Security experts discovered a security issue which allows criminals to access and control Telegram and WhatsApp accounts.
Telegram and WhatsApp Accounts In Danger
Experts have discovered that Telegram and WhatsApp accounts are vulnerable to a dangerous issue which can lead to exposure and remote control use by criminals. The issue was identified in the web interface of the instant messaging services. The hackers can harvest the information and take over control of the victim accounts through it. The researchers discovered that the online versions of the services mirror all correspondence are are synced live with the user devices. The consequences can be serious as the hackers can access all group and personal conversations, videos, photos, contact lists and other types of content. The service providers cannot prevent the intrusion attempts as all messages are encrypted using a strong cipher.
The infection is initiated by following this scenario:
-
The criminals send a file to the victim which features dangerous code. In most cases it is masked as a file of user interest. Based on the targets the hackers can use different mediums – social networks, emails and instant messenger apps.
-
Once the victims interact with the dangerous file the malicious payload is loaded which allows the criminals to access the Telegram and WhatsApp accounts from the local storage.
-
This allows the criminals to access and extract all data associated with the accounts
Both companies have verified the dangerous issue and acknowledges that they are working on a fix that would fix the problem. The vendors suggest that users always update to the latest version of the relevant apps, use only Google Play as source and restart their browsers if they have been running cached versions of the online service. A security patch has been issued which validates all sent content by the services before the encryption process is started. This is a way to prevent possible intrusion attacks.
Expert advise also suggests the following tips:
-
All users should avoid suspicious looking files or links sent from unknown users. Such behavior has been the primary infection source for these dangerous attacks. Also watch out for files sent from people you know that seem out of place. This might indicate that their account has been compromised.
-
Periodically clean the logged-in computers from social media and instant messenger accounts. This prevents browser hijackers or other malware from accessing them.
-
A quality anti-spyware solution should always be employed to provide real-time protection from computer threats.
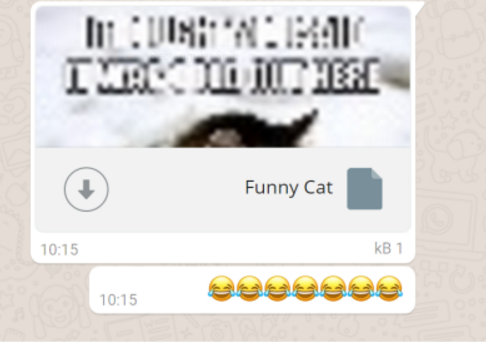
WhatsApp Infection In-Depth Explanation: The WhatsApp service allows file transfer between supported data – Office documents, audio, videos, PDFs and images. Each of them are routed through the company’s servers and then delivered to the chat partner. The security measures have been bypassed in a proof-of-concept attack where the researchers upload a malicious HTML document with a legitimate preview of an image. This tactic can be used to fool the victims into clicking on the links. Once they interact with the link the web client uses an API call to create a unique URL that delivers the necessary download URL. An important characteristic is the fact that the hackers can add a new MIME type to the variable in order to bypass any client restrictions. The attackers can also craft HTML code that can cause the client browser window to hang which disables any possibility of user interference.
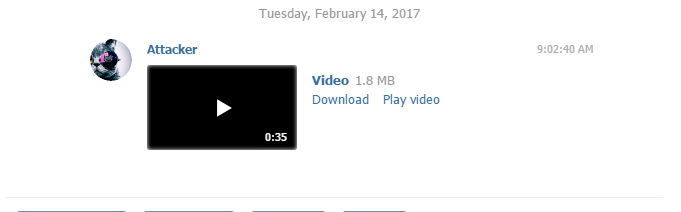
Telegram Infection In-Depth Explanation: Telegram supports the transfer or multiple file types which can be sent using the Web interface. The researchers uncovered that only videos and images on the filesystem section from within the browser. They have managed to bypass the service’s upload policy by placing a malicious HTML code with the mime video that corresponds to a video (video/mp4). When the victims receive the file the attack begins in several stages:
-
The attackers craft the dangerous HTML file which also contains relevant video data.
-
The Telegram servers verify if the stored MIME type corresponds to the service’s whitelist. If this checks then the file will be stored under the client FileSystem URL.
-
Client restrictions can be bypassed by uploading the file which poses as a video.
-
The resulting file looks like a legitimate video file. If the user interacts with the payload the infection is complete. When viewing the counterfeit video a browser opens up a new tab which exposes the victim’s locally stored data which is sent to the attackers. This is done by creating a JavaScript function which checks at a constant rate (of 2 seconds) of new data.



