An infection with the dangerous .spider virus leads to serious security issues. Victims can restore and protect their computers by following our complete removal guide.
Remove .spider virus and Restore PC
Manual Removal Guide
Skip all steps and download anti-malware tool that will safely scan and clean your PC.
SpyHunter anti-malware tool will diagnose all current threats on the computer. By purchasing the full version, you will be able to remove all malware threats instantly. Additional information about SpyHunter / Help to uninstall SpyHunter
Distribution of .spider virus
The .spider virus is a new virus which has been sighted in a limited attack campaign. At the moment the security researchers cannot determine the primary infection strategy. We presume that the most widely used tactics are going to be employed.
Among them are the email messages created in an automated way and sent to large lists of potential victims. The .spider virus can be directly attached to the messages. This is one of the easiest way for the criminals to attempt the infection. However a lot of email hosting providers usually capture the signatures of the virus and as such discard such messages or label them as dangerous or spam. Other infection methods related to this one is the option of inserting hyperlinks in the body content of the messages. The links are usually labelled as leading to a familiar website or a file of user interest. Redirects can redirect to hacker-controlled sites, infected payloads or other instances that can lead to an .spider virus infection.
The computer criminals behind the malware can create malicious sites or download portals which distribute malware of different kinds, including the .spider virus. A popular option is the use of infected documents which may be of different types ‒ spreadsheets, rich text documents, presentations and databases. They are modified to initiate the virus once the built-in scripts are run. Usually when the files are opened a notification will ask the users to run the macros (scripts). If this is done the infection follows.
The hacker-controlled sites are specialist portals that have been created either manually or automatically by the criminals behind the .spider virus. They can either directly distribute the threat by initiating various scripts or automated operations or link to such instances. Redirects are usually caused by email interaction, ad networks or other browsing activity. However one of the main sources is the availability of browser hijackers. They are malicious addons made for the most popular web browsers ‒ Mozilla Firefox, Google Chrome, Internet Explorer, Opera, Microsoft Edge and Safari. Once installed they not only infect the users with the malware, but also redirect the victims to a hacker-controlled site. Depending on the configuration the browser hijackers can also steal sensitive information such as any stored passwords, account credentials, history, bookmarks, form data and settings.
Impact of .spider virus
A global attack wave with the .spider virus has recently caused an outburst of infections. Our in-depth analysis shows that this is considered a brand new malware family strain that does have quite a few interesting characteristics of its own.
The origins of the infections seem to be from the hacker or criminal collective behind it, it is very probable that the .spider virus has been created from scratch as its signature is not identical to any of the famous families.
Further investigation into it has revealed a secret identifier “Halloween_Spider” which suggests that it has been developed quite recently. Global outbreaks were identified only a few days ago which shows that several updates have probably been made or the delivery has been deliberately delayed. The captured strains and attack patterns indicate that at the moment the .spider virus is aimed against English-speaking users.
The complete analysis shows that the .spider virus is made up of a modular framework that can be tweaked and modified based on the target users. The infection engine copies and conceals itself to the %APPDATA% system folder. The analysts discovered that it uses a built-in WebClient which contacts a hacker-operated command and control server that delivers additional threats. This allows the hacker operators to perform various malware tasks and institute additional modules such as the following:
- Information Harvesting — The virus includes the capability to extract sensitive information from the infected hosts. This includes both system data (installed hardware components), applications and user preferences, as well as any user data. In the case of the web browsers (which are among the most popular applications) this includes all form data, bookmarks, history, passwords and account credentials.
- Trojan Component — The criminal operators can institute a Trojan module that would allow the criminal operators to spy on the victims in real time. Advanced versions of it have the ability to record mouse movement, keystrokes and take over control of the machines at any given time.
- Process Hookup — The .spider virus has been observed to be able to hookup to existing processes including systems ones.
- Concealment — The researchers note that the various executable and running files are renamed with standard system utilities and commands in order to fool the users who may be investigating the processes.
- Network Connections — The criminal collective that is behind the threat has configured a command and control server that has the ability to send commands and install additional modules to the compromised networks. In many cases such computers are used in large-scale botnet attacks targeting companies.
Once all prerequisite conditions are met the encryption phase is initiated. It uses a built-in list of target file type extensions that are processed with a strong cipher. The analysts extracted a sample list from the captured samples:
.001, .036, .0411, .1cd, .1st, .2bp, .3dm, .3ds, .3fr, .3g2, .3gp, .3gp, .4db, .4dl, .4mp,
.73i, .7z, .7zip, .8xi, .9png, .a3d, .aaf, .abm, .abs, .abw, .accdb, .accdc, .accde, .accdr,
.accdt, .accdw, .accft, .act, .adn, .adp, .aep, .aepx, .aet, .af2, .af3, .aft, .afx, .agif,
.agp, .ahd, .ai, .aic, .aif, .aim, .albm, .alf, .ani, .ans, .apd, .apk, .apm, .apng, .aps,
.apt, .apx, .arch00, .art, .artwork, .arw, .as, .as3, .asc, .ascii, .ase, .asf, .ask, .asp,
.asset, .asw, .asx, .asy, .aty, .avatar, .awdb, .awp, .awt, .aww, .azz, .backup, .bad, .bak,
.bar, .bat, .bay, .bbs, .bc6, .bc7, .bdb, .bdp, .bdr, .bean, .bib, .big, .bik, .bkf, .bkp,
.blend, .blkrt, .blob, .bm2, .bmp, .bmx, .bmz, .bna, .bnd, .boc, .bok, .brk, .brn, .brt, .bsa,
.bss, .btd, .bti, .btr, .byu, .bzabw, .c, .c4, .c4d, .cal, .cals, .can, .cas, .cd5, .cdb, .cdc,
.cdg, .cdmm, .cdmt, .cdmtz, .cdmz, .cdr, .cdr3, .cdr4, .cdr6, .cdrw, .cdt, .cer, .cf, .cfr, .cfu,
.cgm, .chart, .chord, .cimg, .cin, .cit, .ckp, .class, .clkw, .cma, .cmx, .cnm, .cnv, .colz, .conf,
.contact, .cpc, .cpd, .cpg, .cpp, .cps, .cpt, .cpx, .cr2, .crd, .crt, .crw, .crwl, .cs, .css, .csv,
.csy, .ct, .cv5, .cvg, .cvi, .cvs, .cvx, .cwt, .cxf, .cyi, .d3dbsp, .daconnections, .dacpac, .dad,
.dadiagrams, .daf, .das, .daschema, .dat, .DayZProfile, .dazip, .db, .db0, .db2, .db3, .dbc, .dbf,
.dbfv, .dbk, .dbs, .db-shm, .dbt, .dbv, .db-wal, .dbx, .dc2, .dca, .dcb, .dcr, .dcs, .dct, .dcx, .ddl,
.ddoc, .dds, .ded, .der, .desc, .design, .df1, .dgn, .dgs, .dgt, .dhs, .dib, .dicom, .diz, .djv, .djvu,
.dm3, .dmi, .dmo, .dmp, .dnc, .dne, .dng, .doc, .docb, .docm, .docx, .docxml, .docz, .dot, .dotm, .dotx,
.dp1, .dpp, .dpx, .dqy, .drw, .drz, .dsk, .dsn, .dsv, .dt, .dt2, .dta, .dtsx, .dtw, .dvi, .dvl, .dwg, .dx,
.dxb, .dxf, .dxg, .dxl, .eco, .ecw, .ecx, .edb, .efd, .efx, .egc, .eio, .eip, .eit, .email, .emd, .emf,
.emlx, .ep, .epf, .epk, .epp, .eps, .epsf, .eql, .erf, .err, .esm, .etf, .etx, .euc, .exr, .fadein,
.fal, .faq, .fax, .fb2, .fb3, .fbl, .fbx, .fcd, .fcf, .fdb, .fdf, .fdr, .fds, .fdt, .fdx,
.fdxt, .fes, .ff, .fft, .fh10, .fh11, .fh3, .fh4, .fh5, .fh6, .fh7, .fh8, .fic, .fid, .fif,
.fig, .fil, .fla, .flc, .fli, .flr, .fm5, .fmp, .fmp12, .fmpsl, .fmv, .fodt, .fol, .forge,
.fos, .fountain, .fp3, .fp4, .fp5, .fp7, .fpk, .fpos, .fpt, .fpx, .frt, .fsh, .ft10, .ft11,
.ft7, .ft8, .ft9, .ftn, .fwdn, .fxc, .fxg, .fzb, .fzv, .g3, .gcdp, .gdb, .gdoc, .gdraw, .gem,
.geo, .gfb, .gfie, .ggr, .gho, .gif, .gih, .gim, .gio, .glox, .gmbck, .gmspr, .gpd, .gpn, .gro,
.grob, .grs, .gsd, .gthr, .gtp, .gv, .gwi, .h, .hbk, .hdb, .hdp, .hdr, .hht, .his, .hkdb, .hkx,
.hpg, .hpgl, .hpi, .hpl, .hplg, .hs, .htc, .html, .hvpl, .hwp, .hz, .i3d, .ib, .ibank, .icn, .icon,
.icpr, .icxs, .idc, .idea, .idml, .idx, .iff, .igt, .igx, .ihx, .iil, .iiq, .imd, .indb, .indd, .indl,
.indt, .info, .ink, .int, .inx, .ipf, .ipx, .itc2, .itdb, .itl, .itm, .itw, .iwd, .iwi, .j, .j2c, .j2k,
.jar, .jarvis, .jas, .java, .jb2, .jbig, .jbig2, .jbmp, .jbr, .jfif, .jia, .jis, .jng, .joe, .jp1, .jp2,
.jpe, .jpeg, .jpg, .jpg2, .jps, .jpx, .jrtf, .js, .jtf, .jtx, .jwl, .jxr, .kdb, .kdbx, .kdc, .kdi, .kdk,
.kes, .kf, .kic, .klg, .knt, .kon, .kpg, .kwd, .latex, .layout, .lbf, .lbm, .lbt, .lgc, .lis, .lit, .litemod,
.ljp, .lmk, .lnk, .lnt, .lp2, .lrc, .lrf, .lst, .ltr, .ltx, .lue, .luf, .lvl, .lwo, .lwp, .lws, .lxfml, .lyt,
.lyx, .m2, .m3d, .m3u, .m3u8, .m4a, .m4u, .ma, .mac, .man, .map, .maq, .mat, .max, .mb, .mbm, .mbox, .mcgame,
.mcmeta, .md5txt, .mdb, .mdbackup, .mdbhtml, .mddata, .mdf, .mdn, .mdt, .me, .mef, .mell, .menu, .mft, .mgcb,
.mgmf, .mgmt, .mgmx, .mgtx, .mid, .min, .mkv, .mlx, .mmat, .mng, .mnr, .mnt, .mobi, .mos, .movie, .mp4, .mpa,
.mpf, .mpo, .mpqge, .mrg, .mrwref, .mrxs, .msg, .mt9, .mud, .mwb, .mwp, .mxl, .myd, .myl, .ncf, .ncr, .nct,
.ndf, .nfo, .njx, .nlm, .notes, .now, .nrw, .ns2, .ns3, .ns4, .nsf, .ntl, .nv2, .nwctxt, .nyf, .nzb, .obj,
.oc3, .oc4, .oc5, .oce, .oci, .ocr, .odb, .odc, .odm, .odo, .odp, .ods, .odt, .ofl, .oft, .omf, .openbsd,
.oplc, .oqy, .ora, .orf, .ort, .orx, .ota, .otg, .oti, .ott, .ovp, .ovr, .owc, .owg, .oyx, .ozb, .ozj, .ozt,
.p12, .p7b, .p7c, .p7s, .p96, .p97, .pages, .pak, .pal, .pan, .pano, .pap, .pbd, .pbl, .pbm, .pc1, .pc2, .pc3,
.pcd, .pcs, .pcx, .pdb, .pdd, .pdf, .pdm, .pdn, .pe4, .pef, .pem, .pfd, .pff, .pfi, .pfs, .pfv, .pfx, .pgf, .pgm,
.phm, .php, .pi1, .pi2, .pi3, .pic, .pict, .pix, .pjpeg, .pjpg, .pjt, .pkpass, .pl, .plantuml, .plb, .plt, .pm,
.pmd, .pmg, .png, .pni, .pnm, .pntg, .pnz, .pobj, .pop, .pot, .potm, .potx, .pp4, .pp5, .ppam, .ppj, .ppm, .pps,
.ppsm, .ppsx, .ppt, .pptm, .pptx, .prel, .prproj, .prt, .prw, .ps, .ps1, .psd, .psdx, .pse, .psid, .psk, .psp,
.pspbrush, .pst, .psw, .ptg, .pth, .ptx, .pu, .pvj, .pvm, .pvr, .pwa, .pwi, .pwr, .px, .pxr, .py, .pz3, .pza,
.pzp, .pzs, .qdf, .qdl, .qic, .qmg, .qpx, .qry, .qvd, .r3d, .ra, .rad, .raf, .rar, .ras, .raw, .rb, .rctd, .rcu,
.rdb, .rdl, .re4, .readme, .rft, .rgb, .rgf, .rgss3a, .rib, .ric, .riff, .rim, .ris, .rix, .rle, .rli, .rng, .rofl,
.rpd, .rpf, .rpt, .rri, .rs, .rsb, .rsd, .rsr, .rst, .rt, .rtd, .rtf, .rtx, .run, .rw2, .rwl, .rzk, .rzn, .s2mv,
.s3m, .saf, .safetext, .sai, .sam, .sav, .save, .sb, .sbf, .sc2save, .scad, .scc, .sci, .scm, .scriv, .scrivx,
.sct, .scv, .scw, .sdb, .sdf, .sdm, .sdoc, .sdw, .sep, .ses, .sfc, .sfera, .sfw, .sgm, .sid, .sidd, .sidn, .sie,
.sig, .sis, .sk1, .sk2, .skcard, .skm, .sla, .slagz, .sld, .sldasm, .slddrt, .sldm, .sldprt, .sldx, .slm, .sls,
.smf, .smil, .sms, .snagitstamps, .snagstyles, .snx, .sob, .spa, .spe, .sph, .spj, .spp, .spq, .spr, .sqb, .sql,
.sqlite, .sqlite3, .sqlitedb, .sr2, .srf, .srw, .ssa, .ssfn, .ssk, .st, .ste, .stm, .stn, .stp, .str, .strings,
.stw, .sty, .sub, .sum, .sumo, .sva, .svf, .svg, .svgz, .swf, .sxd, .sxg, .sxw, .syncdb, .t12, .t13, .t2b, .tab,
.tax, .tb0, .tbn, .tcx, .tdf, .tdt, .te, .teacher, .tex, .text, .tfc, .tg4, .tga, .thm, .thp, .thumb, .tif, .tiff,
.tjp, .tlb, .tlc, .tm, .tm2, .tmd, .tmv, .tmx, .tn, .tne, .tor, .tpc, .tpi, .trelby, .trm, .tvj, .txt, .u3d, .u3i,
.udb, .ufo, .ufr, .uga, .unauth, .unity, .unity3d, .unx, .uof, .uot, .upd, .upk, .url, .usertile-ms, .usr, .utf8,
.utxt, .v12, .vault, .vbox, .vbr, .vcf, .vct, .vda, .vdb, .vdf, .vdi, .vec, .vff, .vfs0, .vml, .vnt, .vob, .vpd,
.vpe, .vpk, .vpp_pc, .vrml, .vrp, .vsd, .vsdm, .vsdx, .vsm, .vst, .vstm, .vstx, .vtf, .vue, .vw, .w3x, .wb1, .wb2,
.wbc, .wbd, .wbk, .wbm, .wbmp, .wbz, .wcf, .wdb, .wdp, .webdoc, .webm, .webp, .wgz, .wire, .wmdb, .wmf, .wmo, .wmv,
.wmv, .wn, .wotreplay, .wp, .wp4, .wp5, .wp6, .wp7, .wpa, .wpb, .wpd, .wpe, .wpg, .wpl, .wps, .wpt, .wpw, .wri, .wsc,
.wsd, .wsh, .wtx, .wvl, .x, .x3d, .x3f, .xar, .xbdoc, .xbplate, .xdb, .xdl, .xf, .xhtm, .xla, .xlam, .xld, .xlf, .xlgc,
.xlk, .xll, .xlm, .xls, .xlsb, .xlsm, .xlsx, .xlt, .xltm, .xltx, .xlw, .xmind, .xml, .xmmap, .xpm, .xps, .xqx, .xwp, .xxx,
.xy3, .xyp, .xyw, .y, .yal, .ybk, .yml, .ysp, .z3d, .zabw, .zdb, .zdc, .zif, .zip, .ztmp, .zw
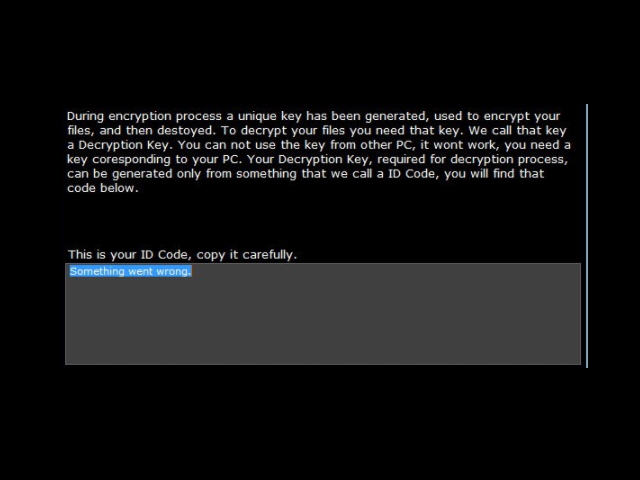
Consequently all processed data is renamed with the .spider extension. The interesting fact about the .spider virus is that the ransomware note is not generated in a document or a text file. The victims are shown a HOW TO DECRYPT FILES.url which is an actual application that displays the message. The contents reads the following:
YOUR PC HAS BEEN INFECTED WITH FILE SPIDER VIRUS
As you may have already noticed, all your important files are encrypted and you no longer have access to them. A unique key has been generated specifically for this PC and two very strong encryption algorithm was applied in that process. Original content of your files are wiped and overwritten with encrypted data so it cannot be recovered using any conventional data recovery tool.
The good news is that there is still a chance to recover your files, you just need to have the right key.
To obtain the key, visit our website from the menu above. You have to be fast, after 96 hours the key will be blocked and all your files will remain permanently encrypted since no one will be able to recover them without the key!
Remember, do not try anything stupid, the program has several security measures to delete all your files and cause the damage to your PC.
To avoid the misunderstanding, pleases read Help section.
The next screen shows the following message:
THIS WILL DECRYPT YOUR FILES
To visit our website you need a install a special web browser Tor Browser. Be aware, our website is reachable only via Tor Browser and if you try to visit it using any other browser eg. Google Chrome, it won’t work. Tor Browser can be downloaded from its official website listed below. Use newly installed browser to visit our website address. On our website there is a online tool that can generate decryption key using your ID Code, use that tool and you will get the key needed to decrypt your files. Also, you will be asked to make a payment for your Decryption key, you will need a Bitcoins for that. More about bitcoins read in Help section. After you get your key, select Decrypter from menu and follow the instructions provided on that page.
This all may seem complicated to you, actually it’s really easy. A link to Video Tutorial with live demonstration can be found inside Help Section. Good Luck!
During encryption process a unique key has been generated, used to encrypt your files, and then destroyed. To decrypt your files you need that key. We call that key a Decryption Key. You can not use the key from the other PC, it won’t work, you need a key coresponding to your PC. Your Decryption Key, required for decryption process, can be generated only from something that we call a ID Code, you will find that code below.
Remove .spider virus and Restore PC
WARNING! Manual removal of the .spider virus requires being familiar with system files and registries. Removing important data accidentally can lead to permanent system damage. If you don’t feel comfortable with manual instructions, download a powerful anti-malware tool that will scan your system for malware and clean it safely for you.
SpyHunter anti-malware tool will diagnose all current threats on the computer. By purchasing the full version, you will be able to remove all malware threats instantly. Additional information about SpyHunter / Help to uninstall SpyHunter
.spider virus – Manual Removal Steps
Start the PC in Safe Mode with Network
This will isolate all files and objects created by the ransomware so they will be removed efficiently. The steps bellow are applicable to all Windows versions.
1. Hit the WIN Key + R
2. A Run window will appear. In it, write msconfig and then press Enter
3. A Configuration box shall appear. In it Choose the tab named Boot
4. Mark Safe Boot option and then go to Network under it to tick it too
5. Apply -> OK
Remove .spider from Windows
Here’s a way to remove the program. This method will work regardless if you’re on Windows 10, 8, 7, Vista or XP. Simply selecting the program and pressing delete won’t work, as it’ll leave a lot of small files. That’s bad because these leftovers can linger on and cause all sorts of problems. The best way to delete a program is to uninstall it. Here’s how you can do that:
1. Hold the “Windows” button (It’s between CTRL and Alt on most keyboards) and press “R”. You’ll see a pop-up window.
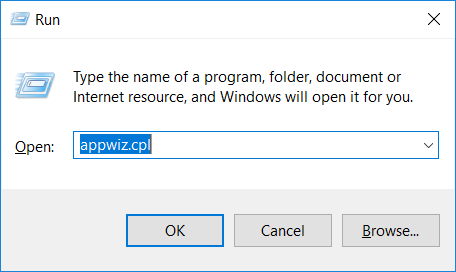
2. In the textbox, type “appwiz.cpl”, then press“ Enter ”.
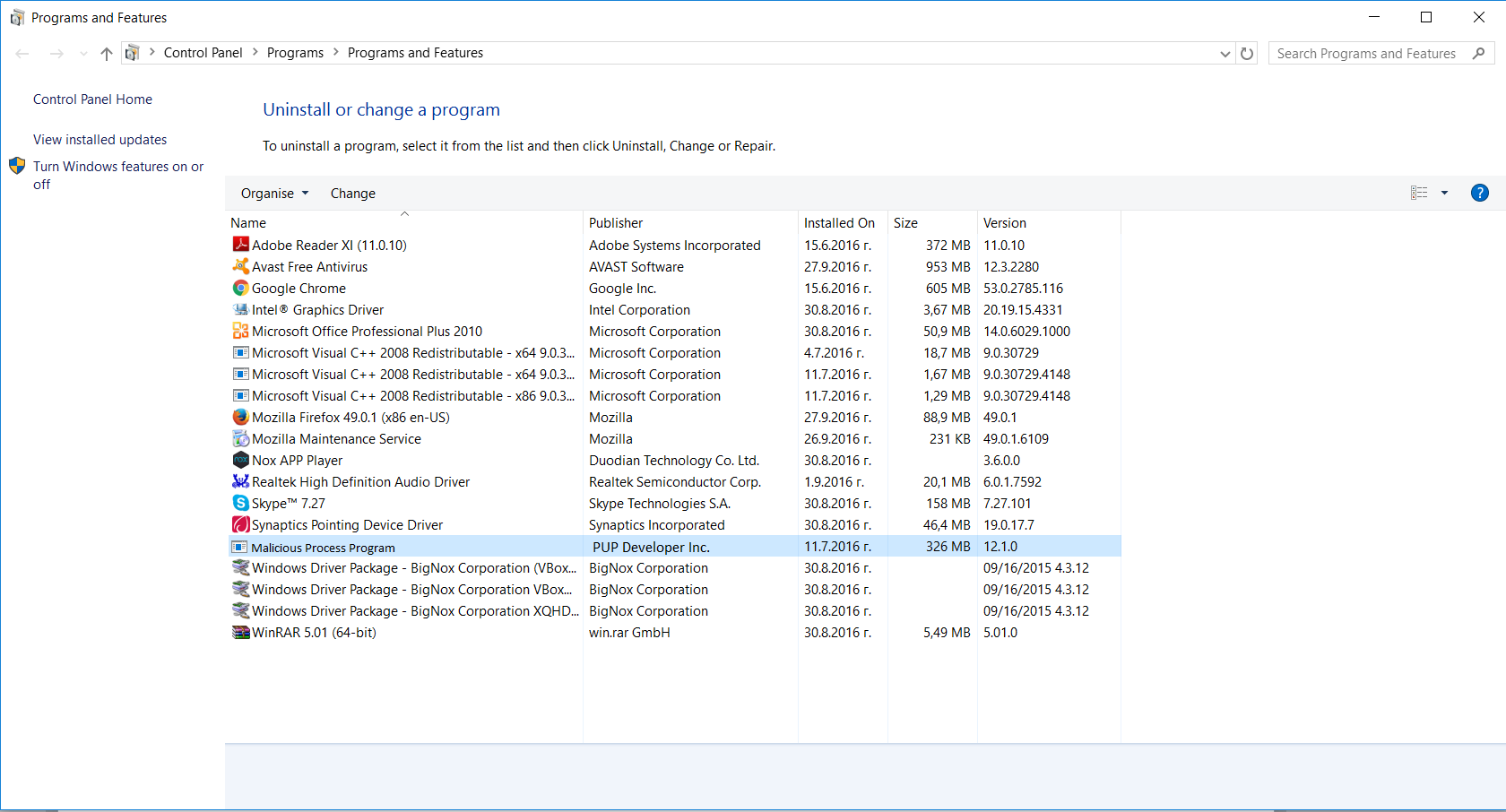
3. The “Programs and features” menu should now appear. It’s a list of all the programs installed on the PC. Here you can find the program, select it, and press “Uninstall“.
Remove .spider Virus From Your Browser
Before resetting your browser’s settings, you should know that this action will wipe out all your recorded usernames, passwords, and other types of data. Make sure to save them in some way.
-
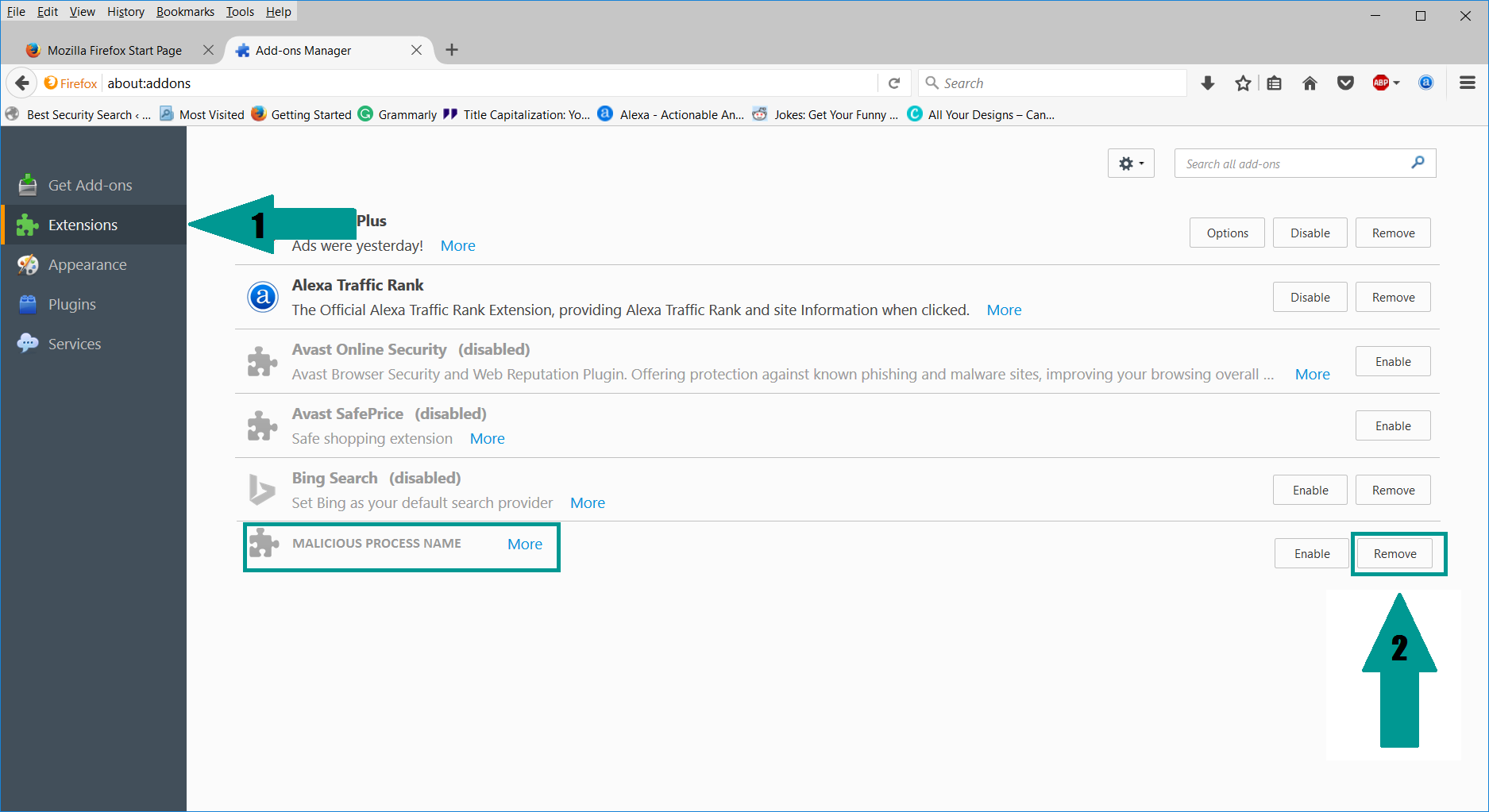
1. Start Mozilla Firefox. In the upper right corner, click on the Open menu icon and select “Add-ons“.

2. Inside the Add-ons Manager select “Extensions“. Search the list of extensions for suspicious entries. If you find any, select them and click “Remove“.
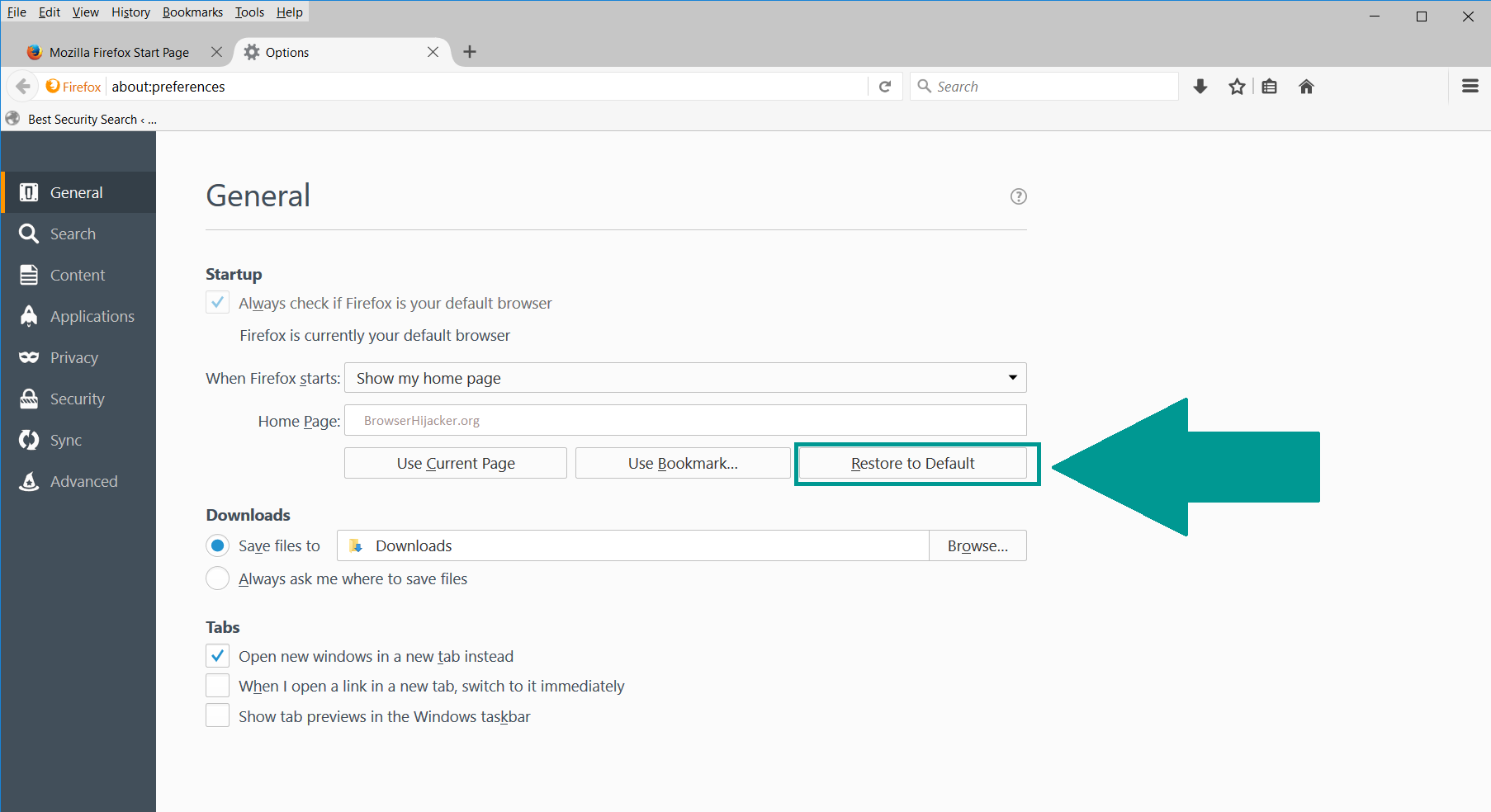
3. Click again on the Open menu icon, then click “Options“.

4. In the Options window, under “General” tab, click “Restore to Default“.
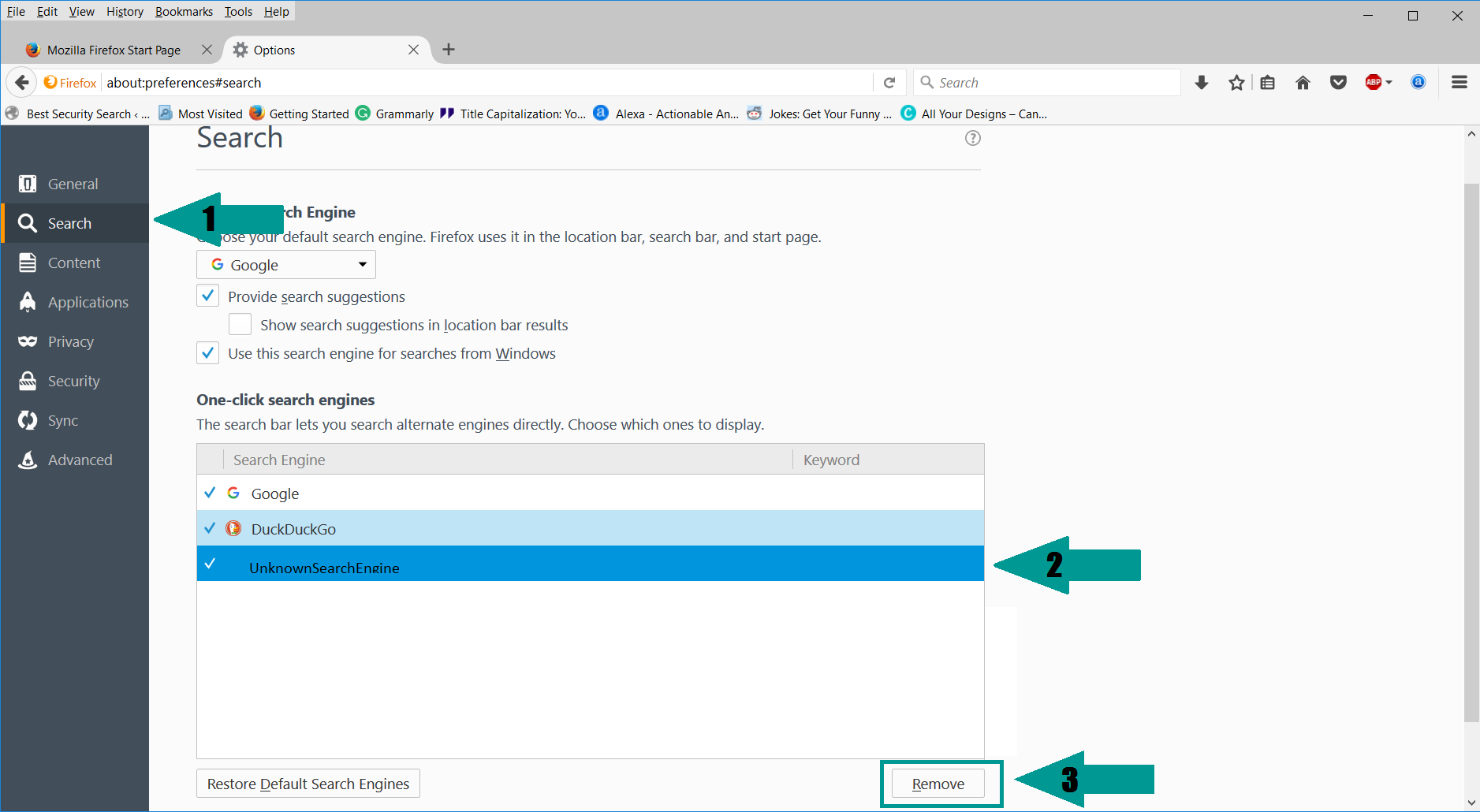
5. Select “Search” in the left menu, mark the unknown search engine and press “Remove”.
-
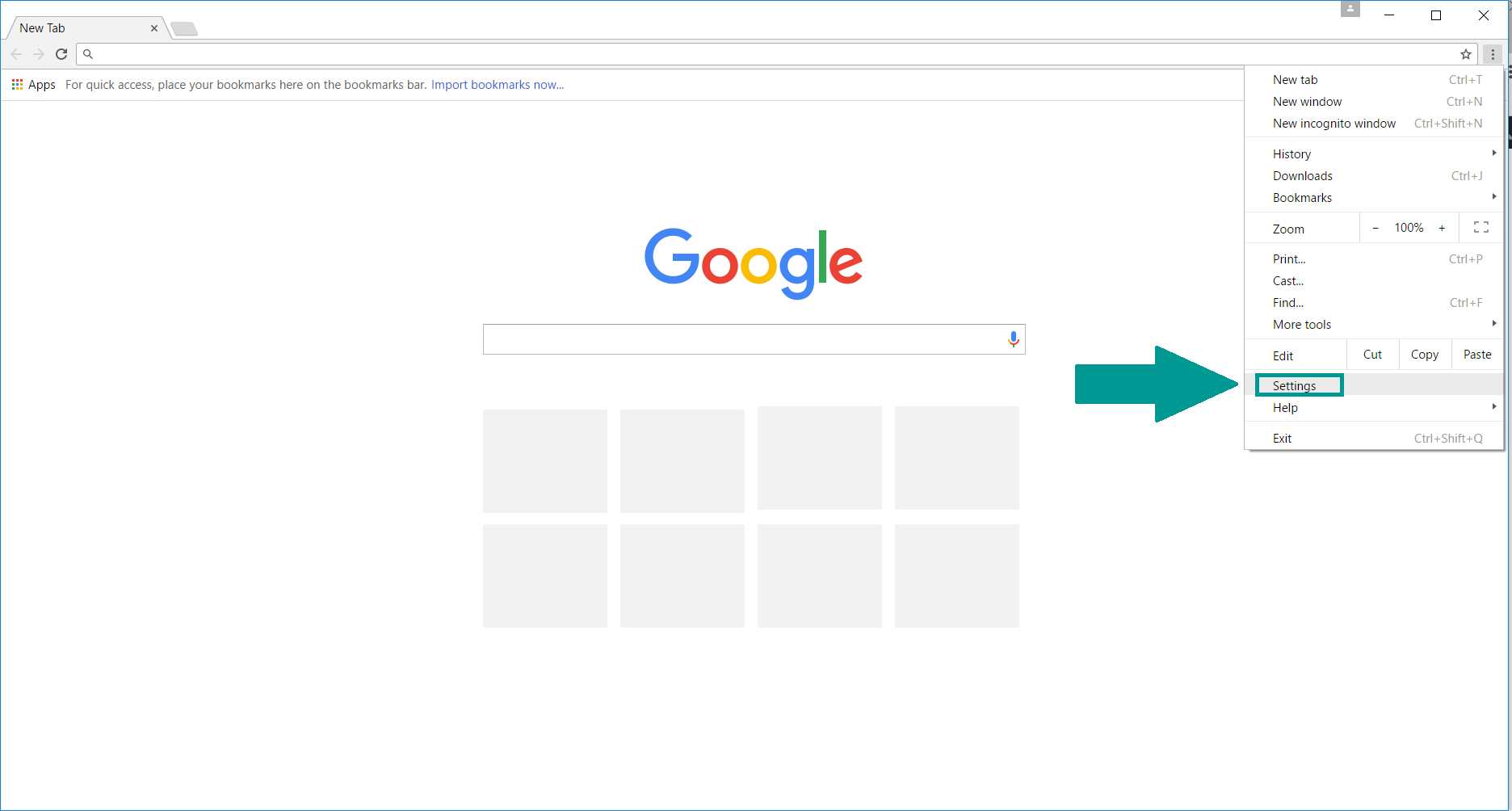
1. Start Google Chrome. On the upper-right corner, there a “Customize and Control” menu icon. Click on it, then click on “Settings“.
2. Click “Extensions” in the left menu. Then click on the trash bin icon to remove the suspicious extension.
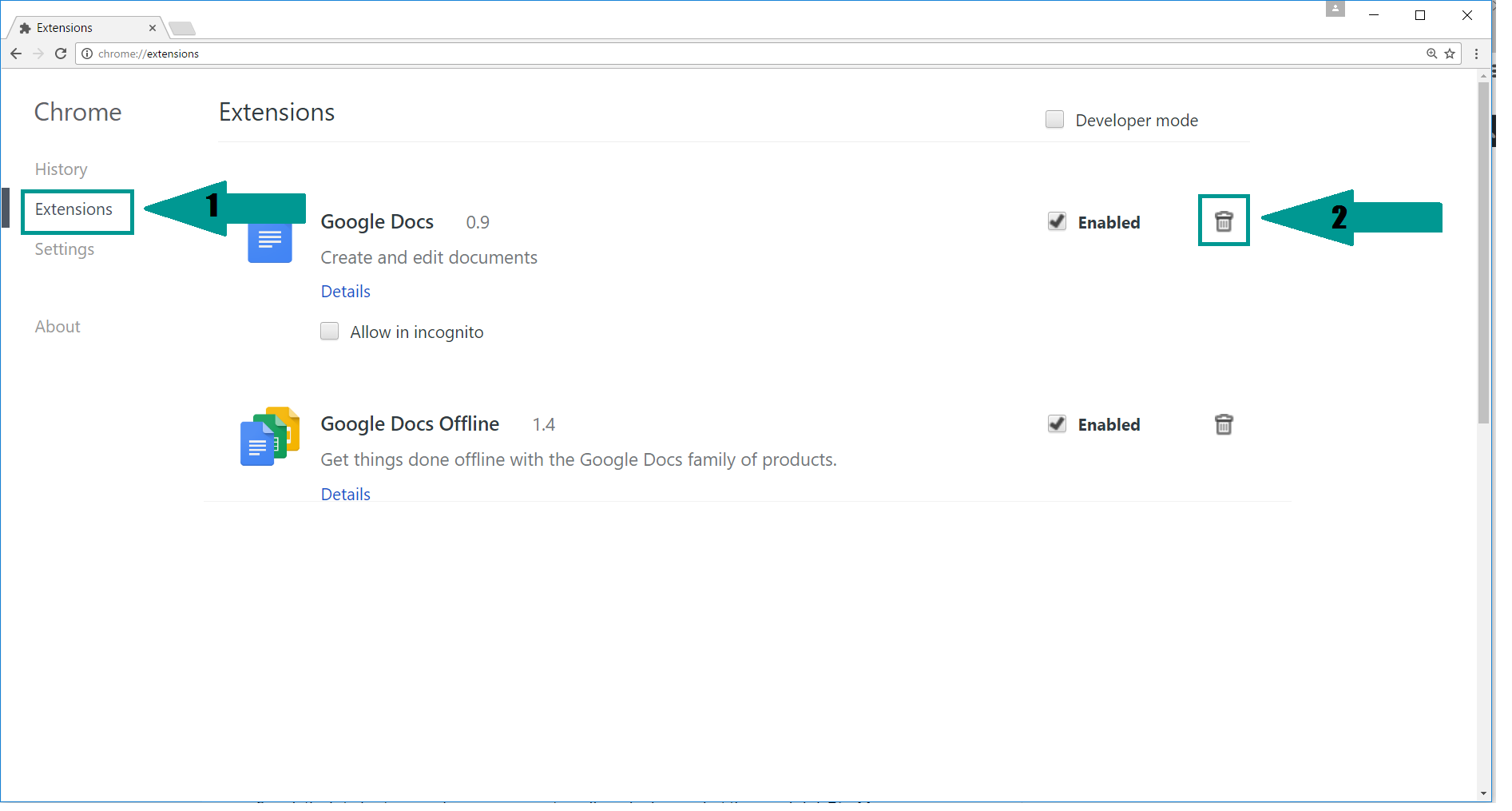
3. Again in the left menu, under Chrome, Click on “Settings“. Go under “On Startup” and set a new page.
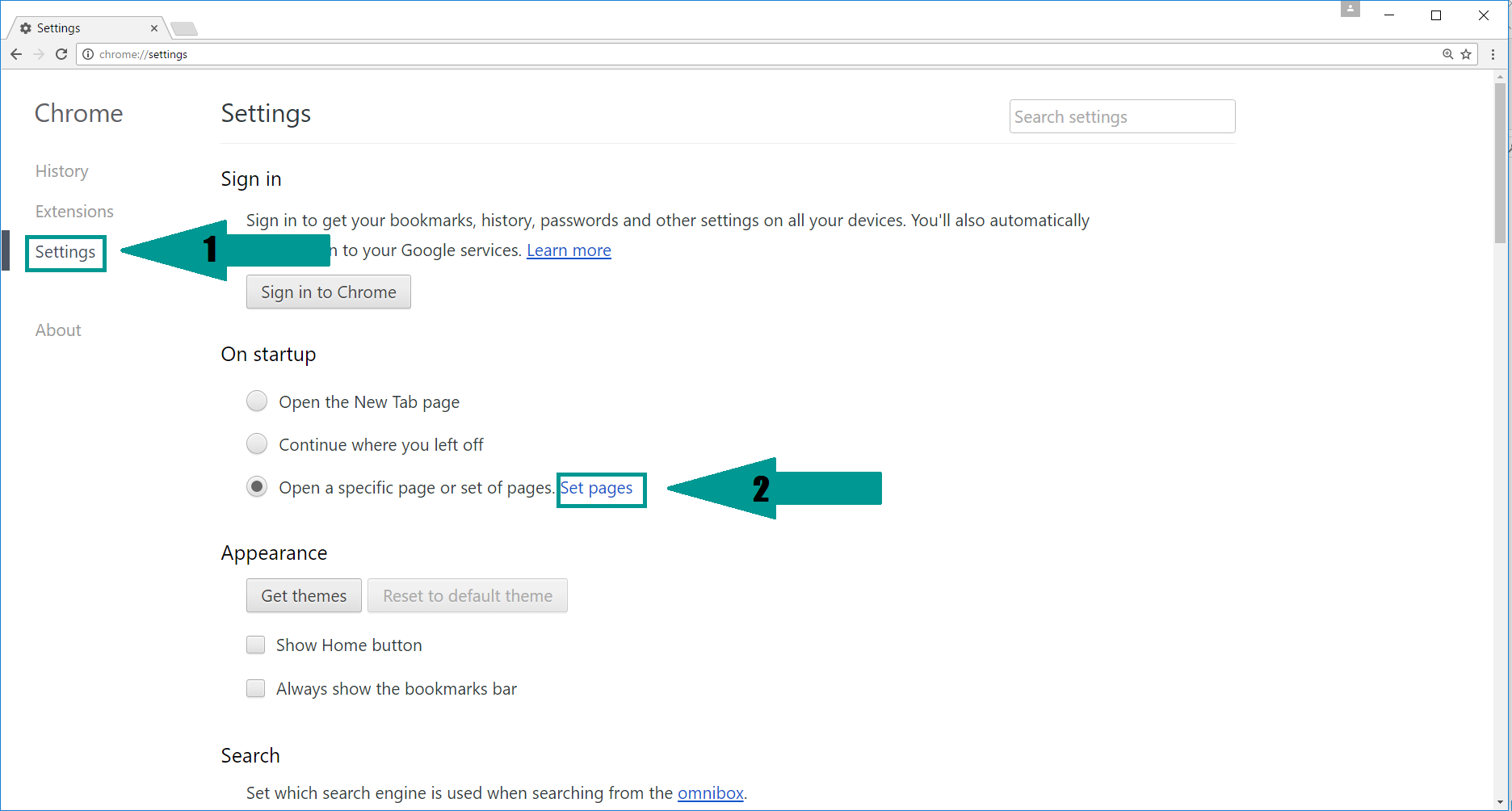
4. Afterward, scroll down to “Search“, click on “Manage search engines“.
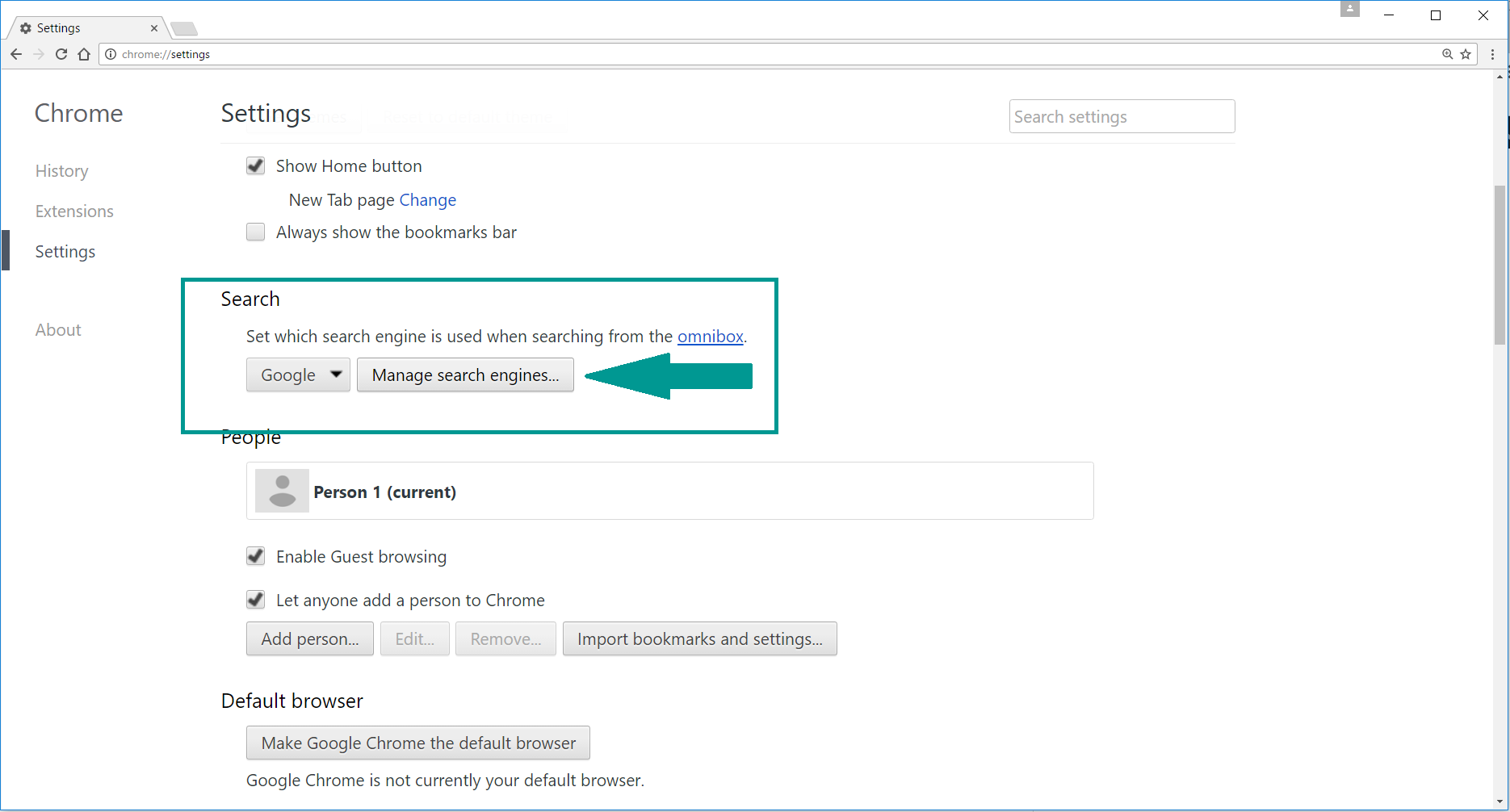
5. In the default search settings list, find the unknown search engine and click on “X“. Then select your search engine of choice and click “Make default“. When you are ready click “Done” button in the right bottom corner.
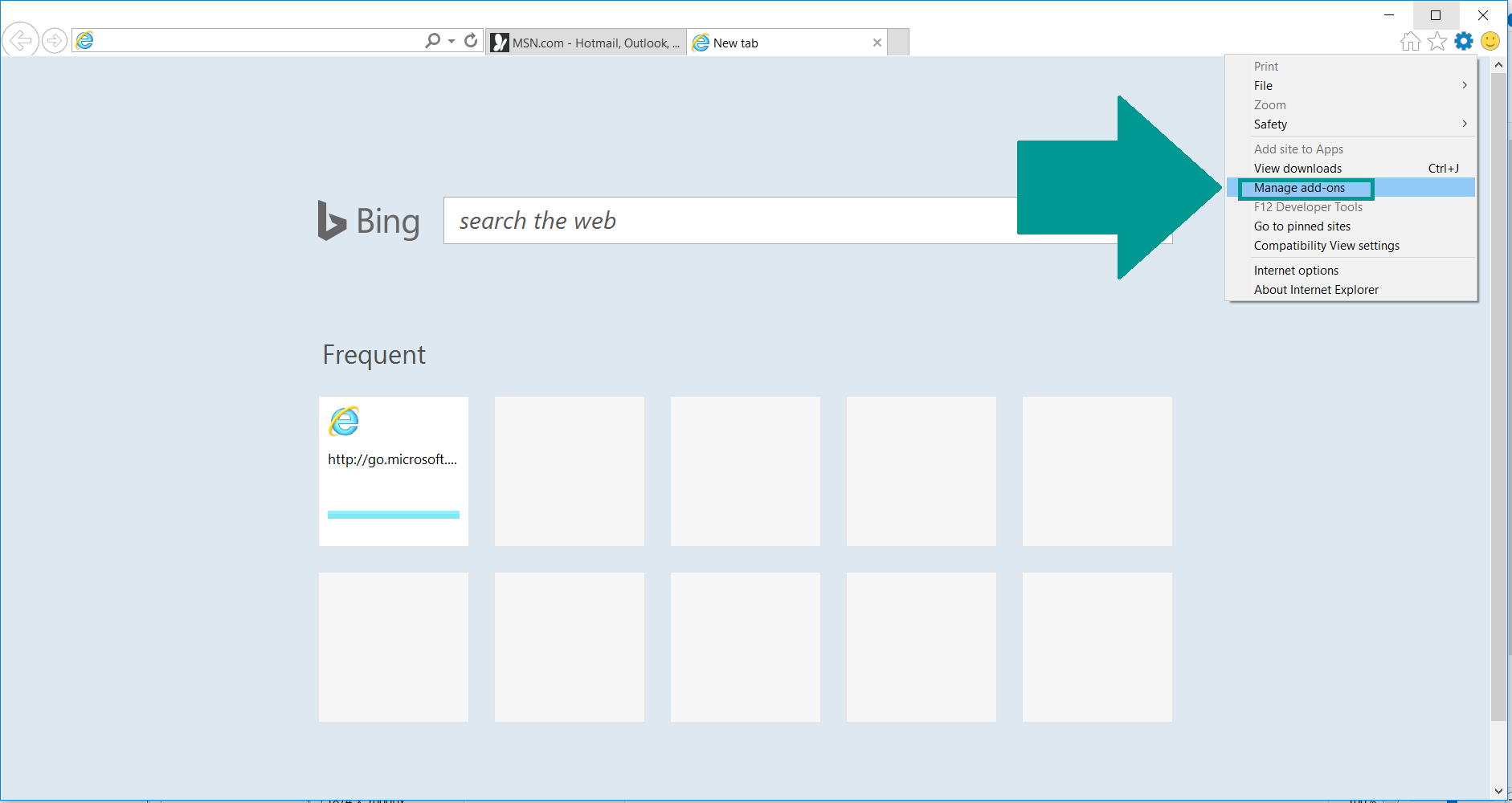
2. In the “Manage add-ons” window, bellow “Add-on Types“, select “Toolbars and Extensions“. If you see a suspicious toolbar, select it and click “Remove“.
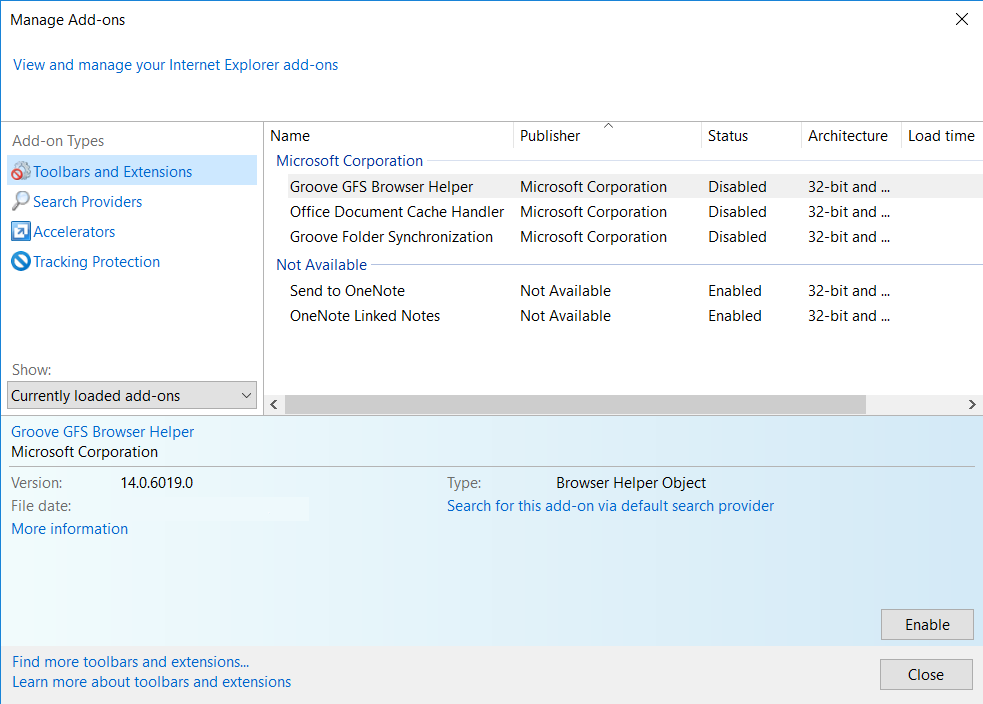
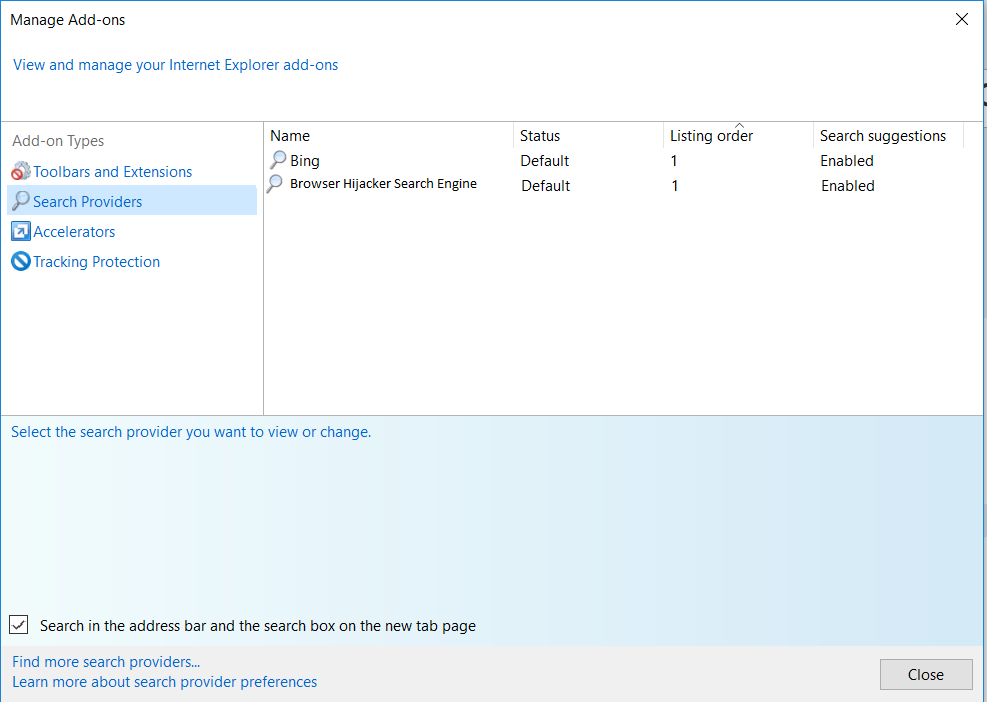
3. Then again in the “Manage Add-ons” window, in “Add-on Types“, Select “Search Providers“. Chose a search engine and click “Set as default“. Select the unknown search engine and click “Remove and Close”.
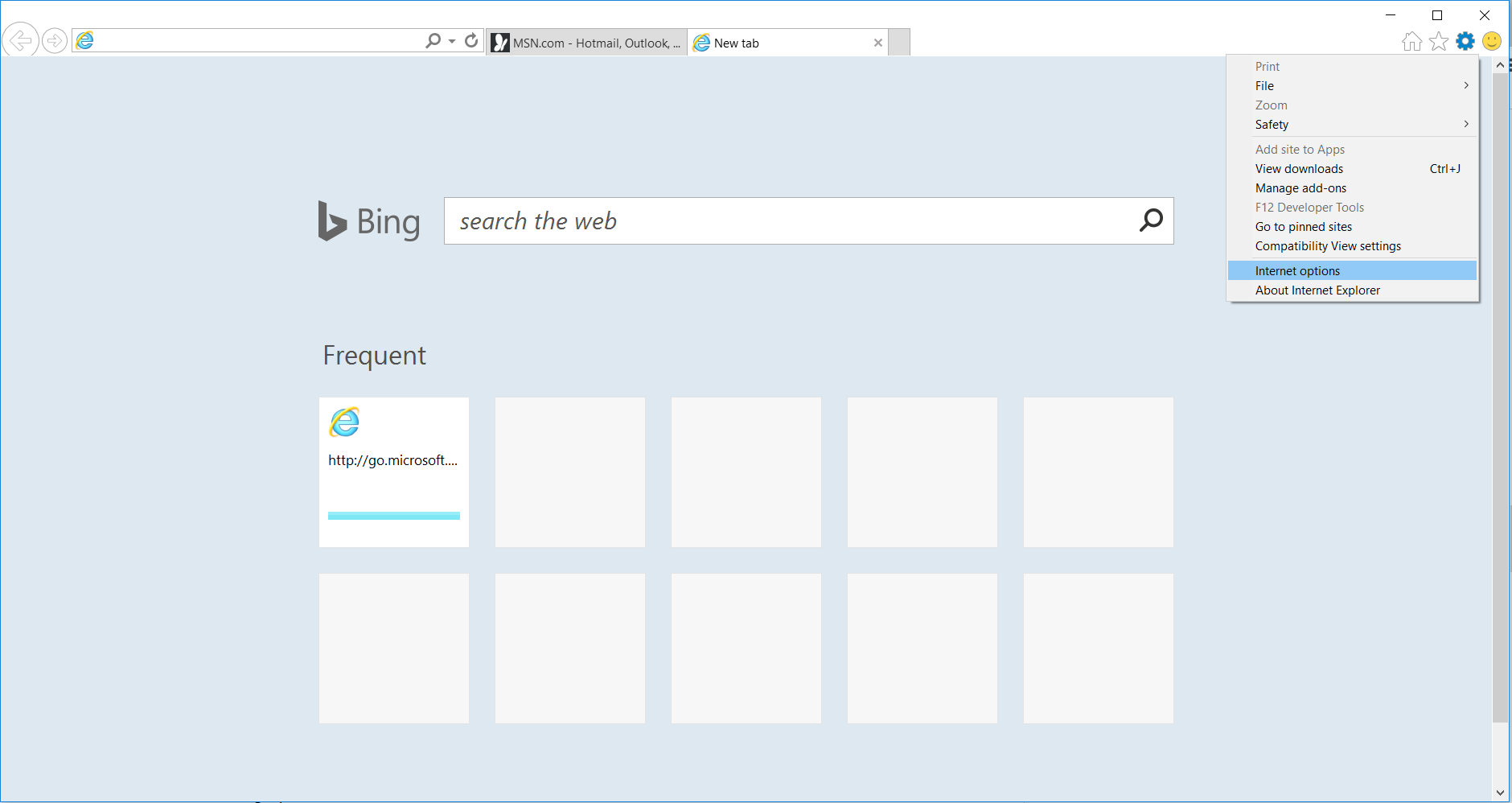
4. Open the Tools menu, select “Internet Options”.
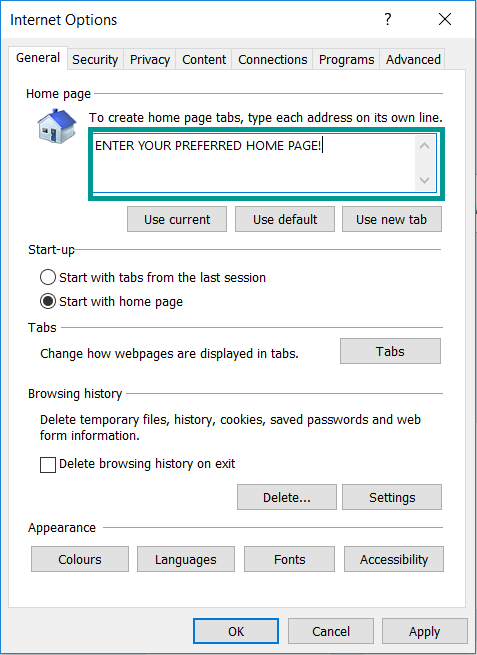
5. In the “General” tab, in “Home page”, enter your preferred page. Click “Apply” and “OK”.
Repair Windows Registry
1. Again type simultaneously the WIN Key + R key combination
2. In the box, write regedit and hit Enter
3. Type the CTRL+ F and then write the malicious name in the search type field to locate the malicious executable
4. In case you have discovered registry keys and values related to the name, you should delete them, but be careful not to delete legitimate keys
Click for more information about Windows Registry and further repair help



