Read our removal guide to learn about the CryptoShield ransomware is a new variant of the CryptoMix ransomware and is being distributed via several exploit kits.
CryptoShield Ransomware Description
Security researchers discovered a new strain known as the CryptoShield ransomware which is derived from the infamous CryptoMix ransomware.
The virus borrows its code from CryptoMix however several major changes have also been introduced.
Upon infection an unique infection ID is associated with every affected host. This identifier is uploaded alongside with the private encryption key to the remote C&C server. After this steps is complete the encryption engine is started. The security researchers were able to extract the full list of target file types:
.ACCDB, .MDB, .MDF, .DBF, .VPD, .SDF, .SQLITEDB, .SQLITE3, .SQLITE, .SQL, .SDB, .DOC, .DOCX, .ODT, .XLS, .XLSX, .ODS, .PPT, .PPTX, .ODP, .PST, .DBX, .WAB, .TBK, .PPS, .PPSX, .PDF, .JPG, .TIF, .PUB, .ONE, .RTF, .CSV, .DOCM, .XLSM, .PPTM, .PPSM, .XLSB, .DOT, .DOTX, .DOTM, .XLT, .XLTX, .XLTM, .POT, .POTX, .POTM, .XPS, .WPS, .XLA, .XLAM, .ERBSQL, .SQLITE-SHM, .SQLITE-WAL, .LITESQL, .NDF, .OST, .PAB, .OAB, .CONTACT, .JNT, .MAPIMAIL, .MSG, .PRF, .RAR, .TXT, .XML, .ZIP, .1CD, .3DS, .3G2, .3GP, .7Z, .7ZIP, .AOI, .ASF, .ASP, .ASPX, .ASX, .AVI, .BAK, .CER, .CFG, .CLASS, .CONFIG, .CSS, .DDS, .DWG, .DXF, .FLF, .FLV, .HTML, .IDX, .JS, .KEY, .KWM, .LACCDB, .LDF, .LIT, .M3U, .MBX, .MD, .MID, .MLB, .MOV, .MP3, .MP4, .MPG, .OBJ, .PAGES, .PHP, .PSD, .PWM, .RM, .SAFE, .SAV, .SAVE, .SRT, .SWF, .THM, .VOB, .WAV, .WMA, .WMV, .3DM, .AAC, .AI, .ARW, .C, .CDR, .CLS, .CPI, .CPP, .CS, .DB3, .DRW, .DXB, .EPS, .FLA, .FLAC, .FXG, .JAVA, .M, .M4V, .MAX, .PCD, .PCT, .PL, .PPAM, .PS, .PSPIMAGE, .R3D, .RW2, .SLDM, .SLDX, .SVG, .TGA, .XLM, .XLR, .XLW, .ACT, .ADP, .AL, .BKP, .BLEND, .CDF, .CDX, .CGM, .CR2, .CRT, .DAC, .DCR, .DDD, .DESIGN, .DTD, .FDB, .FFF, .FPX, .H, .IIF, .INDD, .JPEG, .MOS, .ND, .NSD, .NSF, .NSG, .NSH, .ODC, .OIL, .PAS, .PAT, .PEF, .PFX, .PTX, .QBB, .QBM, .SAS7BDAT, .SAY, .ST4, .ST6, .STC, .SXC, .SXW, .TLG, .WAD, .XLK, .AIFF, .BIN, .BMP, .CMT, .DAT, .DIT, .EDB, .FLVV, .GIF, .GROUPS, .HDD, .HPP, .M2TS, .M4P, .MKV, .MPEG, .NVRAM, .OGG, .PDB, .PIF, .PNG, .QED, .QCOW, .QCOW2, .RVT, .ST7, .STM, .VBOX, .VDI, .VHD, .VHDX, .VMDK, .VMSD, .VMX, .VMXF, .3FR, .3PR, .AB4, .ACCDE, .ACCDR, .ACCDT, .ACH, .ACR, .ADB, .ADS, .AGDL, .AIT, .APJ, .ASM, .AWG, .BACK, .BACKUP, .BACKUPDB, .BANK, .BAY, .BDB, .BGT, .BIK, .BPW, .CDR3, .CDR4, .CDR5, .CDR6, .CDRW, .CE1, .CE2, .CIB, .CRAW, .CRW, .CSH, .CSL, .DB_JOURNAL, .DC2, .DCS, .DDOC, .DDRW, .DER, .DES, .DGC, .DJVU, .DNG, .DRF, .DXG, .EML, .ERF, .EXF, .FFD, .FH, .FHD, .GRAY, .GREY, .GRY, .HBK, .IBANK, .IBD, .IBZ, .IIQ, .INCPAS, .JPE, .KC2, .KDBX, .KDC, .KPDX, .LUA, .MDC, .MEF, .MFW, .MMW, .MNY, .MONEYWELL, .MRW, .MYD, .NDD, .NEF, .NK2, .NOP, .NRW, .NS2, .NS3, .NS4, .NWB, .NX2, .NXL, .NYF, .ODB, .ODF, .ODG, .ODM, .ORF, .OTG, .OTH, .OTP, .OTS, .OTT, .P12, .P7B, .P7C, .PDD, .MTS, .PLUS_MUHD, .PLC, .PSAFE3, .PY, .QBA, .QBR, .QBW, .QBX, .QBY, .RAF, .RAT, .RAW, .RDB, .RWL, .RWZ, .S3DB, .SD0, .SDA, .SR2, .SRF, .SRW, .ST5, .ST8, .STD, .STI, .STW, .STX, .SXD, .SXG, .SXI, .SXM, .TEX, .WALLET, .WB2, .WPD, .X11, .X3F, .XIS, .YCBCRA, .YUV, .MAB, .JSON, .MSF, .JAR, .CDB, .SRB, .ABD, .QTB, .CFN, .INFO, .INFO_, .FLB, .DEF, .ATB, .TBN, .TBB, .TLX, .PML, .PMO, .PNX, .PNC, .PMI, .PMM, .LCK, .PM!, .PMR, .USR, .PND, .PMJ, .PM, .LOCK, .SRS, .PBF, .OMG, .WMF, .SH, .WAR, .ASCX, .K2P, .APK, .ASSET, .BSA, .D3DBSP, .DAS, .FORGE, .IWI, .LBF, .LITEMOD, .LTX, .M4A, .RE4, .SLM, .TIFF, .UPK, .XXX, .MONEY, .CASH, .PRIVATE, .CRY, .VSD, .TAX, .GBR, .DGN, .STL, .GHO, .MA, .ACC, .DB
All affected data is encrypted using the AES-256 cipher and receives the .CRYPTOSHIELD extension. In addition the file names preceeding the extension are scrambled using using the ROT-13 substitution cipher modeled in Ancient Rome.
A ransomware note is created in two version in each folder where a file has been encrypted – # RESTORING FILES #.HTML and # RESTORING FILES #.TXT. In addition the virus disables the Windows Startup recovery option and deletes all Shadow Volume Copies from the computer which makes data recovery difficult.
The CrytoShield ransomware displays a counterfeit alert stating that an application error has been caused in Explorer.exe:
The instruction at 0xe9c71f6c referenced memory at 0x46c8f91a. The momory could not be read.
Click on Yes in the next wiindow for restore work explorer.exe
As you can see there are some serious spelling and grammar mistakes which are unusual and can server as a warning to the users. Once the user clicks the OK prompt they are presented with a UAC prompt which requests the execution of a command – “C:\Windows\SysWOW64\wbem\WMIC.exe” process call create “C:\Users\User\SmartScreen.exe”.
The next step is to display the ransomware note which contains the following the message:
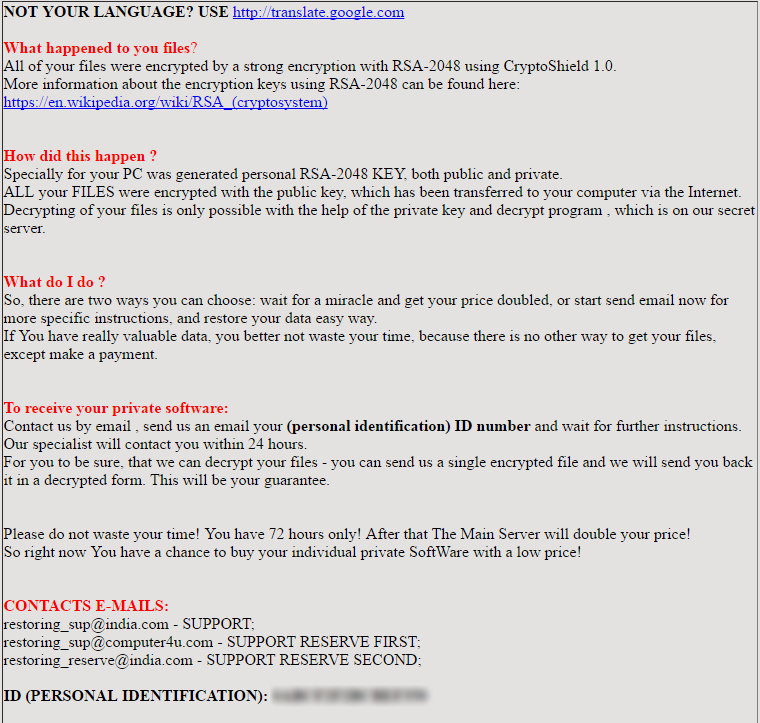
NOT YOUR LANGUAGE? USE http: translate.google.com
What happened to you files?
All of your files were encrypted by a strong encryption with RSA-2048 using CryptoShield 1.0.
More information about the encryption keys using RSA-2048 can be found here: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/RSA (cryptosystem)
How did this happen ?
Specially for your PC was generated personal RSA-2048 KEY, both public and private.
ALL your FILES were encrypted with the public key, which has been transferred to your computer via the Internet.
Decrypting of your files is only possible with the help of the private key and decrypt program, which is on our secret server.
What do I do ?
So, there are two ways you can choose: wait for a miracle and get your price doubled, or start send email now for more specific instructions…
CryptoShield Ransomware Distribution
The CryptoShield ransomware is primarily distributed via ElTest and the RIG exploit kit.
ElTest uses JavaScript code that is injected into hacked sites. The other attack method is the use of the RIG exploit kit which is popular at launching some of the dangerous and advanced ransomware variants.
Other ways of getting infected woth the CryptoShield ransomware include spam email messages, browser hijackers, malicious ads and infected software installers that bundle the dangerous code.
What Can I Do To Prevent CryptoShield Ransomware?
A ransomware infection is a clear signal that your computer lacks the necessary protection. The problem may be solved by:
- Better anti-spam measures – don’t download shady attachments
- Don’t give your email to sites with pirated content
- Never install suspicious ZIP or RAR files from spammed emails
- Get an anti-malware tool
Summary
| Name |
CryptoShield |
| File Extensions |
.CRYPTOSHIELD |
| Ransom |
Varies |
| Easy Solution |
You can skip all steps and remove CryptoShield ransomware with the help of an anti-malware tool. |
|
Manual Solution |
CryptoShield ransomware can be removed manually, though it can be very hard for most home users. See the detailed tutorial below. |
| Distribution |
Spam Email Campaigns, malicious ads & etc. |
CryptoShield Ransomware Removal
STEP I: Start the PC in Safe Mode with Network
This will isolate all files and objects created by the ransomware so they will be removed efficiently.
-
1) Hit WIN Key + R

- 2) A Run window will appear. In it, write “msconfig” and then press Enter
3) A Configuration box shall appear. In it Choose the tab named “Boot”
4) Mark “Safe Boot” option and then go to “Network” under it to tick it too
5) Apply -> OK
Or check our video guide – “How to start PC in Safe Mode with Networking”
STEP II: Show Hidden Files
-
1) Open My Computer/This PC
2) Windows 7
-
– Click on “Organize” button
– Select “Folder and search options”
– Select the “View” tab
– Go under “Hidden files and folders” and mark “Show hidden files and folders” option
3) Windows 8/ 10
-
– Open “View” tab
– Mark “Hidden items” option

4) Click “Apply” and then “OK” button
STEP III: Enter Windows Task Manager and Stop Malicious Processes
-
1) Hit the following key combination: CTRL+SHIFT+ESC
2) Get over to “Processes”
3) When you find suspicious process right click on it and select “Open File Location”
4) Go back to Task Manager and end the malicious process. Right click on it again and choose “End Process”
5) Next you should go folder where the malicious file is located and delete it
STEP IV: Remove Completely CryptoShield Ransomware Using SpyHunter Anti-Malware Tool
SpyHunter anti-malware tool will diagnose all current threats on the computer. By purchasing the full version, you will be able to remove all malware threats instantly. Additional information about SpyHunter / Help to uninstall SpyHunter
STEP V: Repair Windows Registry
-
1) Again type simultaneously the Windows Button + R key combination
2) In the box, write “regedit”(without the inverted commas) and hit Enter
3) Type the CTRL+F and then write the malicious name in the search type field to locate the malicious executable
4) In case you have discovered registry keys and values related to the name, you should delete them, but be careful not to delete legitimate keys
Further help for Windows Registry repair
STEP VI: Recover Encrypted Files
-
1) Use present backups
2) Restore your personal files using File History
-
– Hit WIN Key
– Type “restore your files” in the search box
– Select “Restore your files with File History”
– Choose a folder or type the name of the file in the search bar
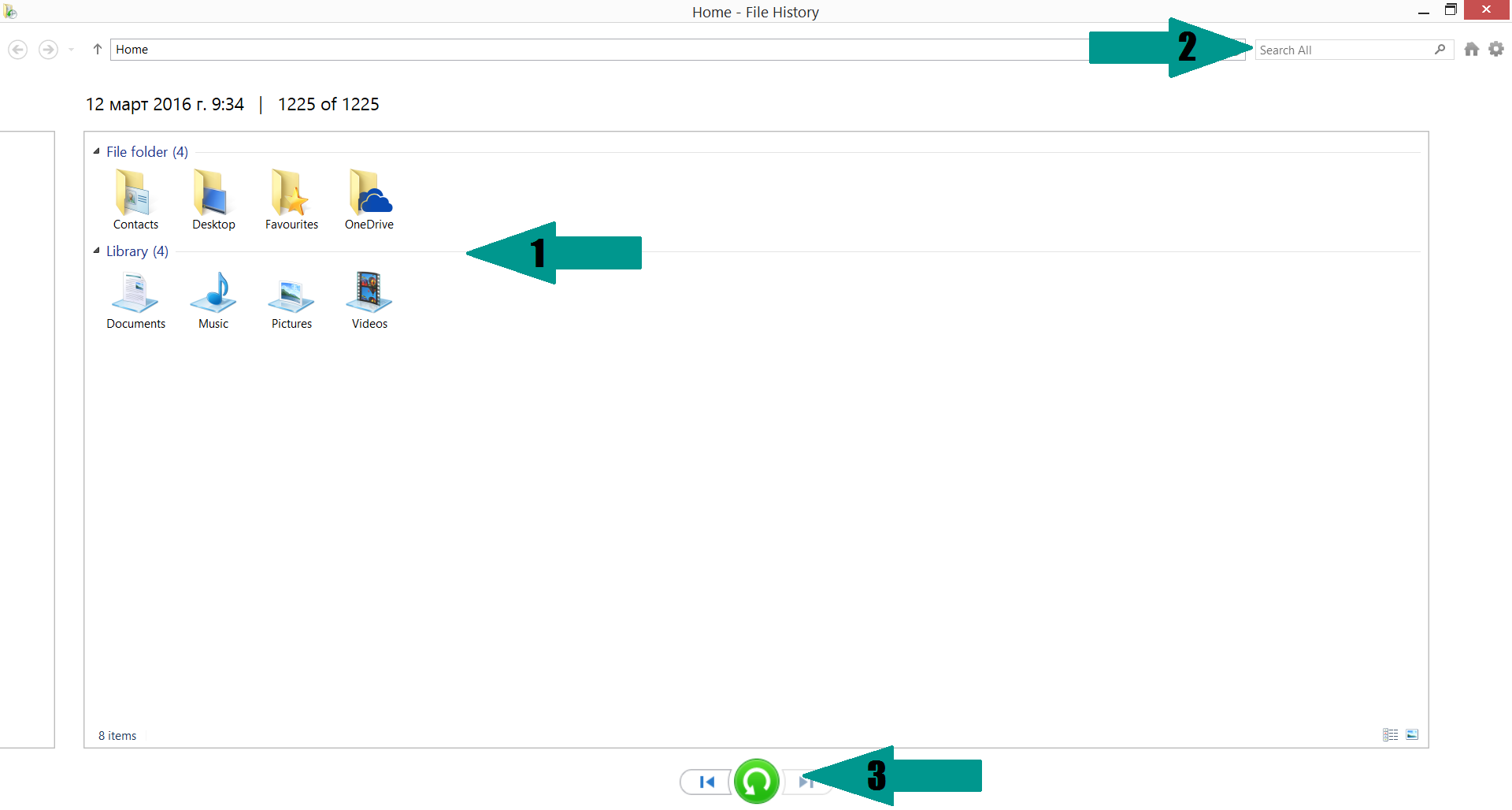
- – Hit the “Restore” button
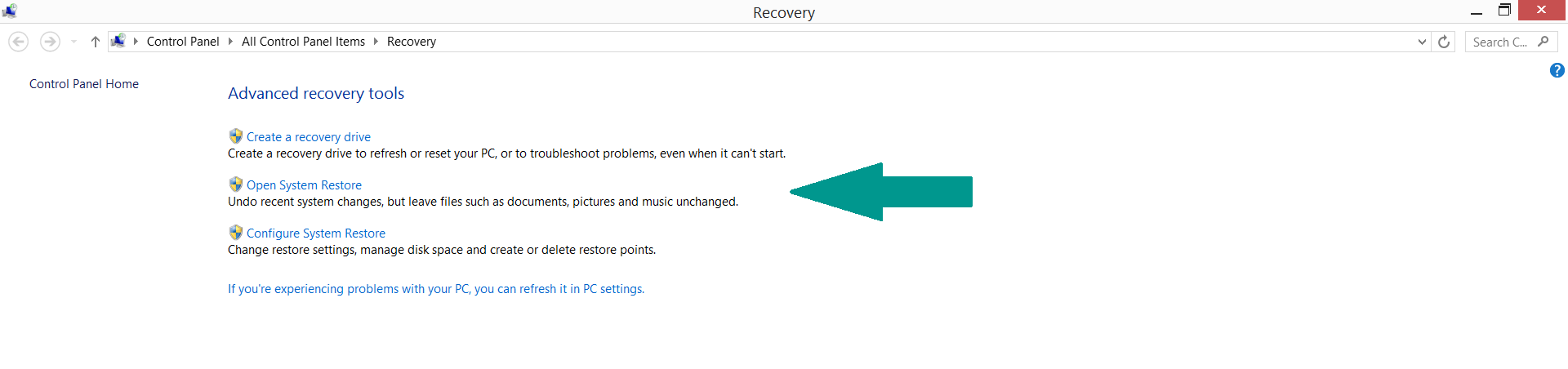
3) Using System Restore Point
-
– Hit WIN Key
– Select “Open System Restore” and follow the steps
STEP VII: Preventive Security Measures
-
1) Enable and properly configure your Firewall.
2) Install and maintain reliable anti-malware software.
3) Secure your web browser.
4) Check regularly for available software updates and apply them.
5) Disable macros in Office documents.
6) Use strong passwords.
7) Don’t open attachments or click on links unless you’re certain they’re safe.
8) Backup regularly your data.



