The frequency of exploiting JavaScript files as an infection vector of cyber attacks has increased. Application of this technique is not a new thing, but our research team has noticed a significant growth of using malicious JavaScript files that deliver malware to the computer. The method is primarily used by cyber criminals that aim to grant access to the system so they can easily modify the default system and browser settings and corrupt sensitive user data.
Infected JavaScript files can expose the whole system at high risk due to some cunning features that make the infection process invisible to the user. In some cases, the attack runs only in the background and could be triggered without user interaction.
So in this article, we will reveal more details about JavaScript malware hoping that anyone will learn how to get protected against this type of attacks.
JavaScript and .JS File
First, let’s state that Java is something completely different from JavaScript, they only share similar names. Java is a general-purpose computer programming language now owned by Oracle Corporation and developed by Sun Microsystems. JavaScript is a programming language developed by Netscape Inc. and is one of the three core technologies for World Wide Web content creation. The majority of websites all around the world employ JavaScript alongside HTML and CSS. Furthermore, all modern Web browsers support support JavaScript. Some PDF documents and desktop widgets also use JavaScript code.
JavaScript files have the extension .JS and here is how they look like on your PC:

The default Windows icon for .JS scripts is a conventionalized scroll illustrated in a low-resolution graphics.
How Do Malicious Intenders Use JavaScript for Malware Distribution?
Cyber criminals utilize different ways to abuse JavaScript programming language so they can efficiently distribute malware.
Mreover, it’s worth mentioning that there is evidence of ransomware developed in JavaScript called Ransom32. Here you could read a short explanation of the threat given by ItProPortal:
“ … A new strain called Ransom32 has a twist: it was fully developed in JavaScript, HTML and CSS which potentially allows for multi-platform infections after repackaging for Linux and MacOS X. Using JavaScript brings us one step closer to the “write-once-infect-all” threat, which is something to be aware of. “
We will continue with a closer look at the two most frequent distribution techniques of JavaScript malware.
Malicious JavaScript Attachments
Most ransomware infections today are distributed via email attachments along with a message that urges the victim to open the attached file. Usually, the crooks cling to words that look noteworthy for both individuals and enterprises.
All major email services have been disabled messages that contain JavaScript inside. However, numerous spam email campaigns are distributing ransomware and Trojans via .ZIP or .RAR file attachments. We noticed that most of the recent ransomware cases use such .ZIP/.RAR files for distribution of JScript, .JS/.JSE files. Once the file is clicked it is by default opened with WSH program. Thus the ransomware infection is triggered as the malicious payloads of the threat are hidden in the .JS file.
Once a .JS file is saved on the hard disk of your PC, it is by default run via a Windows program called Windows Script Host or WSH for short. In case that the JavaScript’s code is malicious, it can expose the security of the whole system at high risk of insidious malware infection.
For example one of the latest Locky ransomware variants associated with the malicious file extension .zzzzz is reported to use the same distribution technique.
But JavaScript files can not only spread ransomware, other types of malware are also generated via this infection vector. The criminal developers of Svpengg Android banking Trojan have also used a malicious JavaScript code inserted inside a Google AdSense advertisement for targeting Russian sites. Additionally, Rowhammer attack could gain root privileges of a compromised Android device with the help of JavaScript code that bypasses the protection measures.
SpyHunter anti-malware tool will diagnose all current threats on the computer. By purchasing the full version, you will be able to remove all malware threats instantly. Additional information about SpyHunter / Help to uninstall SpyHunter
Let’s continue with the second widely used technique that endangers the security of your PC by executing malicious JavaScript (.JS) files.
A Drive-By Attack
By visiting a website a series of JavaScript (.JS), files are downloaded and executed on your browser. This action contributes to visualization of website’s content, online ads (banners) and enables the performance of various activities like downloading files. As we mention in the beginning, JavaScript is one of three core technologies of World Wide Web content creation. According to Web Technology Surveys, 94.4% of all existing websites are currently using JavaScript. Statistics show that vendors like Facebook, Google and Twitter are using JavaScript technologies as well.
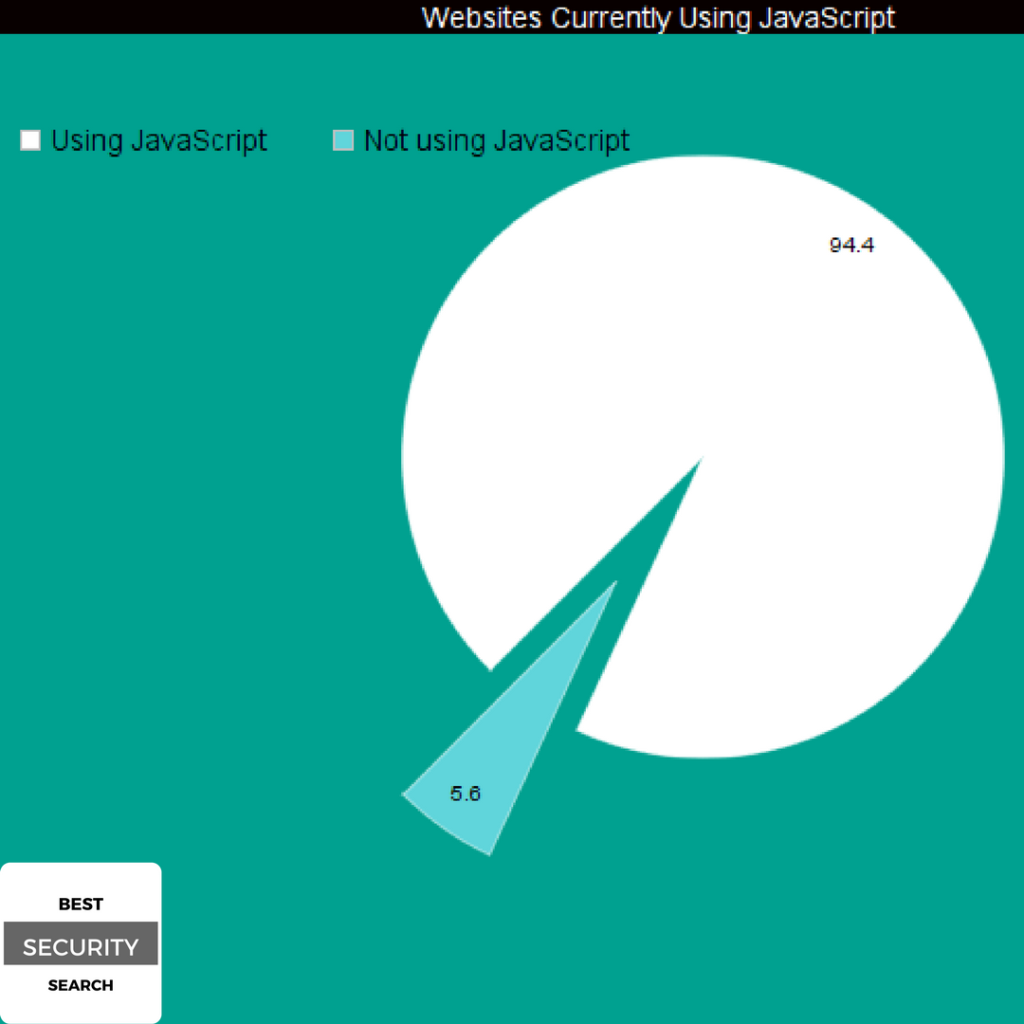
Obviously, these facts are well known to cyber criminals too, and they don’t waste their time but applying different tricks to infect users via malicious JavaScript files all over the Web. How do they compromise a website?
-
Inject malicious JavaScript code into the site’s database.
Compromise the online ads/banners displayed on the website.
Inject malicious JavaScript code on the website.
Establish connection with remote server, so they can load malicious content or software.
The simple act of visiting a compromised website is enough to get your PC infected with malware. When you are browsing an infected website, malicious JavaScript files are automatically downloaded to your computer. This malware delivery technique is called a drive-by or drive-by-download attack.
A drive-by attack is s a malware delivery method that is generated right after the user visit a compromised website. All stages of the infection process are happening in the background and stay invisible to the user.
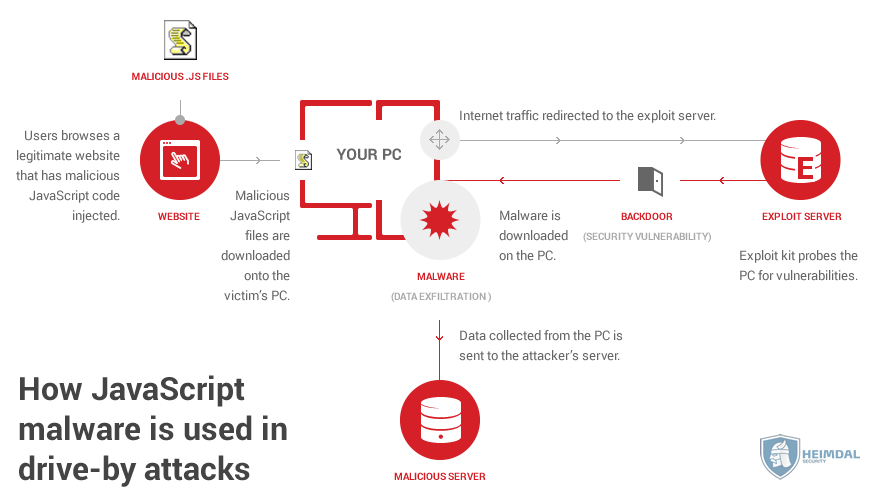
Image Source: Heimdal Security
Currently, online attacks are one of the most common vectors used for malware infections.
How to Protect Yourself from JavaScript Malware
The threats that we face today are so advanced that no single security solution is enough for full protection. Cyber criminals are always changing the ways they distribute malware in order to bypass the traditional security measures.
Malicious JavaScript (.js) files will no longer endanger the security of your computer if you apply some basic rules:
-
Upload all suspicious files and URLs to online services that will analyze them even before you download or open them. Such type of services can detect viruses, worms, Trojans, and all kinds of malware. VirusTotal is an excellent example as it has one of the largest web databases for malware.
Ensure spam email protection by creating rules that will filter your incoming emails. Enter the official website of your email service provider and search for options on how to manage your incoming mail.
Install anti-malware software to keep you safe in real time. Anti-malware programs have databases of known malware that are updated on a daily basis. Thus they will detect all malicious .JS files and stop the infection process on time. Furthermore, an anti-malware program contains many technologies to prevent all types malware intrusion on your computer.
Keep your software updated – your operating system, browsers, apps, antivirus, etc. Performing software updates will decrease the possibility of malicious hackers to exploit an unpatched vulnerability in your software.



