Critical security flaws were discovered in the software that runs the BTS towers, allowing attackers to hijack the cellular phone towers. The vulnerabilities affect products from multiple manufacturers and rely on exploits found on software packages that are used by the BTS stations.
Cellular Phone Towers Are Now Hacker Assets
The mobile security company Zimperium, famous for uncovering the Stagefright bug, has discovered three serious flaws in software installations that run on cellular phone towers. Mobile security is seriously threatened as other software solutions not tested by the security experts may also be affected.
The BTS (Base Transceiver Station) stations, known as cellular phone towers, are the main components of every mobile network. These provide all services that we use: calling, SMS messaging services and mobile network connects.
The affected software products include Legba Incorporated (YateBTS <= 5.0.0), Range Networks (OpenBTS <= 4.0.0 and OpenBTS-UMTS <= 1.0.0), and OsmoCOM (Osmo-TRX <= 0.1.10 and Osmo-BTS <= 0.1.10).
Zimperium uncovered three distinct security issues that can be exploited by malicious users.
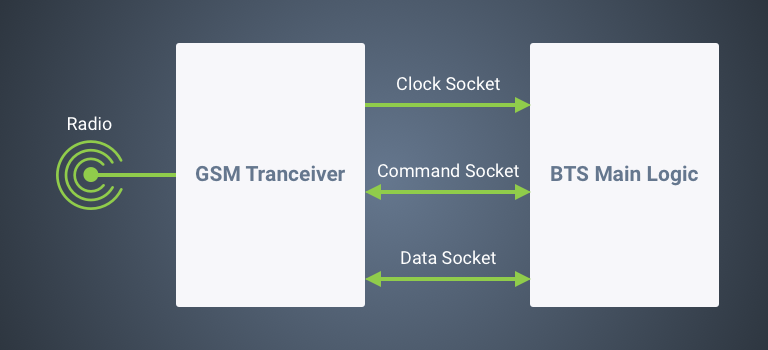
- Bugs in the core BTS software services expose the devices to untrusted remote connections. This vulnerability allows attackers to access the tower transceivers over the Network. Security implications include the sending of UDP packets to management ports (5700 and 5701), thus giving attackers remote control capabilities. As the cellular phone towers route information between subscribers and the network, the malicious user can also alter GSM traffic, harvest data or disrupt access to the provided mobile services. Zimperium experts recommend mobile network administrators to bind the socket for control and data exchange to the local interface (127.0.0.1) or to deploy a firewall that blocks external traffic.
- The second vulnerability is a memory buffer overflow that is caused by oversized UDP packets. This remote code execution flaw (RCE) lets malicious users execute arbitrary code on the target device. The potential damage depends on the hacker’s skills and expertise.
- The third flaw is related to the first vulnerability. Upon sending custom UDB packets to the BTS tower, the criminal user can control the transceiver module. Access to the control channel makes it possible for the malicious users to shutdown the cellular phone towers on and off, jam frequencies at will or change the BTS identity. Changing main configuration settings may give attackers the ability to impersonate networks, thereby carrying out Man-in-the-middle attacks.
All affected vendors have developed patches for their software products.
An in-depth description of the vulnerabilities is available on Zimperium’s blog.



