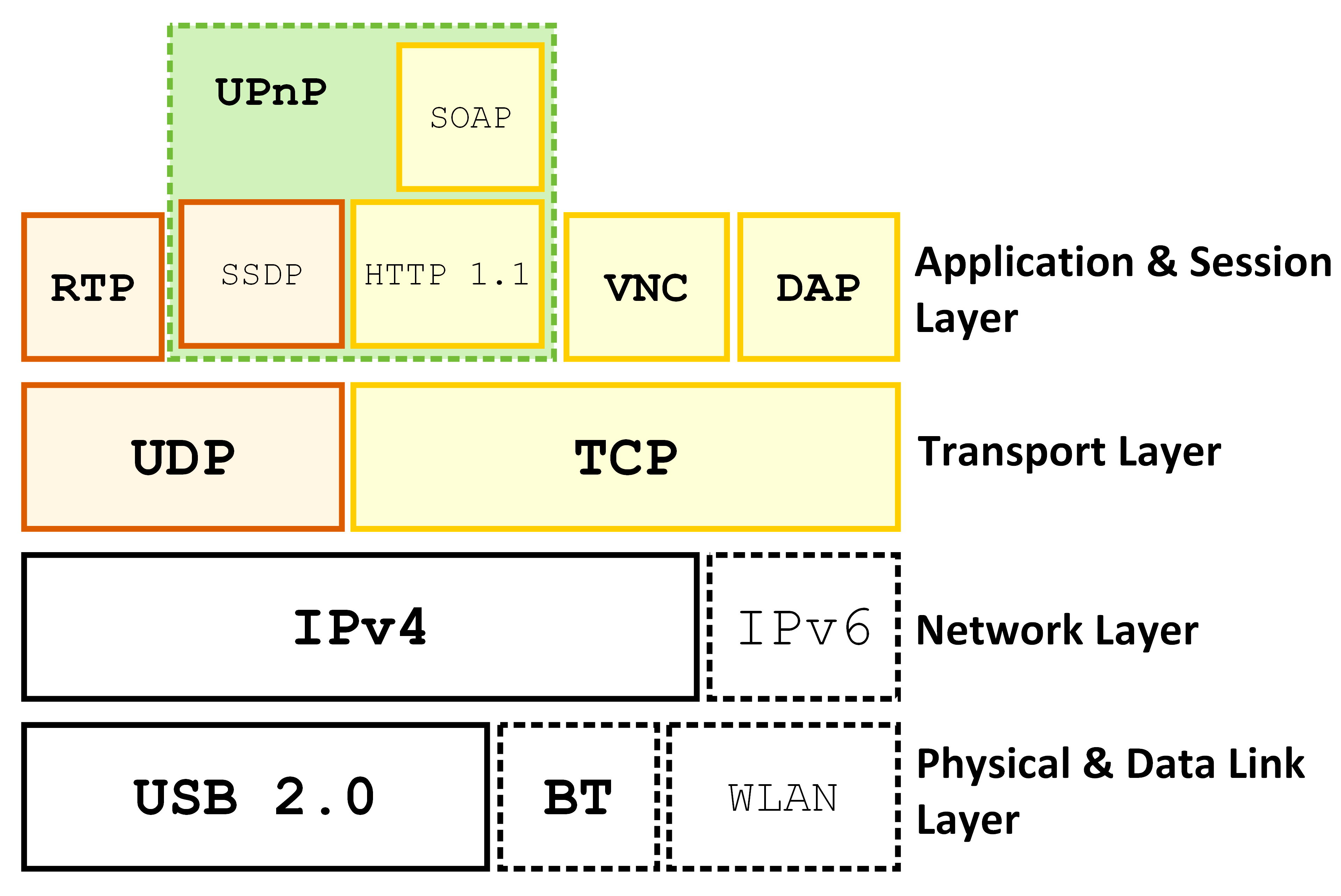
The MirrorLink protocol is one of the most popular standards that allow smartphone integration with the infotainment systems of the cars. The MirrorLink uses non-proprietary technologies and connections such as RTP, UPnP, USB, WiFi and others. The baseline protocol for displaying the user interface is VNC, often used in desktop computing for remote desktop sharing.
The main goal of the protocol is to display (mirror) the smartphone application on the larger screen available on the car. This allows users to use their navigation systems or other user case scenarios. There are two main security mechanisms that are used as per protocol specifications.
- Device Attestation Protocol (DAP) – Used by the UPnP protocol to confirm compliance with the MirrorLink Server software and hardware.
- Content Attestation – Contained by the link and transport layer. The MirrorLink client uses attestation messages to verify the received content. The security implications are that this method prevents man-in-the-middle attacks.
Discovered MirrorLink Security Issues
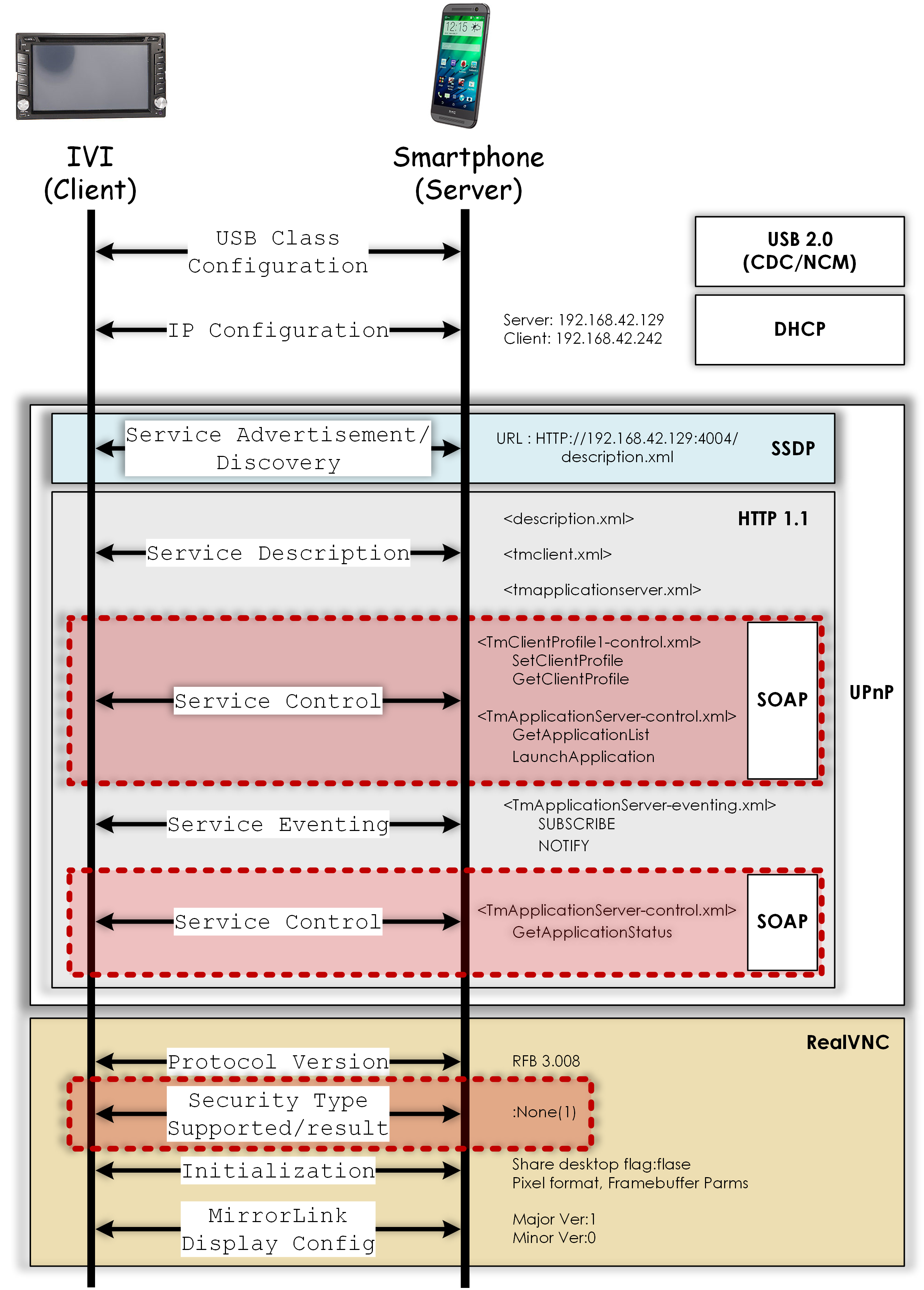
The research team evaluated the security mechanisms of the MirrorLink standard assuming that the potential attacker does not have access to the specific IVI system, but does have access to a copy of it and tools that can physically reverse engineer and construct remote exploits.
The discovered vulnerabilities are similar to those found in previous studies of car systems. MirrorLink does not have any secure device pairing method. The serious discovered issues can be exploited if an attacker can get access to the IVI and CAN controller. They can send arbitrary messages over the connection that could potentially effect the critical safety systems.
The sample MirrorLink client is written in a memory unsafe programming language (C++) and executed with administrative privileges on a bare metal WinCE operating systems. A criminal who can leverage several heap overflow bugs against the client.
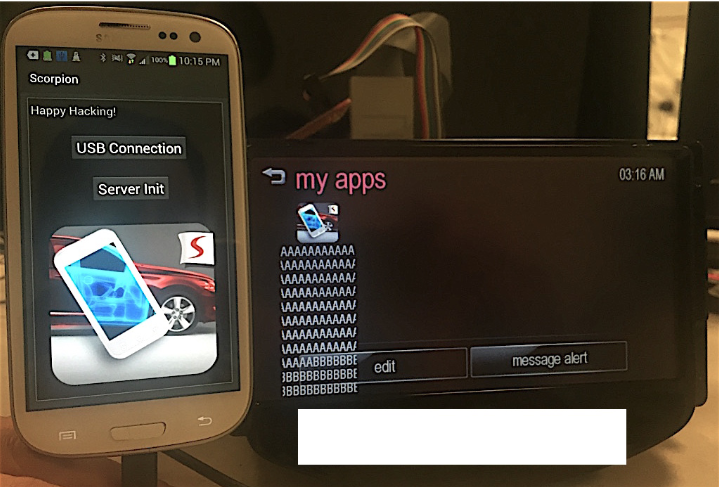
The security analysis has pointed out that at least one 2015 model car is affected. The researchers have also created a proof of concept malicious app that showcases the security bugs. For more information, you can download the research paper.